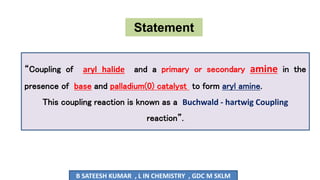
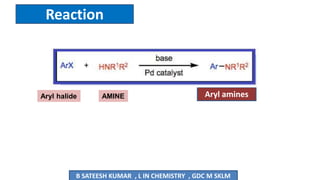
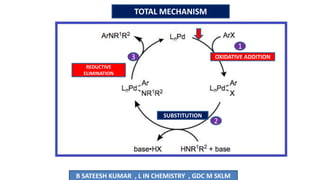
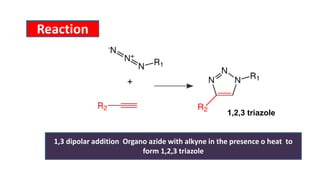
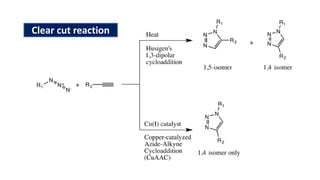
The document summarizes the Buchwald-Hartwig coupling reaction and click reaction. The Buchwald-Hartwig reaction involves the coupling of an aryl halide and a primary or secondary amine in the presence of a base and palladium catalyst to form an aryl amine. The reaction proceeds by oxidative addition, substitution, and reductive elimination steps. The click reaction refers to the copper-catalyzed cycloaddition of an azide and alkyne to form a 1,2,3-triazole ring. This reaction has simple reaction conditions and provides products with high atom economy.

![Unit-5
[New synthetic reactions]
1. Baylis-Hillmann reaction
2. Grubbs catalysts
3. Grubbs RCM olefin metathesis reaction
4. Mukayama aldol reaction
5. Mcmurry reaction
6. Mitsnobu reaction
7. Julia-lythgoe olefination
8. Peterson olefination
9. Heck reaction
10. Suzuki coupling
11. Stille coupling
12. Sonogishira coupling
13. Buchwald - hartwig coupling
14. Click reaction
15. Ugi reaction
B SATEESH KUMAR , L IN CHEMISTRY , GDC M SKLM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buchwaldhartwigcoupling-230815084434-7f78bbb7/85/buchwald-hartwig-coupling-ppt-3-320.jpg)