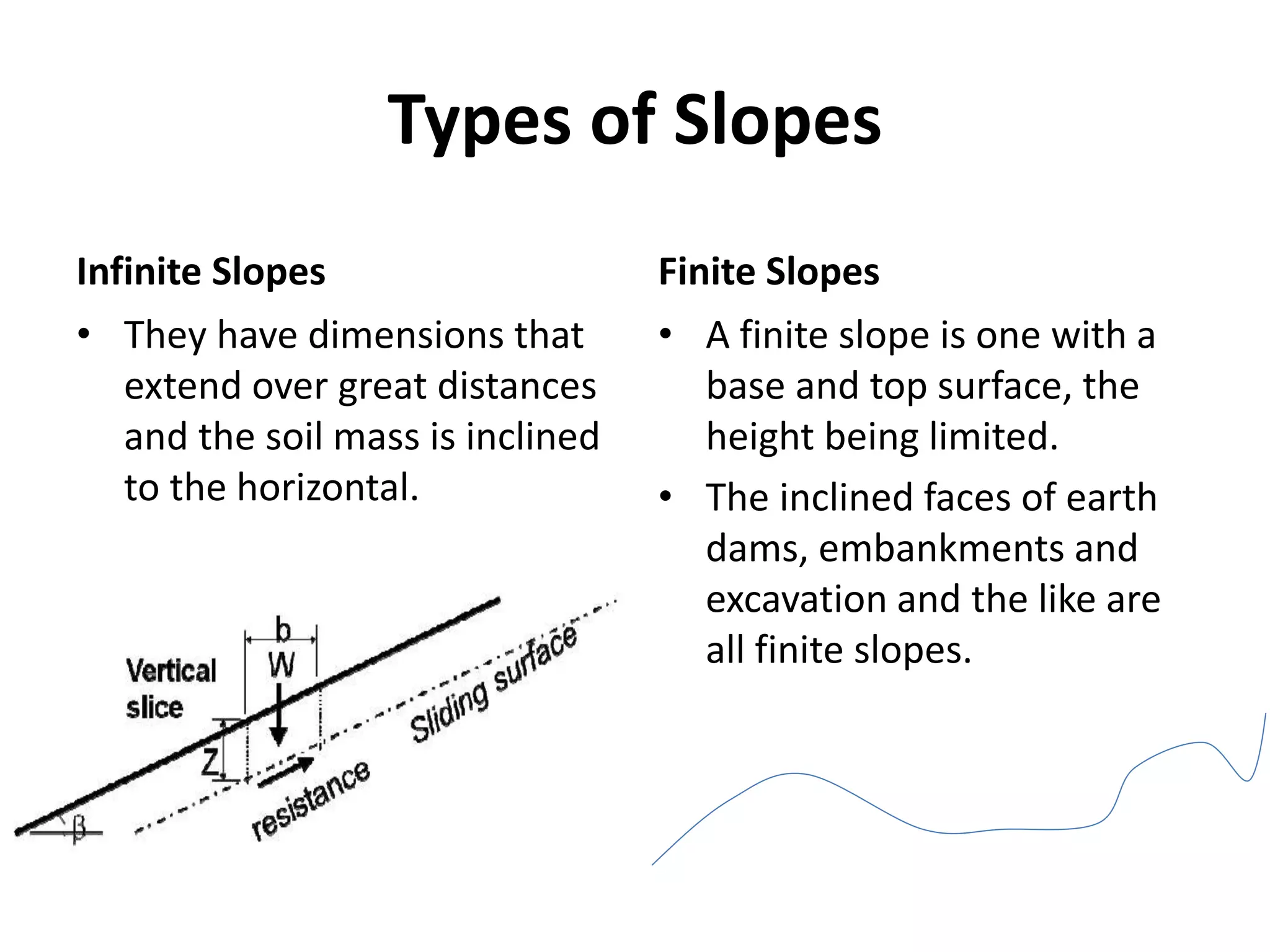
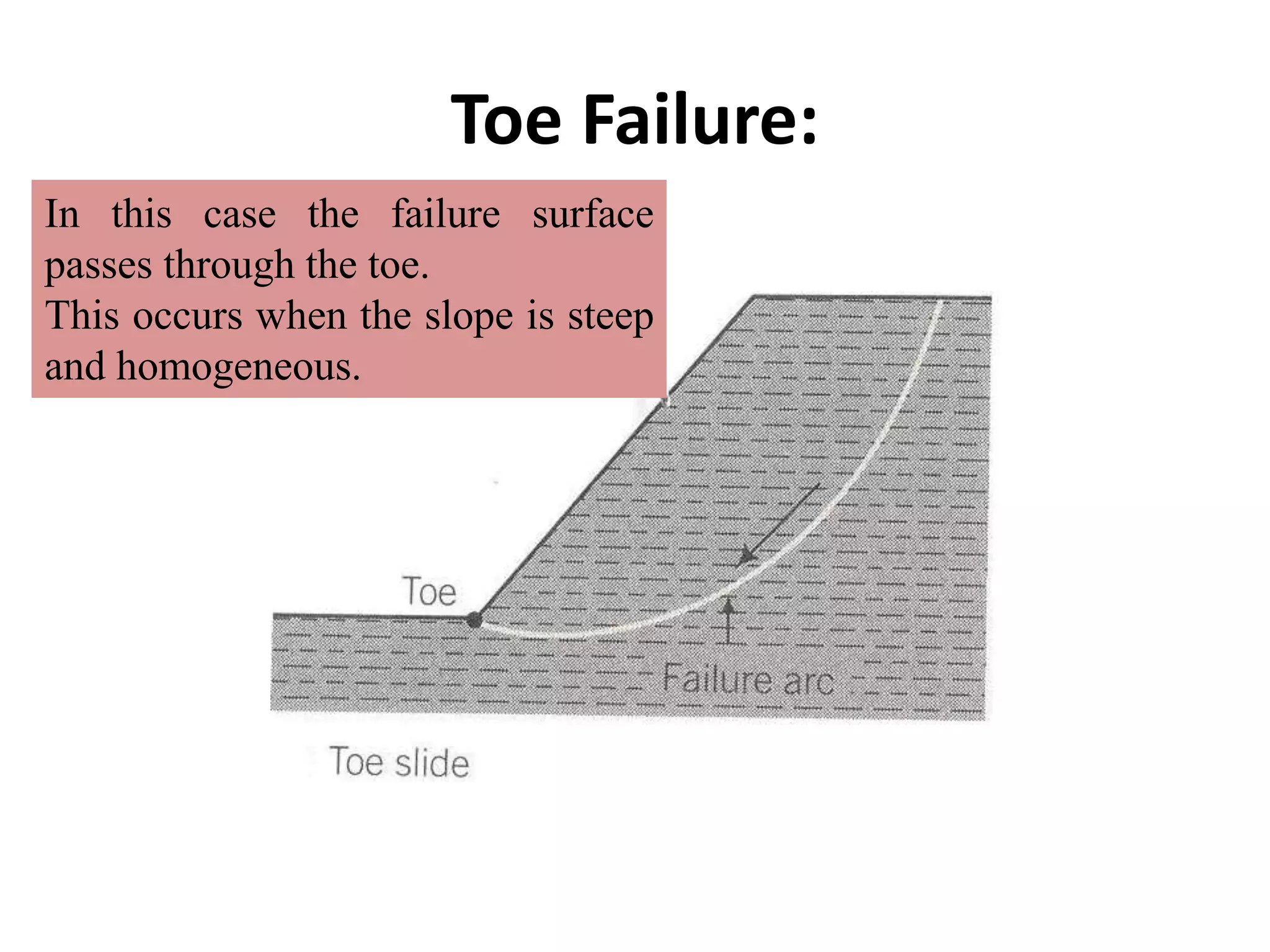
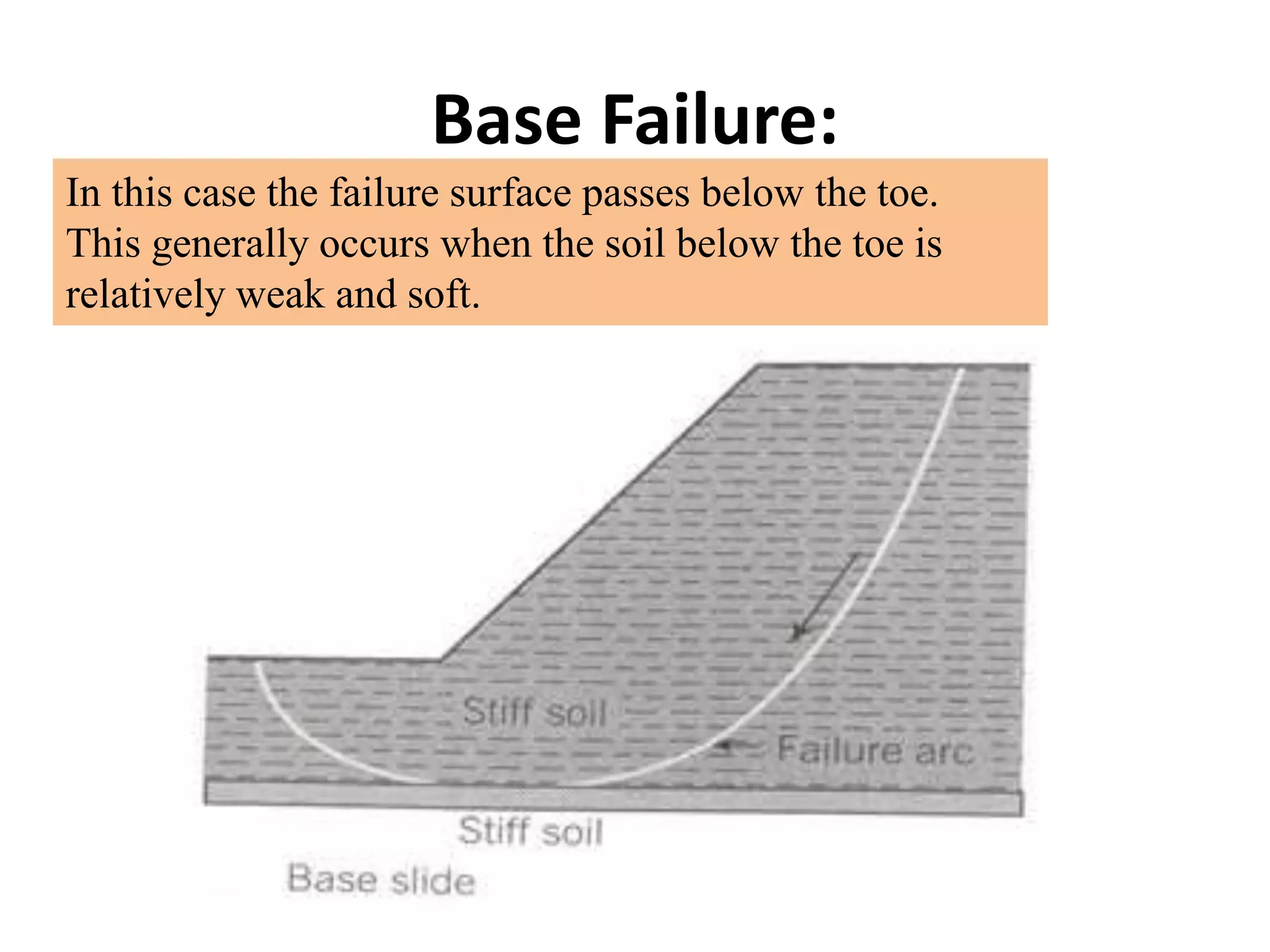
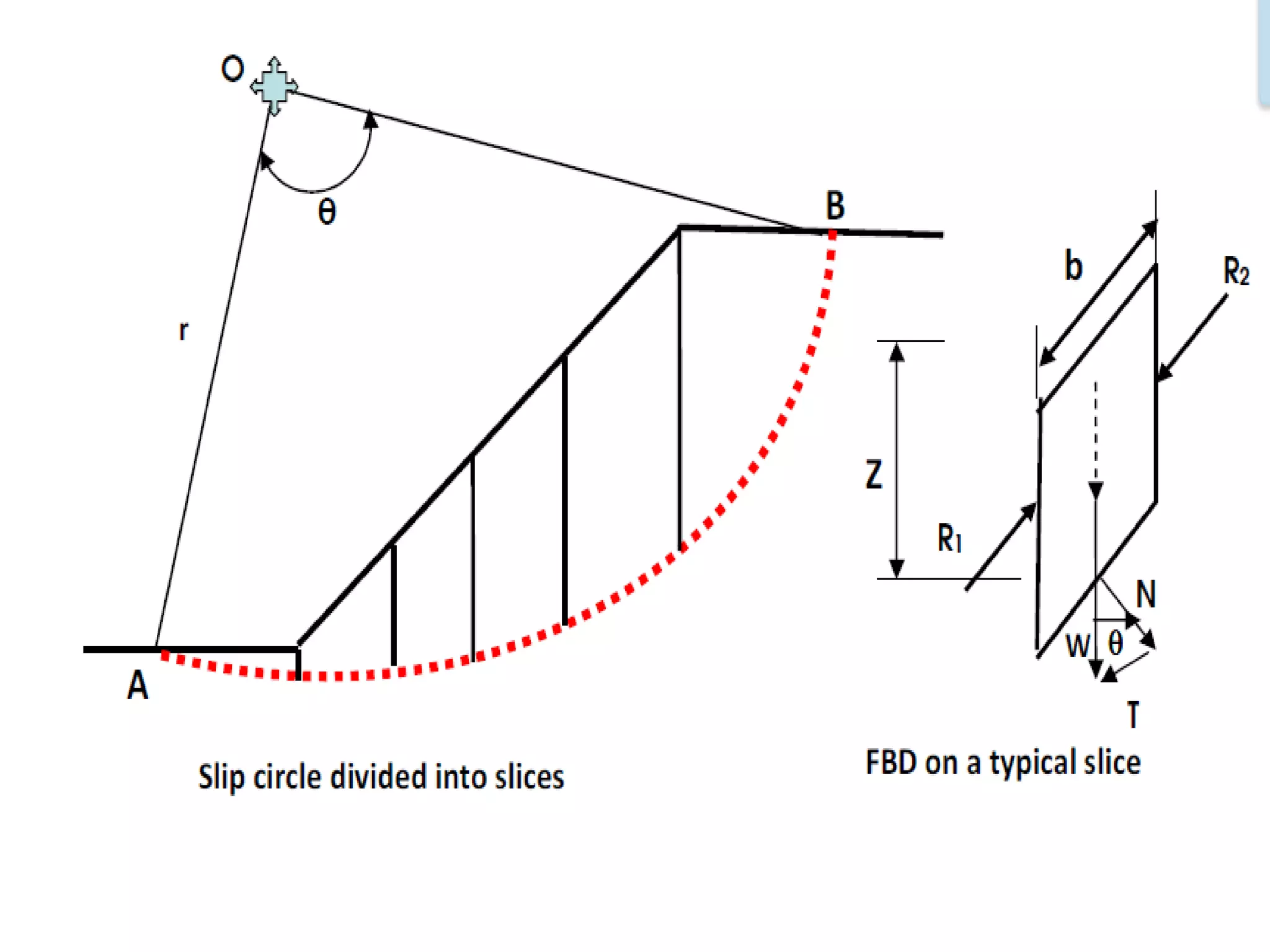
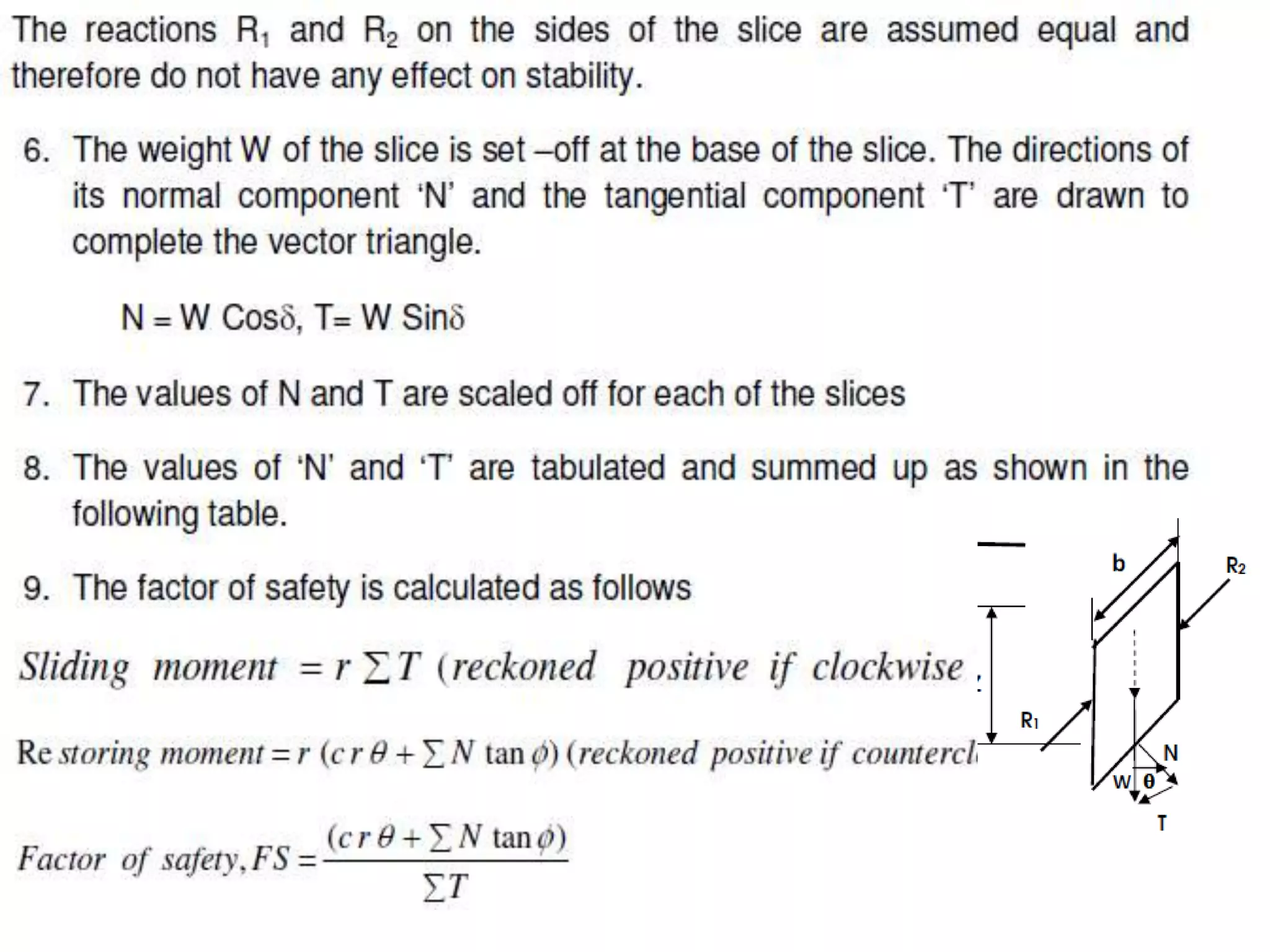
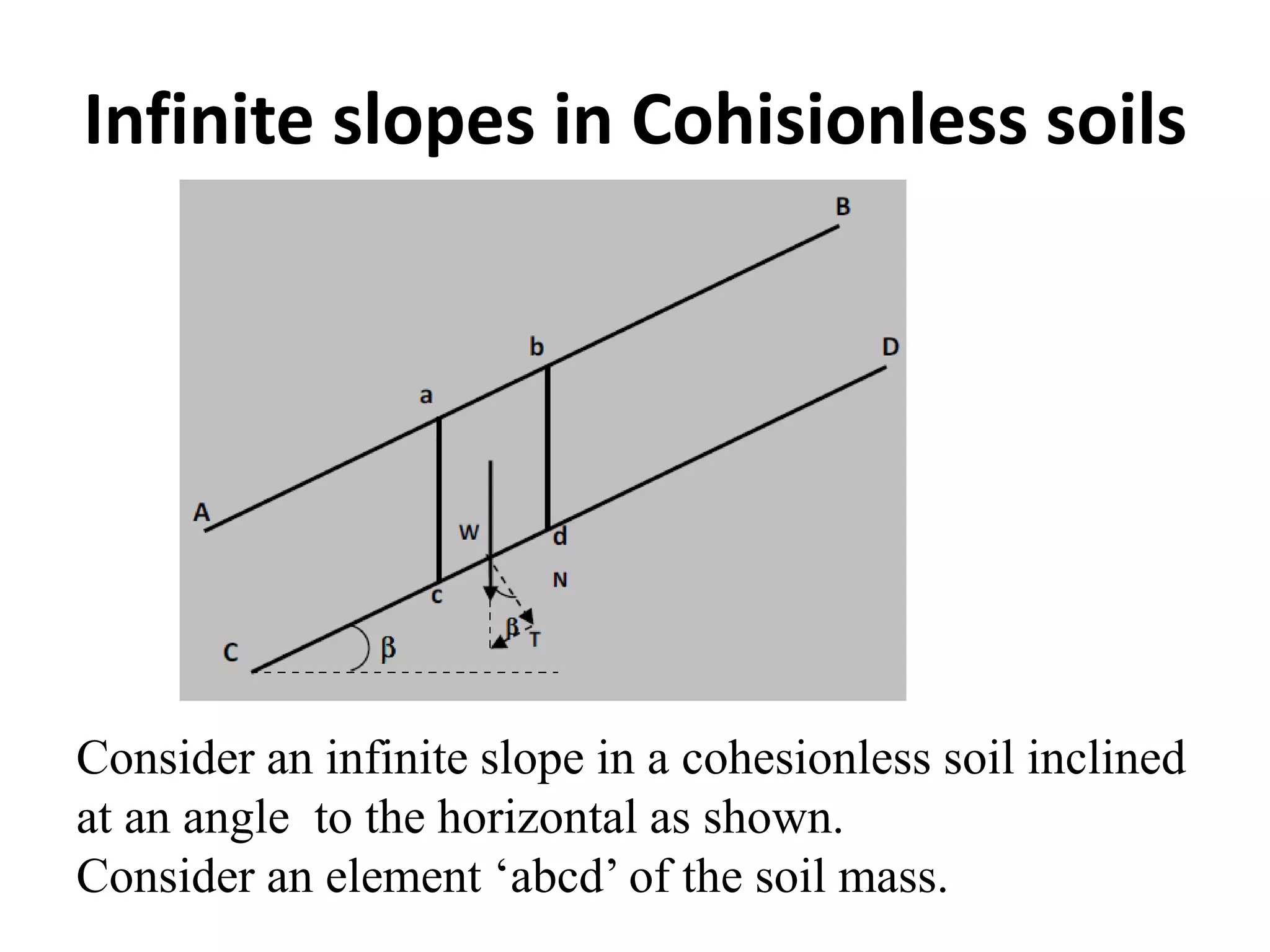
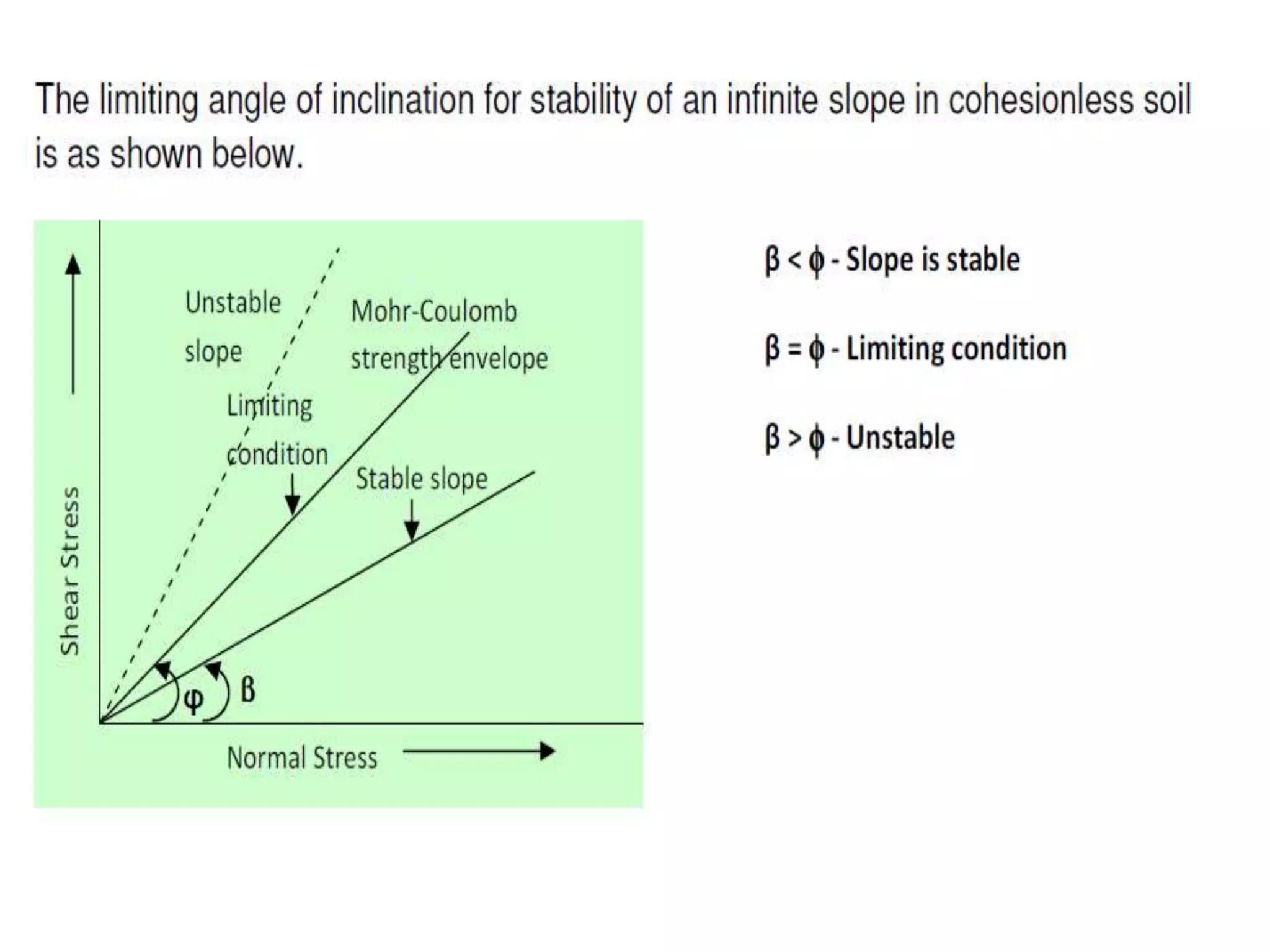
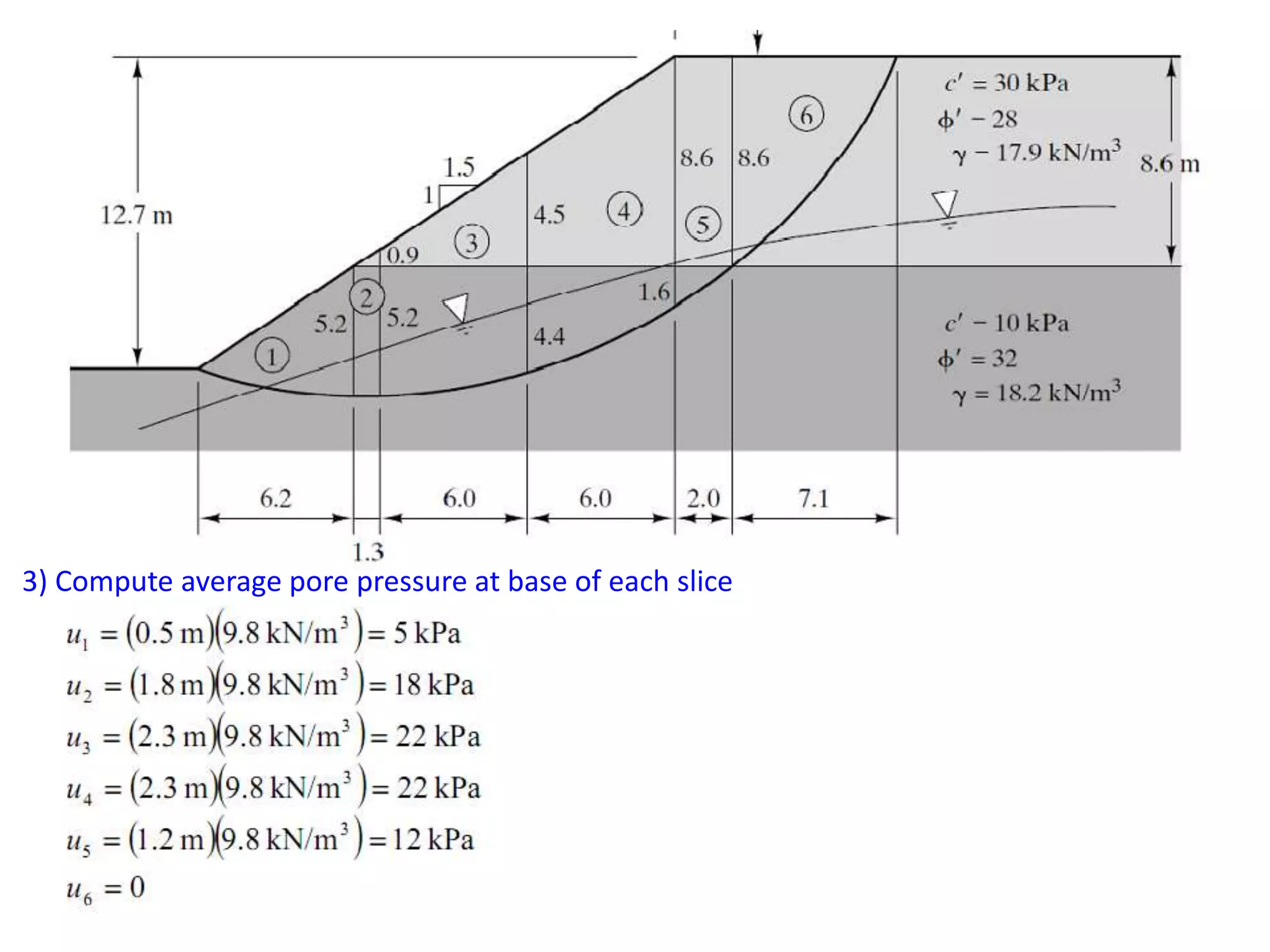
This document provides an overview of slope stability and analysis. It defines different types of slopes as natural, man-made, infinite and finite. Common causes of slope failure like erosion, seepage, drawdown, rainfall, earthquakes and external loading are described. Key terms used in slope stability are defined, including slip zone, slip plane, sliding mass and slope angle. Types of slope failures are identified as face/slope failure, toe failure and base failure. Methods for analyzing finite slope stability, like Swedish circle method, Bishop's simplified method and Taylor's stability number are introduced. Infinite slope analysis is described for cohesionless, cohesive and cohesive-frictional soils. Example tutorial problems on slope stability calculations are