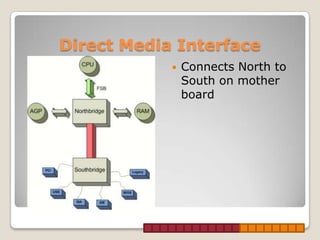
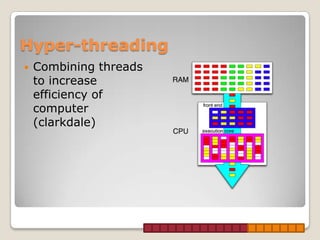
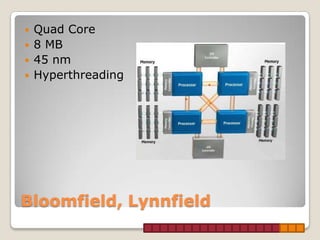
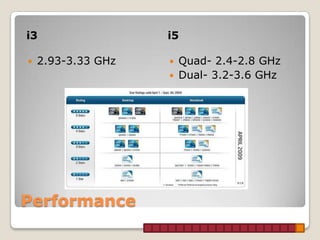
This document provides information about Intel processors, specifically the i3, i5, and i7 models. It discusses the basic features of each line including core counts, clock speeds, cache sizes, and the inclusion of technologies like hyperthreading. The i3 is positioned as the entry-level option with dual cores, lower speeds and smaller caches. The i5 is mid-range with quad cores on some models and larger caches. The i7 is the high-end option with support for quad, hex, and octa-core configurations along with the largest caches and inclusion of hyperthreading across all models.