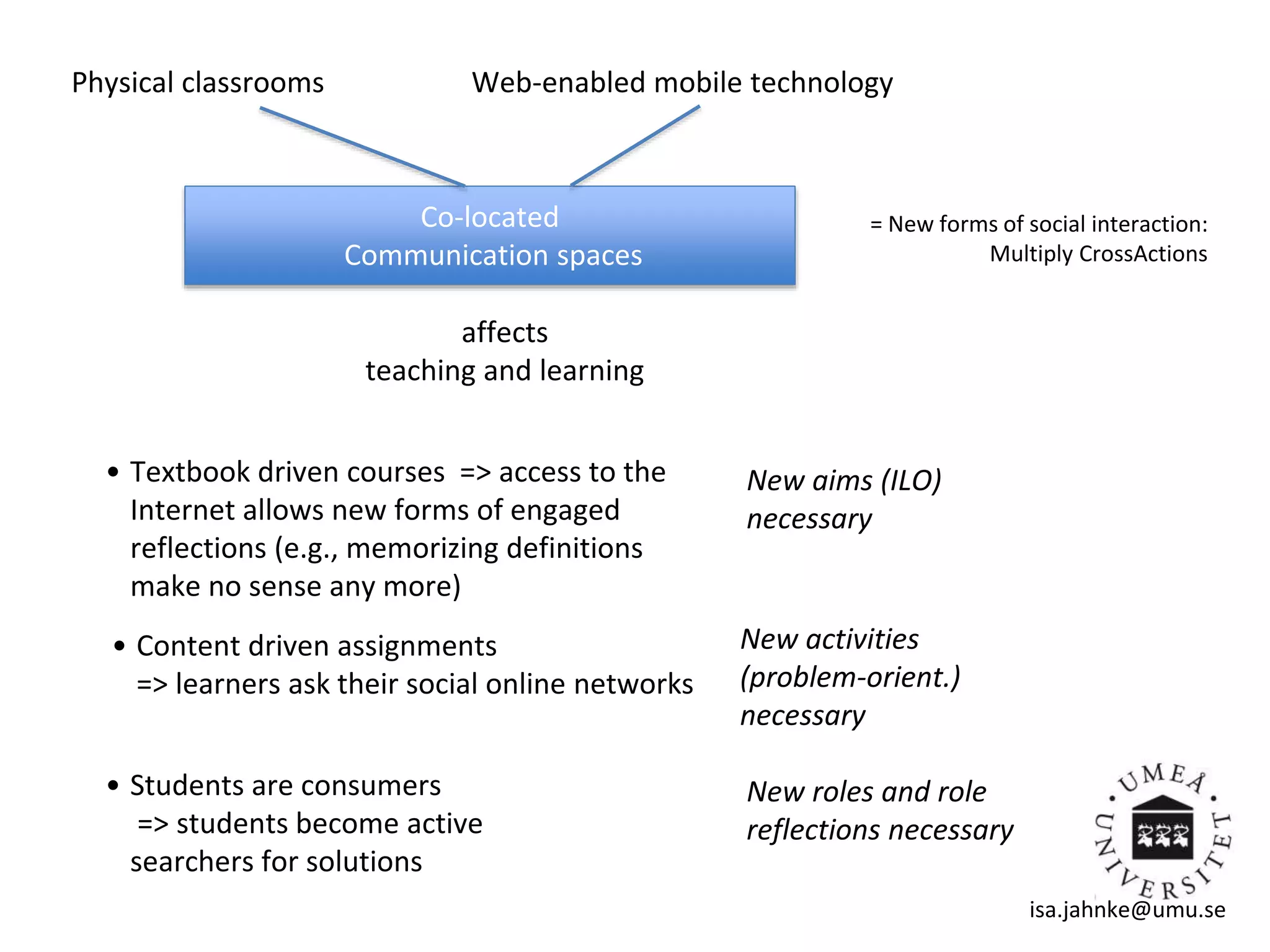
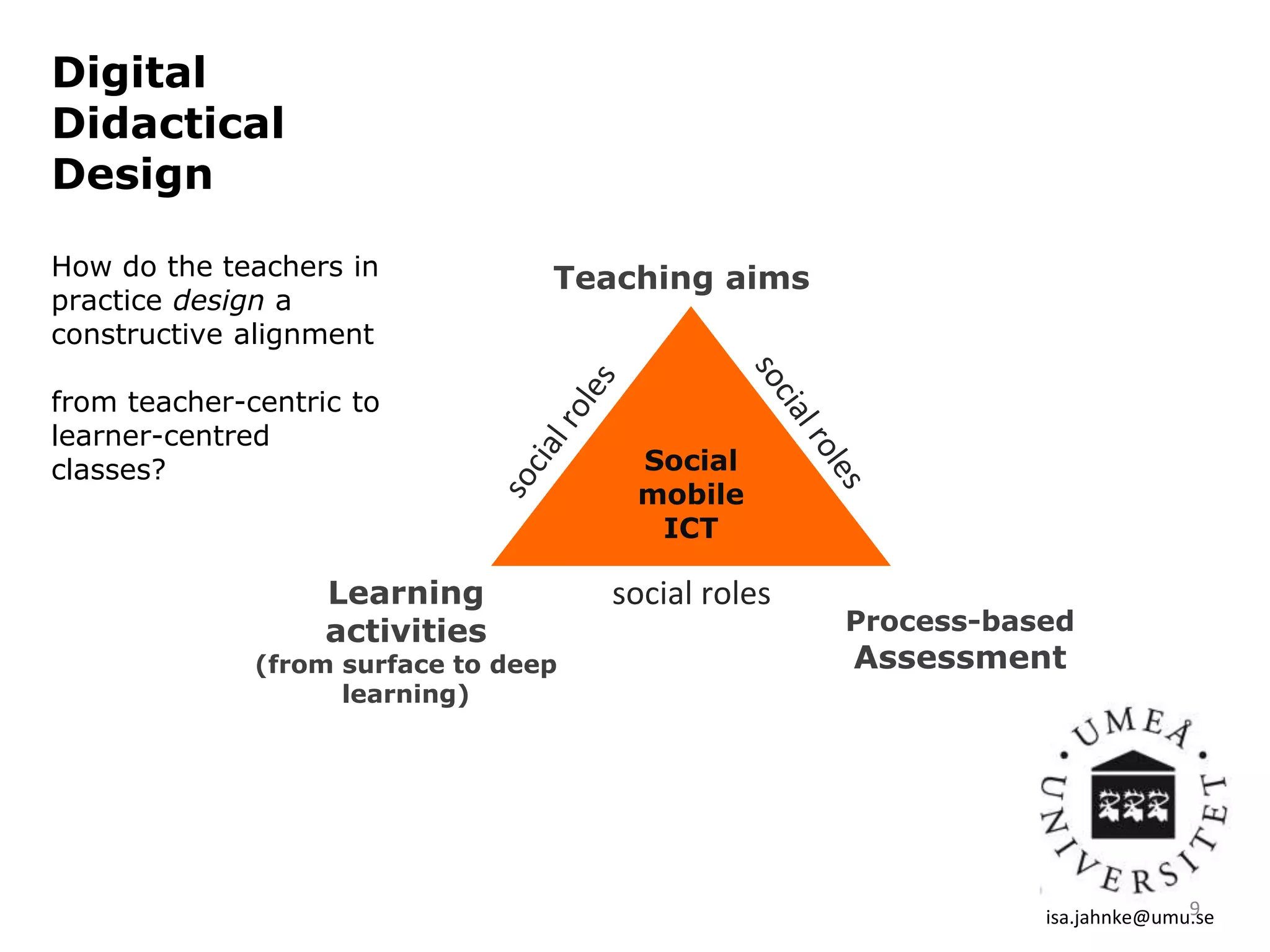
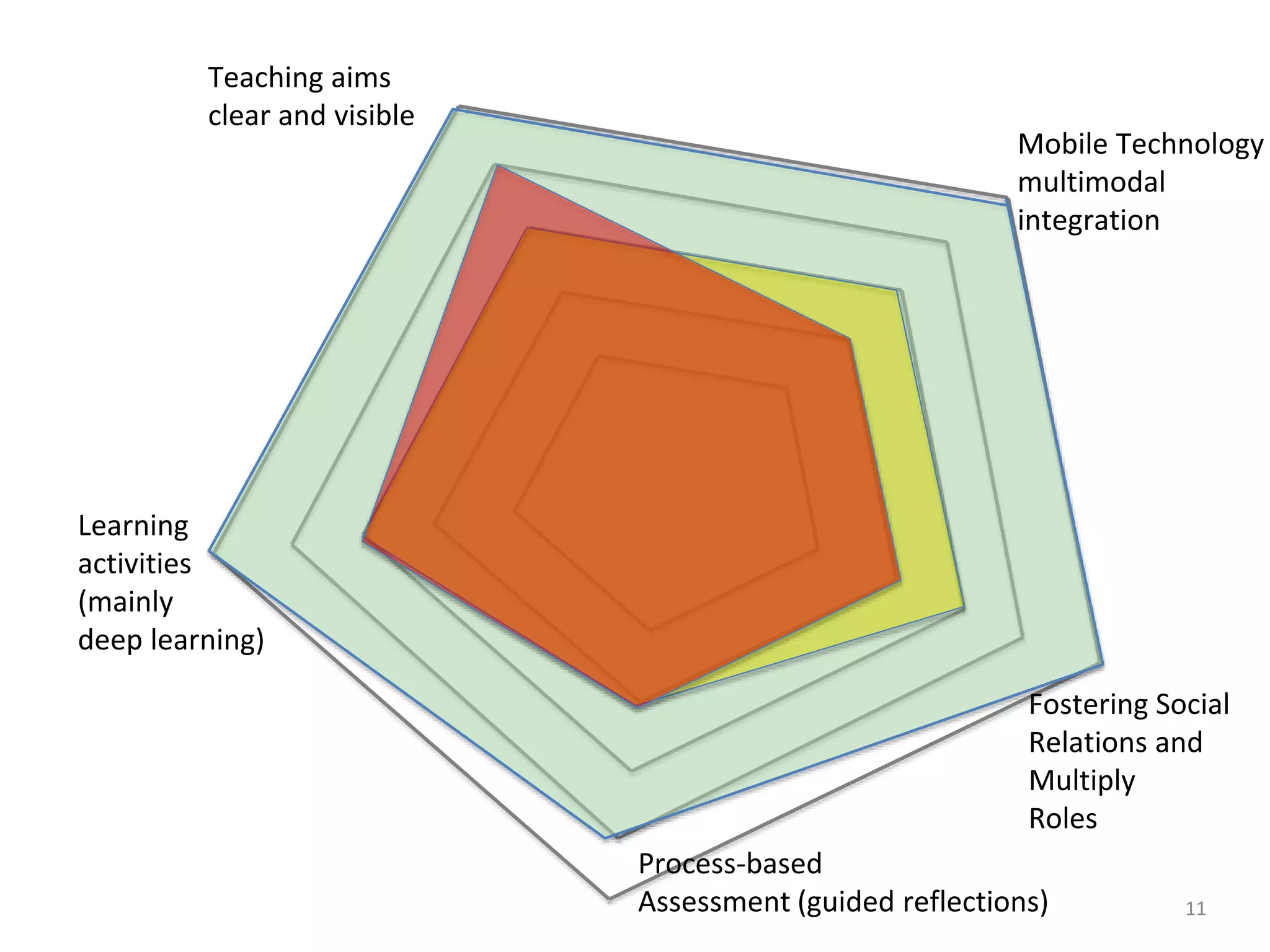
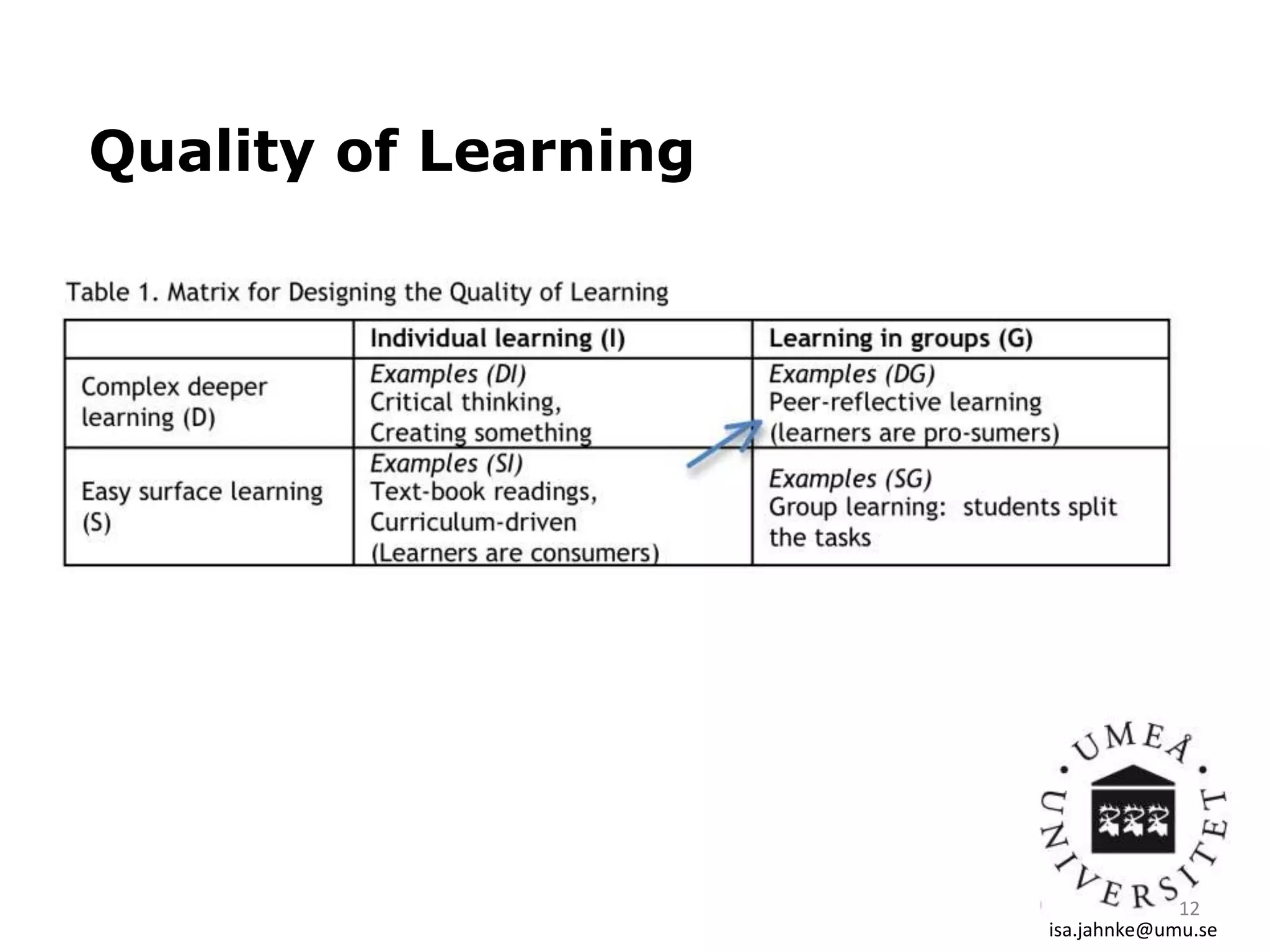
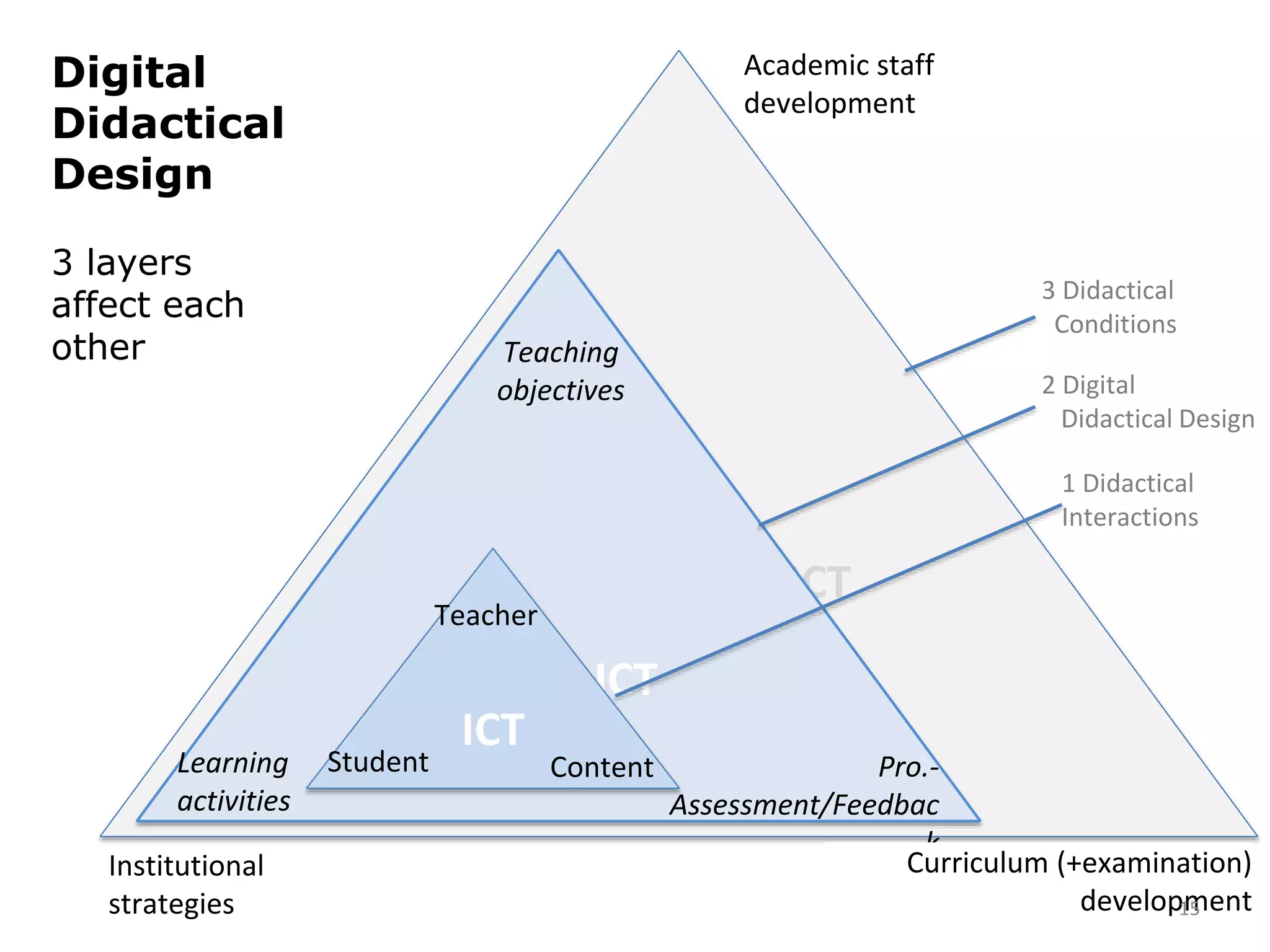
This document discusses digital didactical design (DDD), which is designing teaching practices that enable learning using mobile technology. It provides examples of empirical studies using mobile devices in higher education. DDD involves three layers - interactions, design, and conditions - that influence each other. The document proposes designing from teacher-centric to learner-centered practices by establishing clear learning aims and activities, process-based assessment, integrating mobile technology, and fostering social roles and relations. It suggests moving from traditional course-based learning to more open-ended "learning expeditions" and reflecting that teaching is evolving from a routine activity to a design project approach.