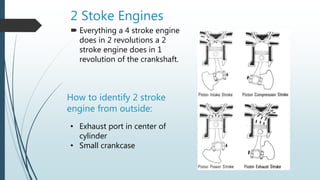
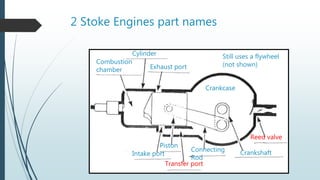
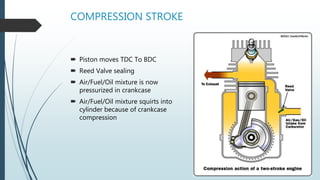
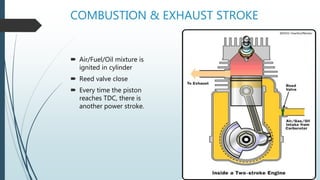
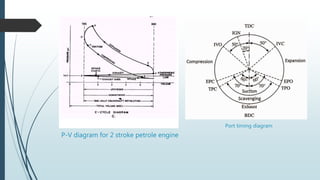
A two-stroke petrol engine completes the combustion cycle in two strokes of the piston rather than four as in a four-stroke engine. In a two-stroke engine, the intake and exhaust strokes are eliminated and ports instead of valves are used, with the exhaust gases driven out by the fresh fuel charge entering near the end of the power stroke. Everything a four-stroke engine does over two revolutions, a two-stroke engine accomplishes in one crankshaft revolution. Two-stroke engines are smaller, lighter, cheaper to produce but wear out faster and are less fuel efficient than four-stroke engines due to their greater pollution output.