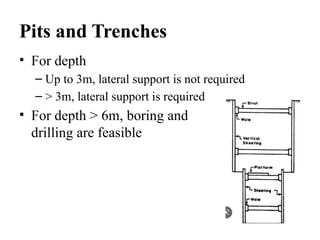
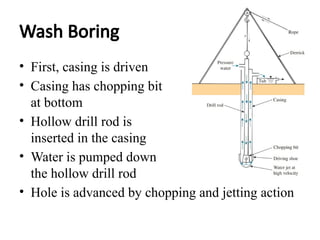
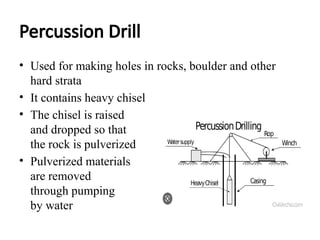
The document outlines the soil exploration process, which involves identifying soil layers, analyzing physical properties, and assessing conditions for foundation design. Various methods, such as pits, boring, and geophysical techniques, are employed depending on depth and soil characteristics. The purpose of soil exploration is to inform the selection of foundation type, evaluate bearing capacity, estimate settlement, and identify potential issues like expansive soils.