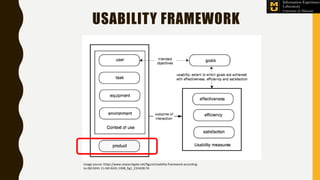
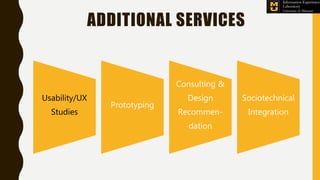
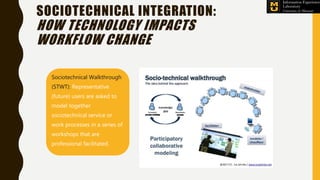
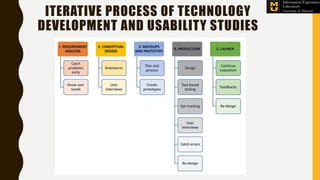
The Information Experience Laboratory (IE Lab) at the University of Missouri, founded in 2003, focuses on improving usability and user experience in digital technologies across various sectors like healthcare and education. It offers services such as professional usability evaluations, human-centered studies, and has partnered with numerous clients including corporate and academic institutions to enhance technology impact. The lab emphasizes that effective usability leads to better designs, heightened user satisfaction, and ultimately, improved business outcomes.