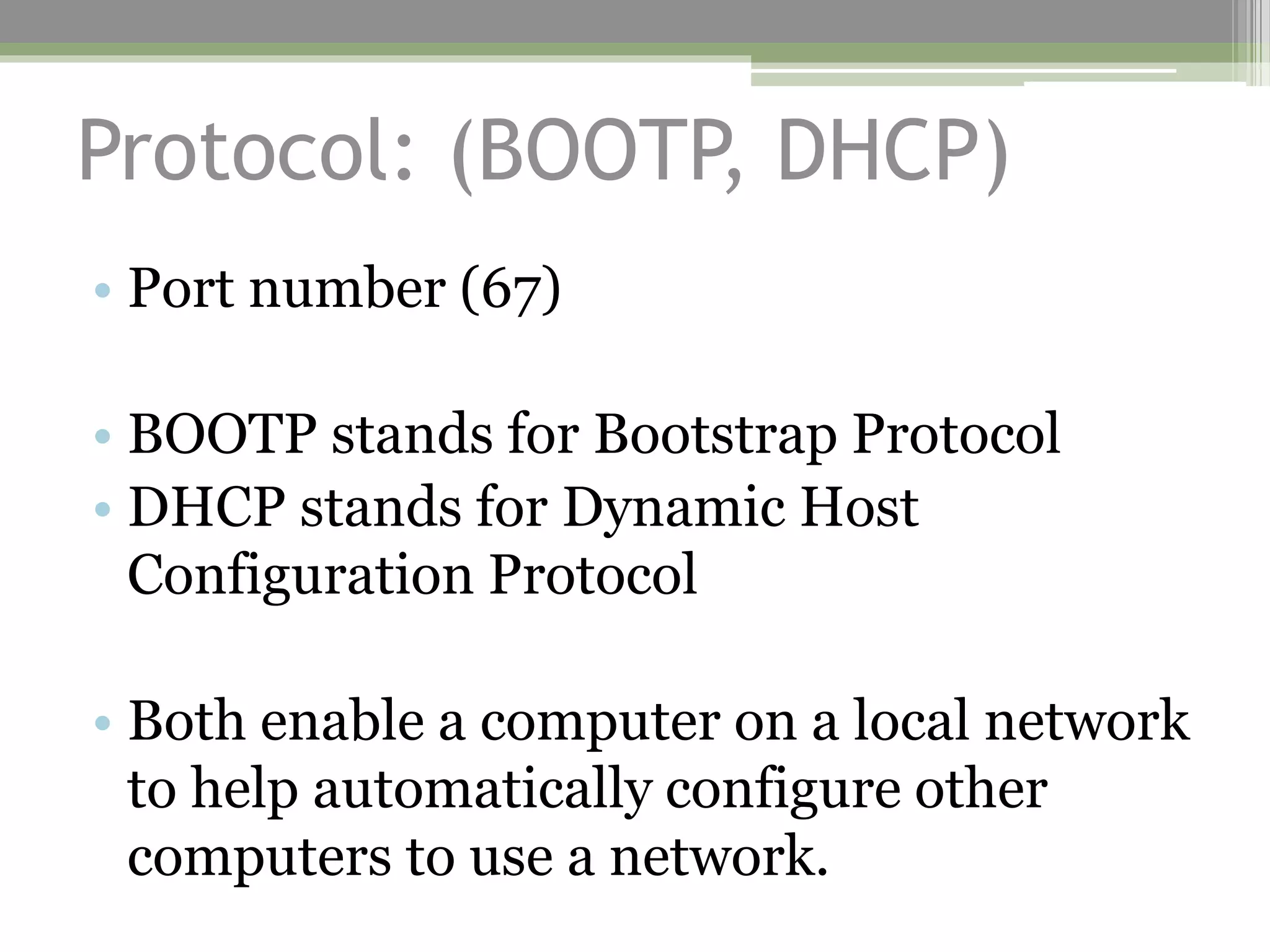
This document lists 20 common port numbers and their associated protocols, providing brief descriptions of each. It covers protocols for file transfer (FTP, SSH, Telnet), email (SMTP, POP2/3, IMAP), networking (DNS, BOOTP/DHCP, HTTP, SQL, SMB/CIFS, LDAP, NFS), and secure variants (HTTPS). The port numbers, protocol names and basic functions are provided for each entry.