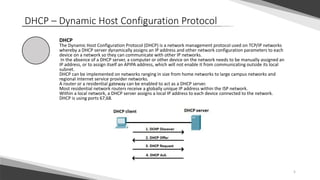
This document provides an overview of common network services and the ports they use. It describes services like DNS (port 53), DHCP (ports 67, 68), HTTP (port 80), HTTPS (port 443), FTP (port 21), SMTP (port 25), SMB (ports 445, 139), RDP (port 3389), and SQL (port 3306). Each service is defined along with the typical function it provides over a computer network and the client-server architecture most often used to deliver that service.