This presentation summarizes concepts in supramolecular host-guest design, including:
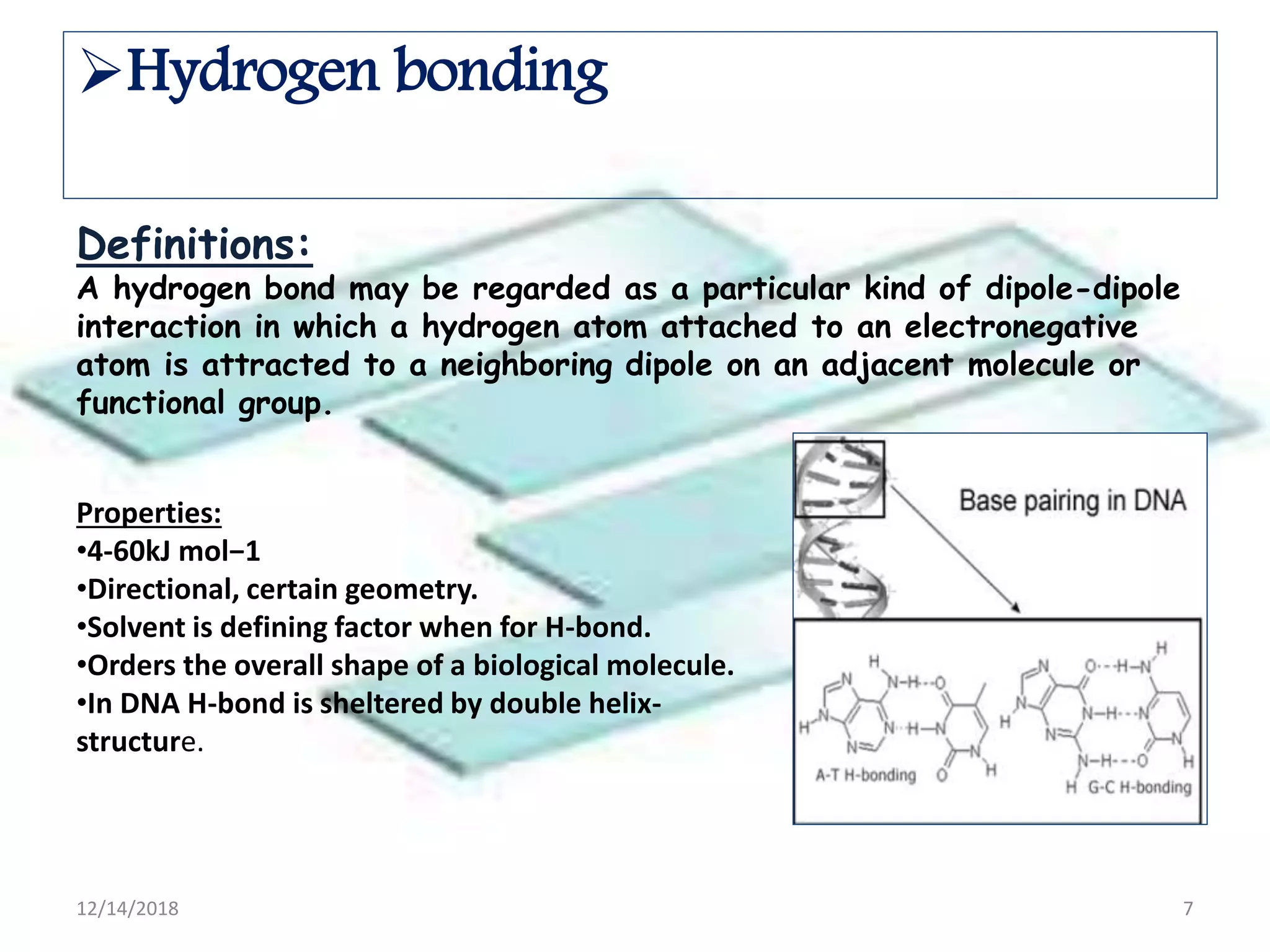
- Host-guest chemistry involves noncovalent interactions between a host molecule and guest, such as electrostatic interactions or hydrogen bonding.
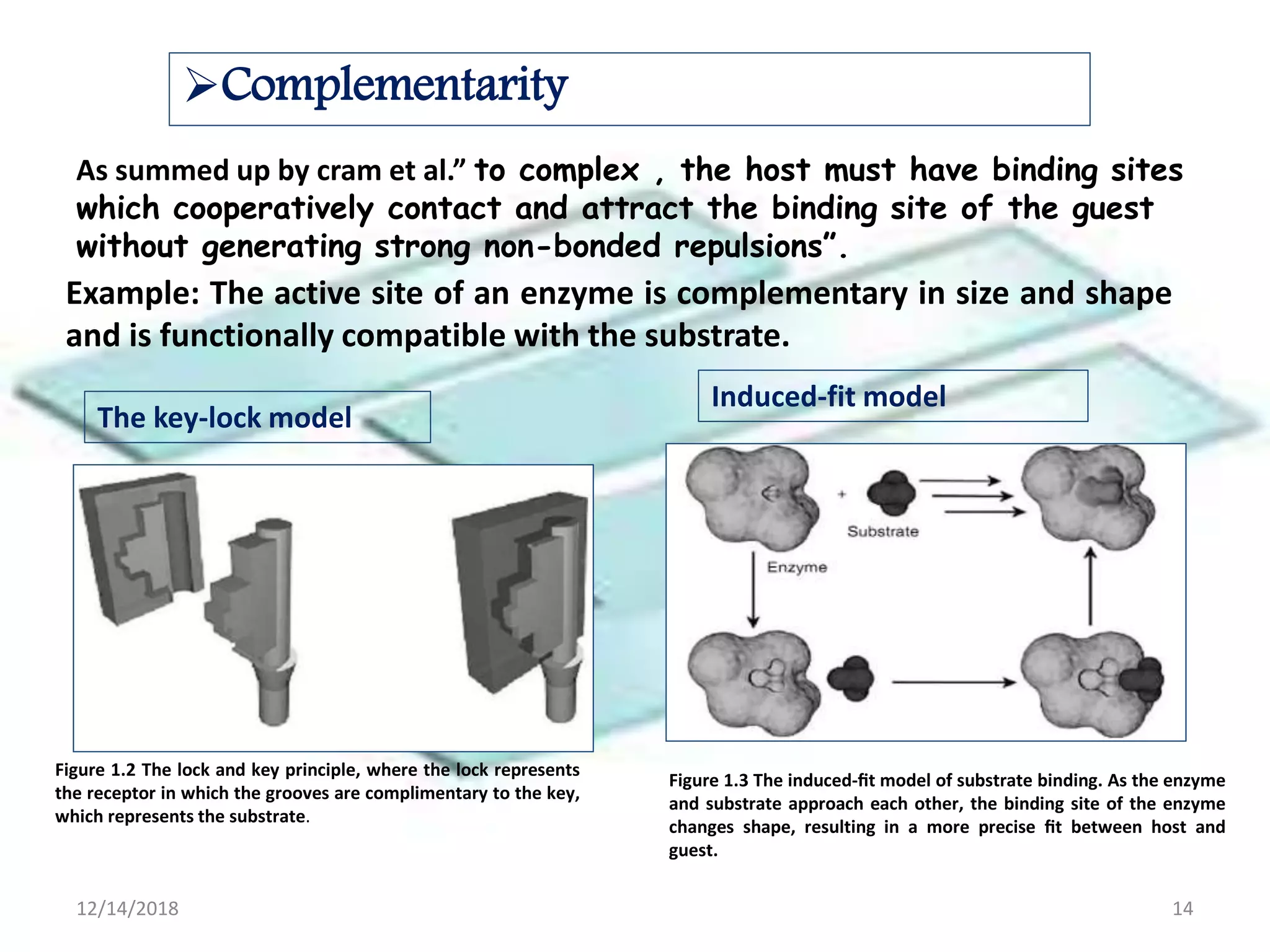
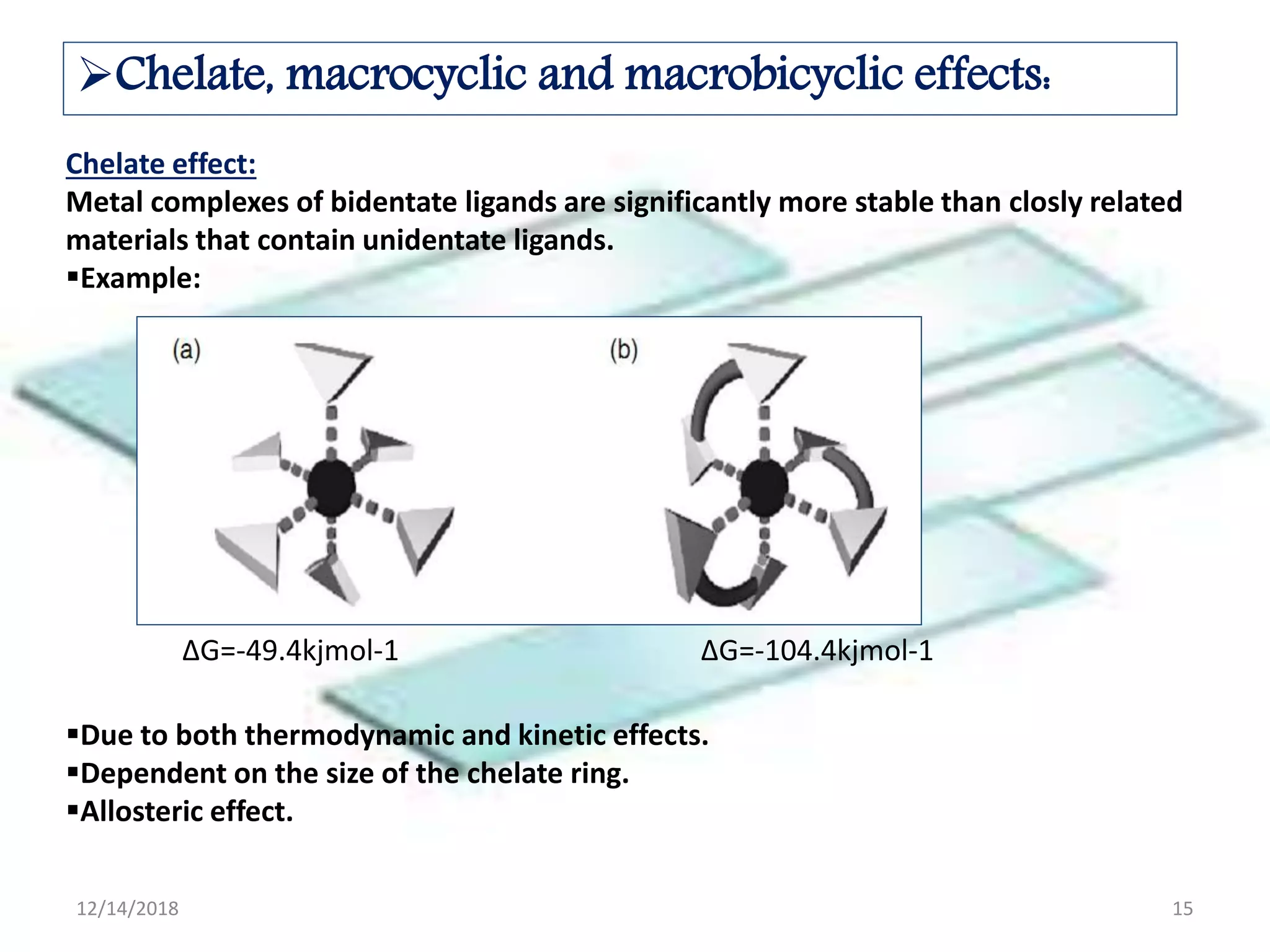
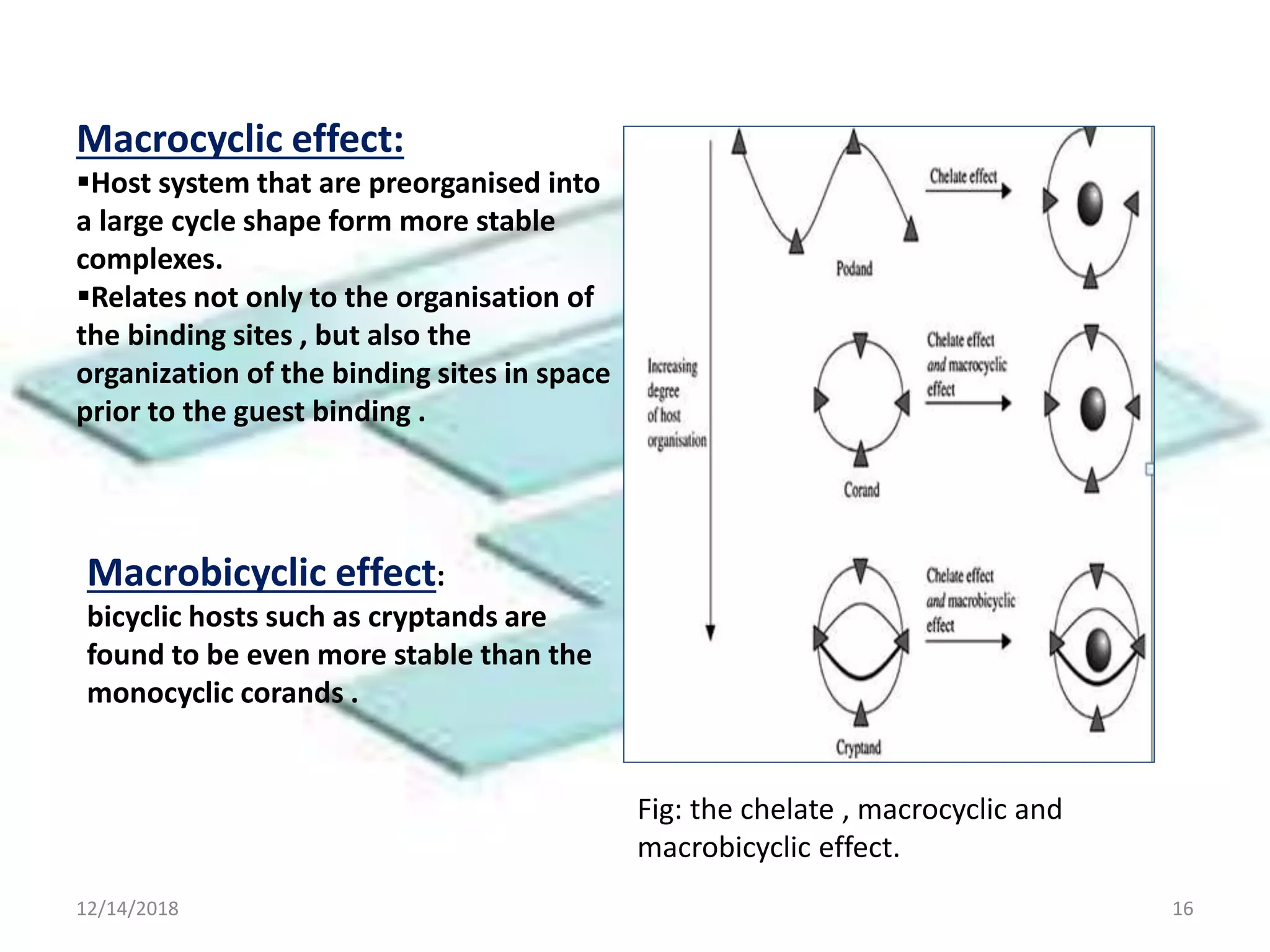
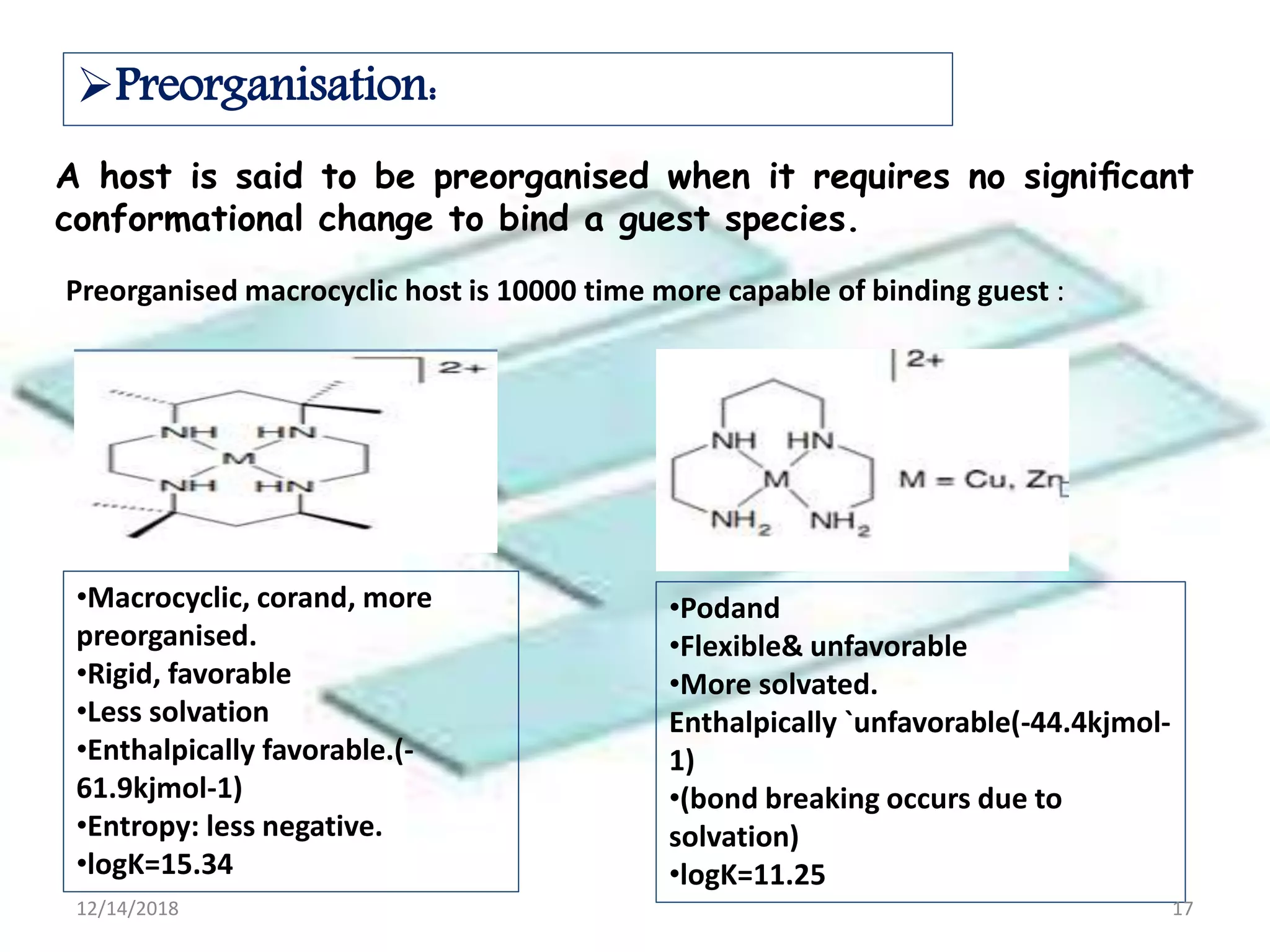
- Successful host-guest complexes rely on complementarity between the host's binding sites and the guest's structure, as well as preorganization of the host.
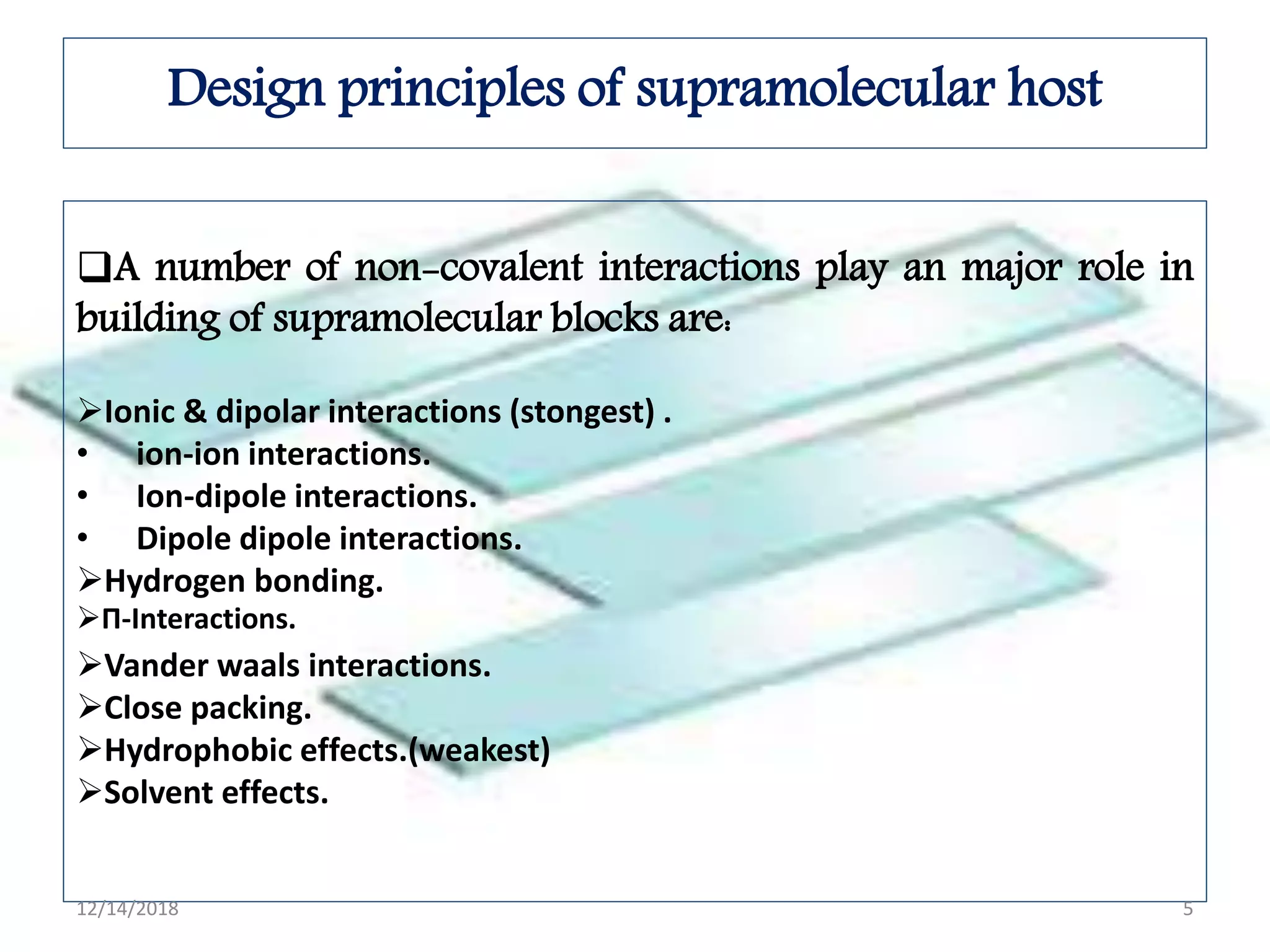
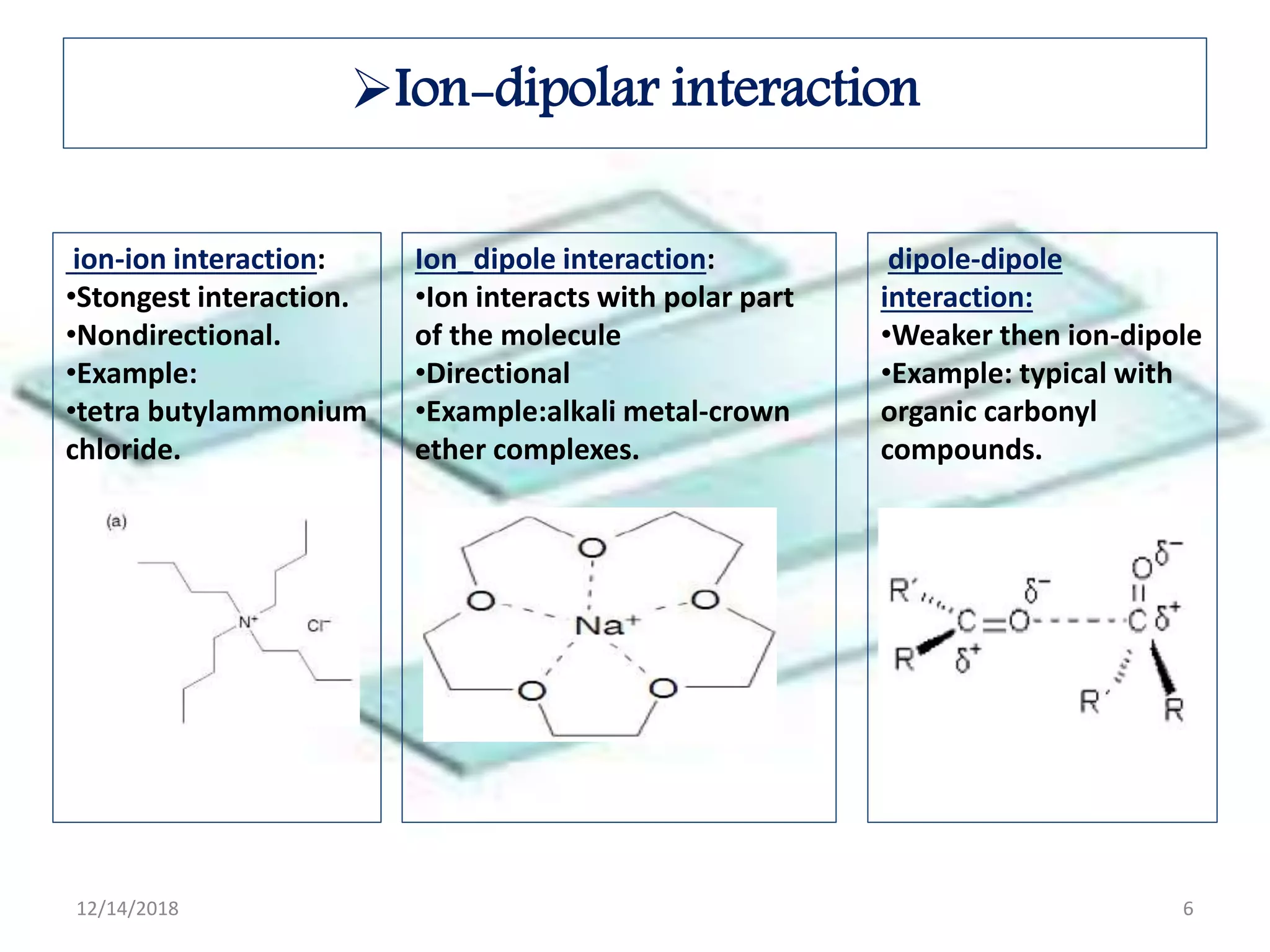
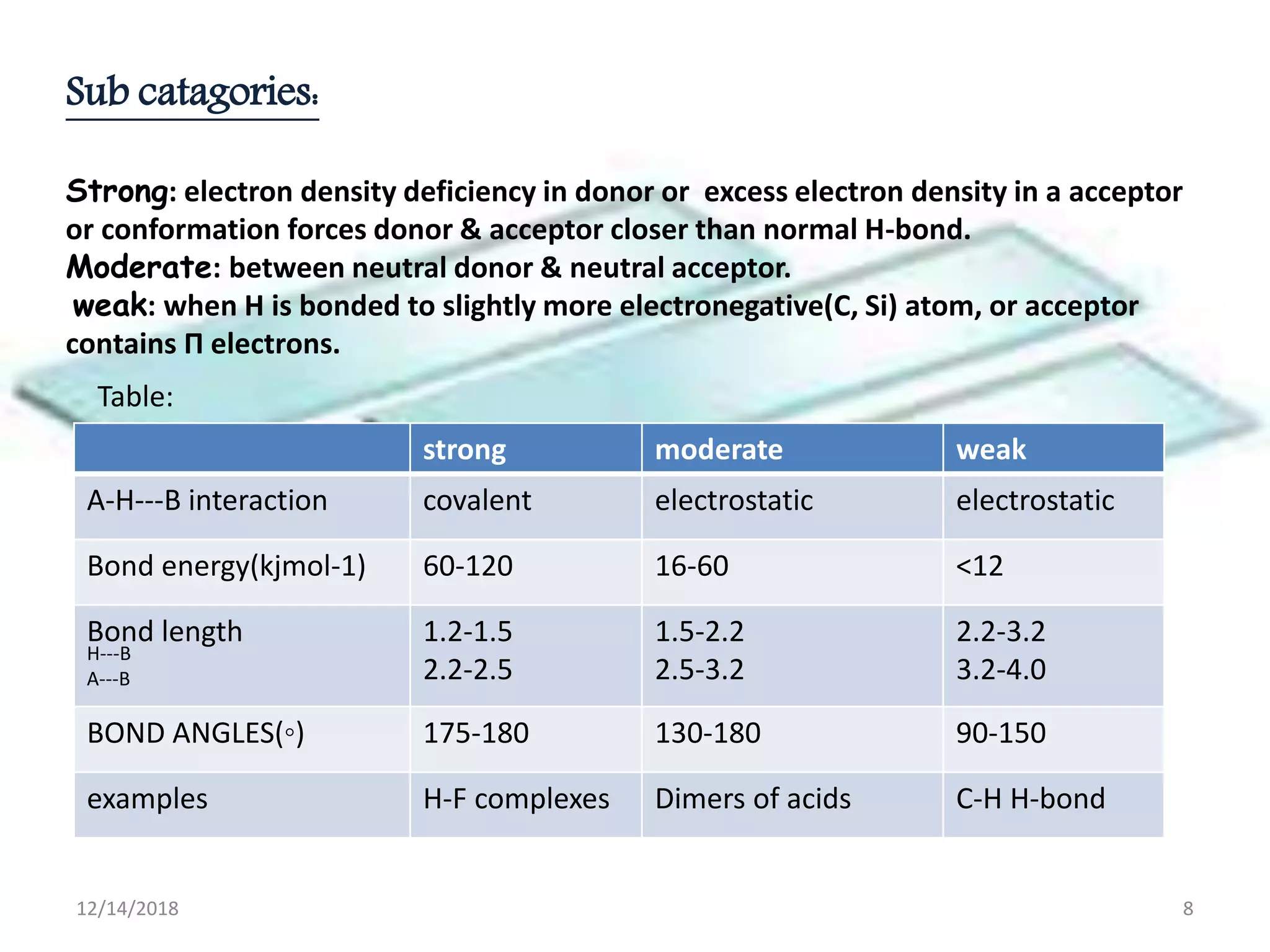
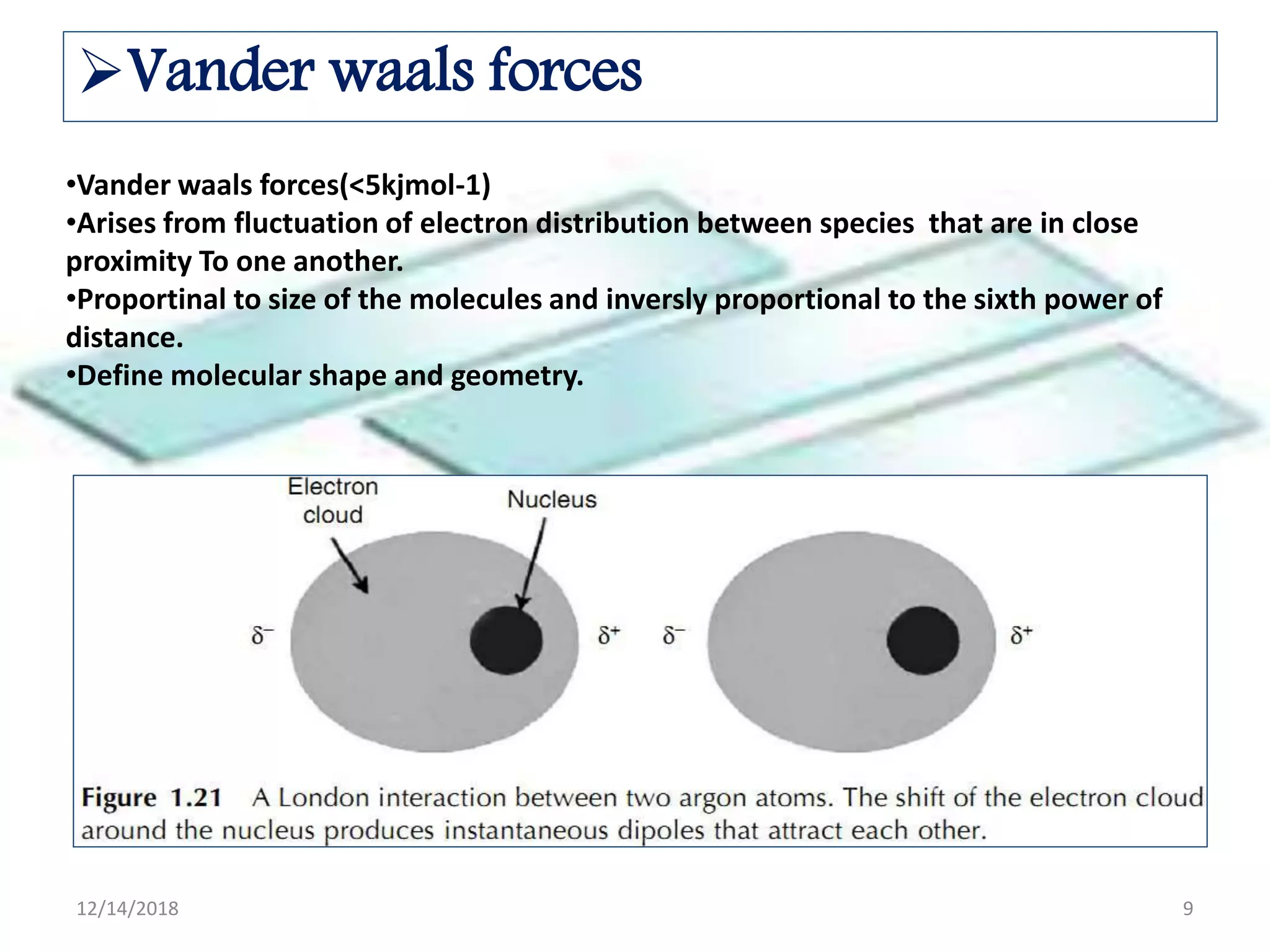
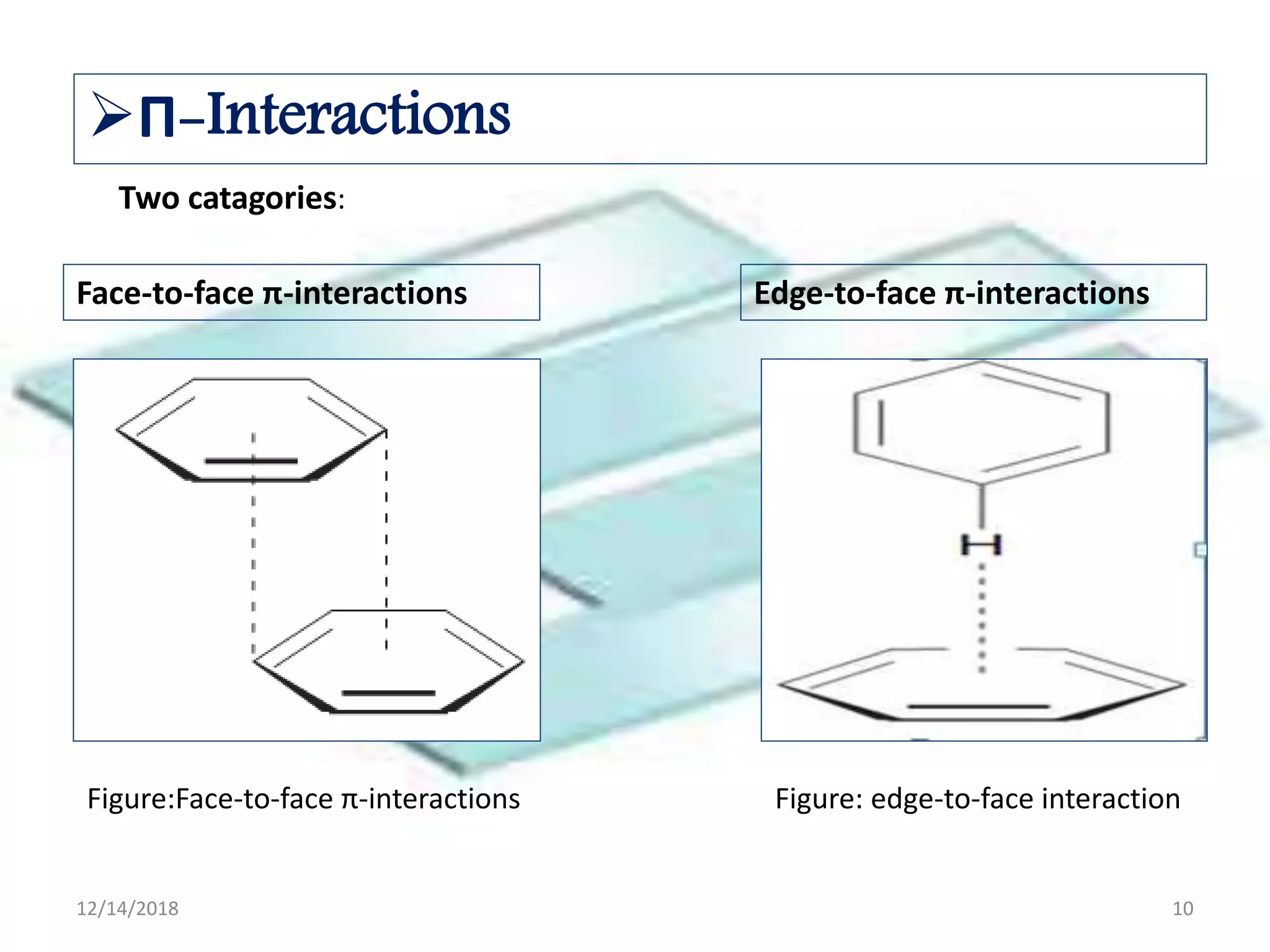
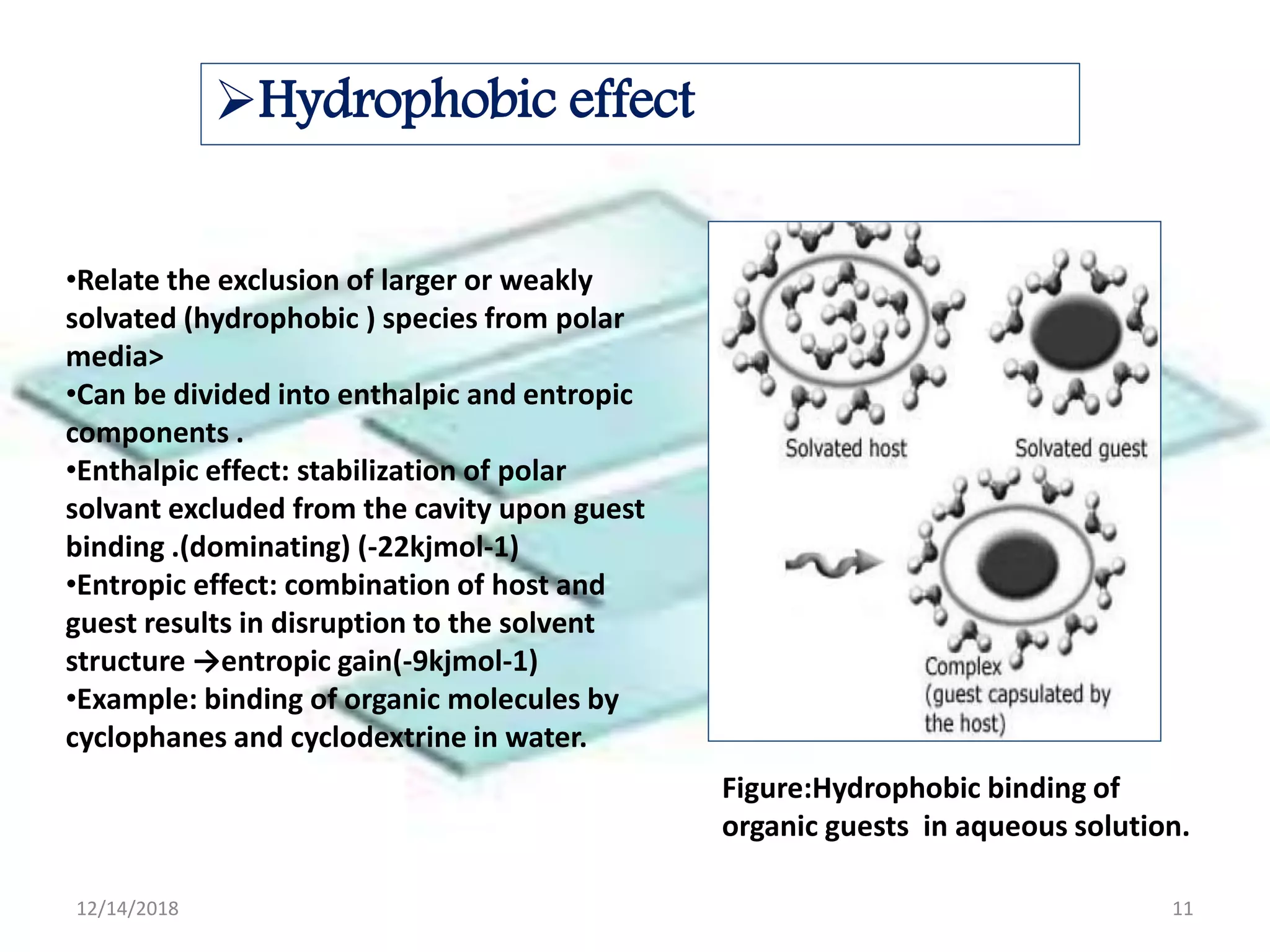
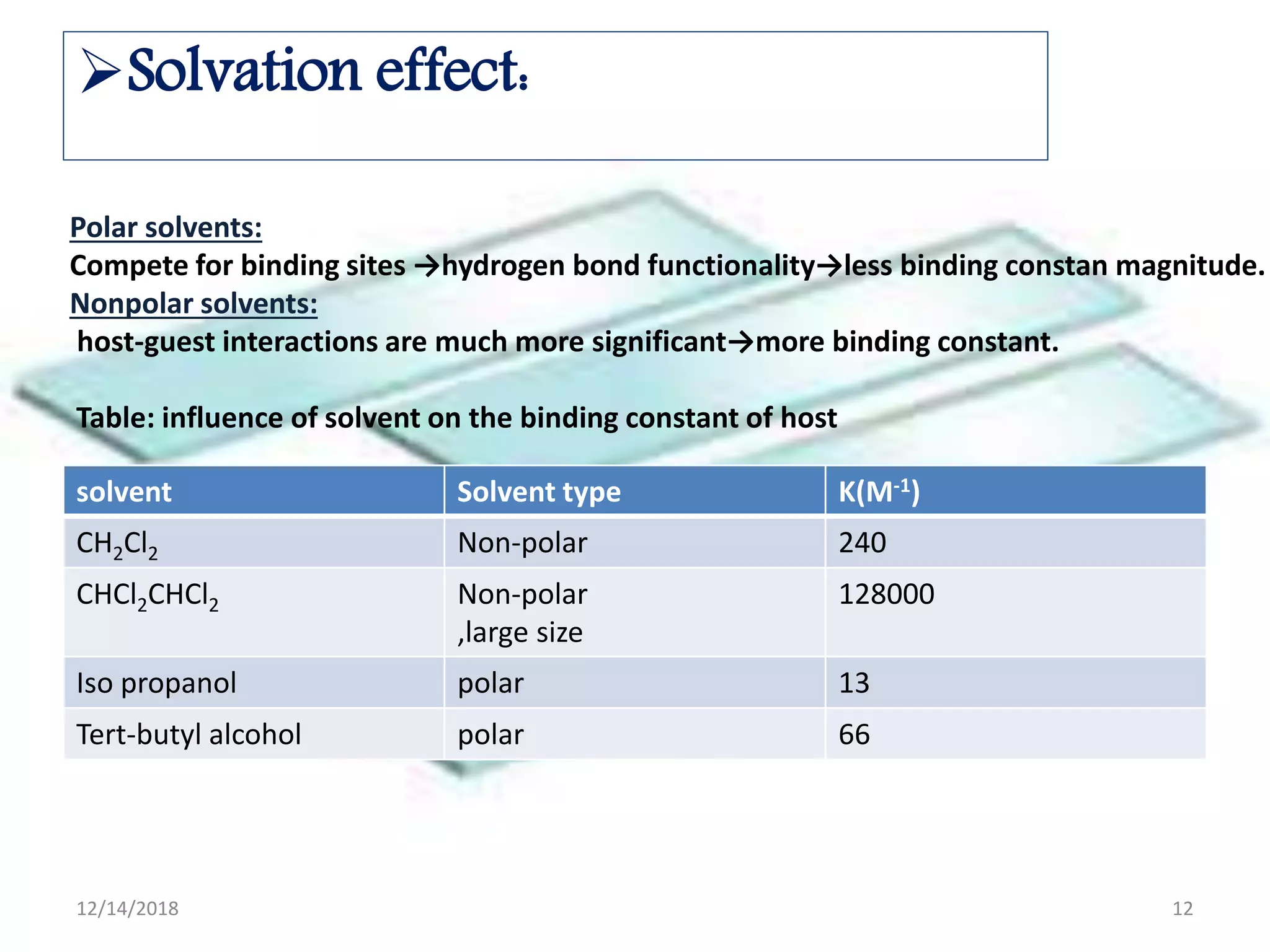
- Common noncovalent interactions that contribute to host-guest binding include ion-dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, π-π interactions, and hydrophobic effects. The interplay of these interactions allows for selective and stable complex formation.
- Host design considerations include selectivity, complementarity between binding sites