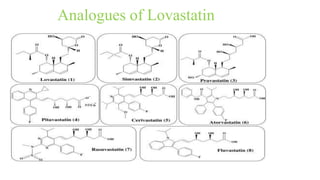
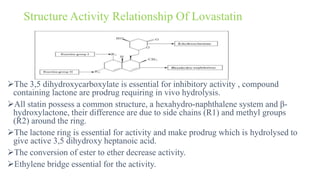
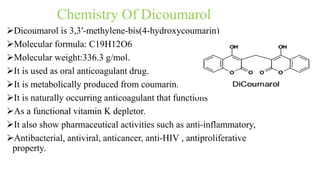
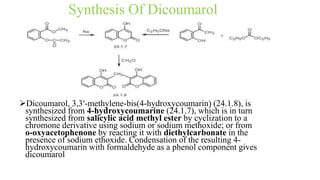
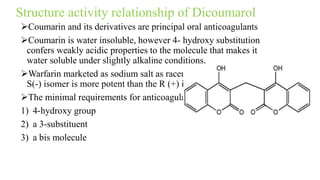
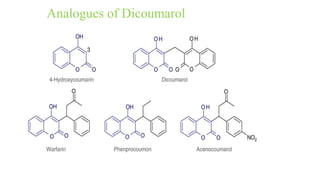
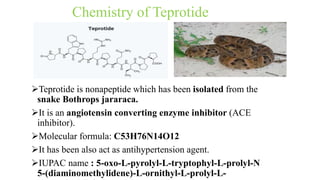
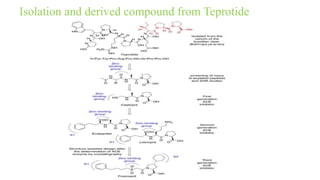
This document discusses three cardiovascular drugs: lovastatin, dicoumarol, and teprotide. It provides details on the chemistry, synthesis, mechanisms of action, analogs, structure-activity relationships, and therapeutic uses of each drug. Lovastatin is a statin drug that lowers cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Dicoumarol is an oral anticoagulant that functions as a vitamin K depletor. Teprotide was the first isolated angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor derived from snake venom, though it is no longer used clinically due to less potency than drugs like captopril.


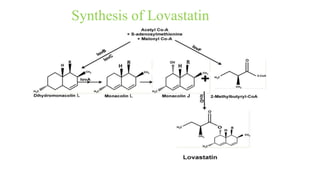
![Chemistry of Lovastatin
Lovastatin, 2-methylbutanoic acid 1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-
4-hydroxy 6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, mevinolin,MK-803
(Mevacor) (formerly called mevinolin), is a potentinhibitor of HMG-CoA.
The drug was obtained originally from the fermentation product of the fungi Aspergillus
terreus and Monascus ruber.
Molecular formula: C24H36O5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiovasculardrug-210726060929/85/Cardiovascular-drug-7-320.jpg)