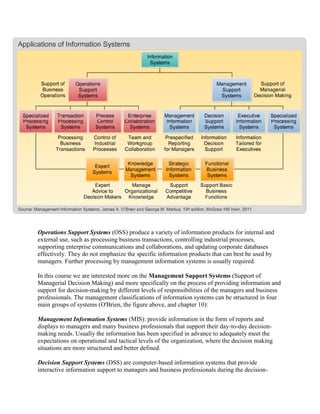
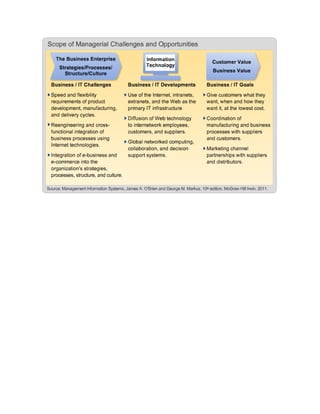
Management Information Systems and Decision-Making: An Overview discusses different types of information systems that support decision-making at various management levels. It describes strategic, tactical, and operational management and the kind of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured decisions made at each level. The document also outlines different types of information systems like Management Information Systems, Decision Support Systems, Executive Information Systems, and Specialized Processing Systems that provide information to managers and professionals. Finally, it notes that real-world information systems typically integrate various types of systems to support multiple management levels and business functions.