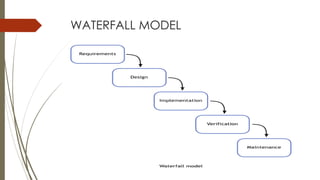
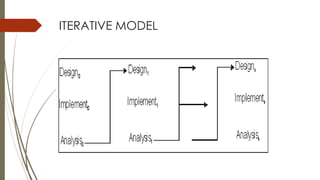
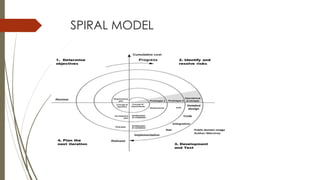
This document discusses different software development life cycle (SDLC) models. It describes the waterfall model as having distinct phases including requirements definition, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. The iterative model develops software incrementally in iterations. The spiral model involves risk assessment and reduction at each phase through objective setting, development/validation, and planning. The document compares the advantages and disadvantages of each model.