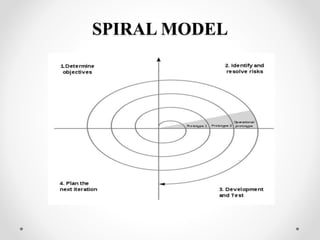
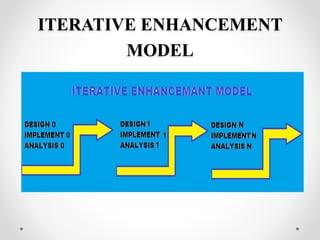
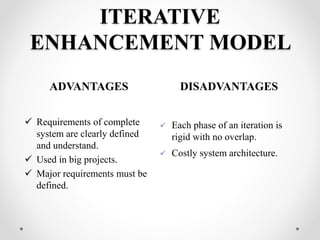
This document discusses different software development life cycle (SDLC) models. It describes the waterfall model as the first introduced process model where each phase must be completed before the next begins. The spiral model is presented as a combination of waterfall and risk analysis, with iterative cycles to reduce risk. The iterative enhancement model implements parts of software in cycles to identify further requirements through review.

![CONTENTS
1. Software Development Life Cycle Models[SDLC]
2. Types of SDLC Models
3.Waterfall Model
4. Iterative Model
5. Spiral Model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-141108082247-conversion-gate02/85/1-sdlc-2-320.jpg)