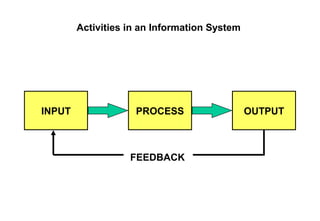
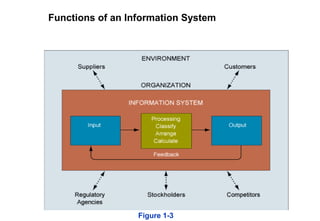
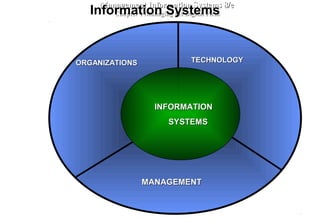
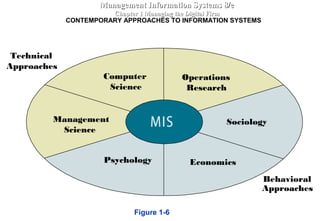
An information system is comprised of interrelated components that collect, process, store, and distribute information to support decision making and operations within an organization. It relies on computer hardware and software to process and disseminate data, which has been organized into a meaningful form, to support both formal systems operating with predefined rules and human users. An information system includes input, processing, output, and feedback activities to transform raw data into useful information.