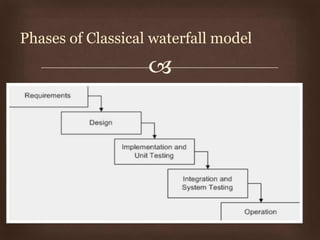
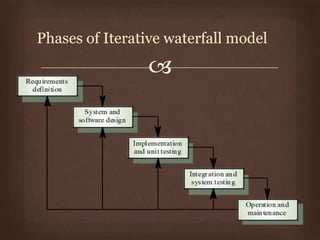
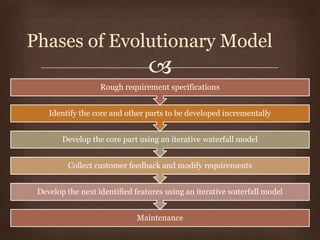
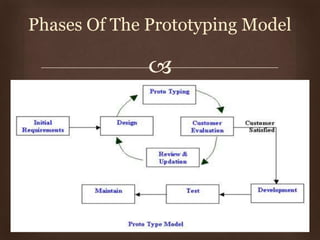
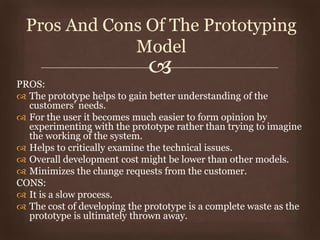
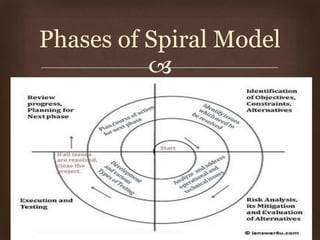
This document discusses different software life cycle models, including the classical waterfall model, iterative waterfall model, evolutionary model, prototyping model, and spiral model. It describes the phases and advantages and disadvantages of each. The classical waterfall model is considered theoretical while the iterative model is more practical but rigid. The evolutionary and prototyping models are useful when requirements are unclear. The spiral model subsumes other models but is complex. The appropriate model depends on the project's risks and understanding. Adhering to a model helps produce quality software systematically.