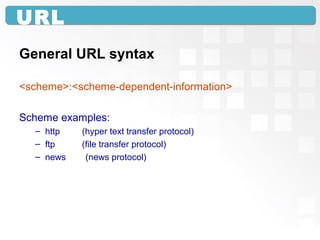
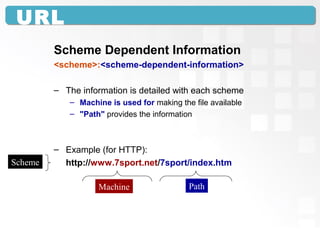
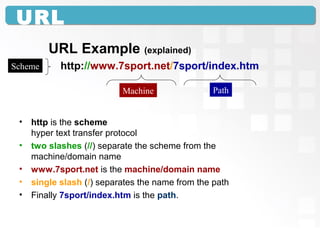
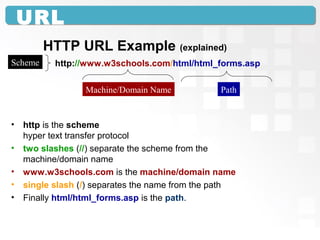
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL) specifies the location of an electronic resource and follows a general syntax of <scheme>:<scheme-dependent information>. The URL components include the scheme (such as http), machine/domain name (such as www.example.com), and path to identify the specific resource. URLs allow both humans and software to directly access resources over the internet or local networks. Common issues that can prevent accessing a URL include typing mistakes, the site being unavailable, or files being moved to a new location.