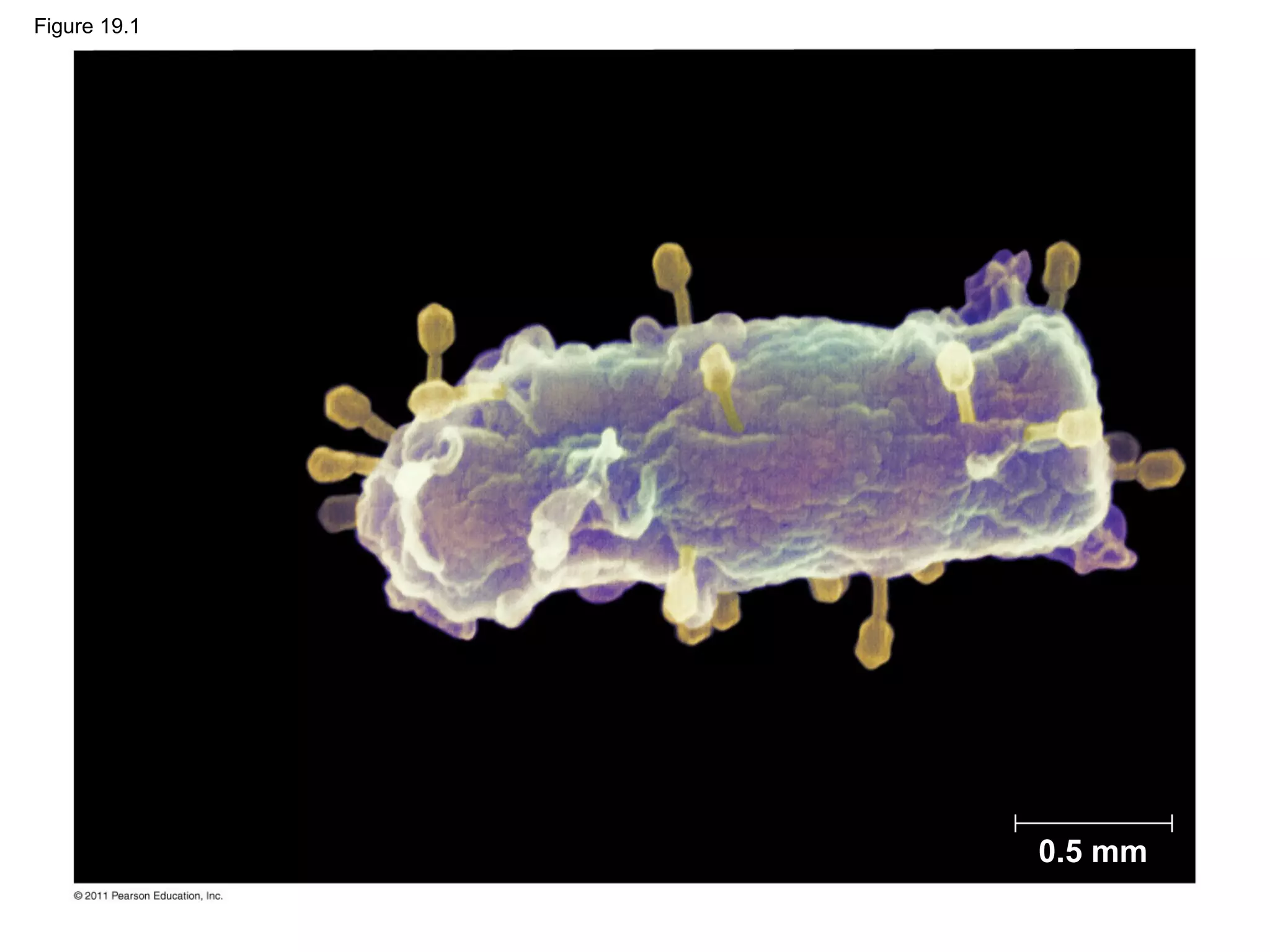
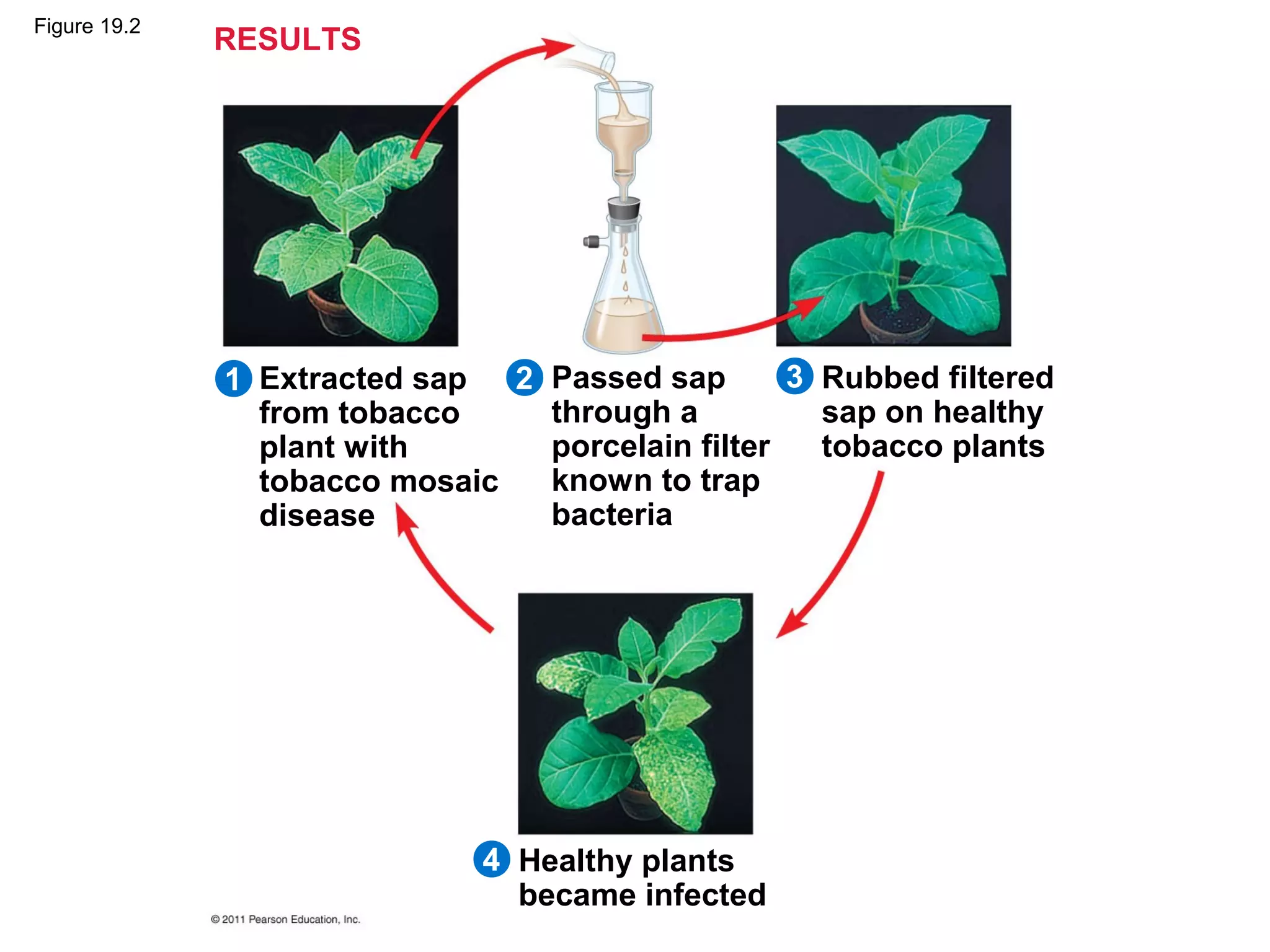
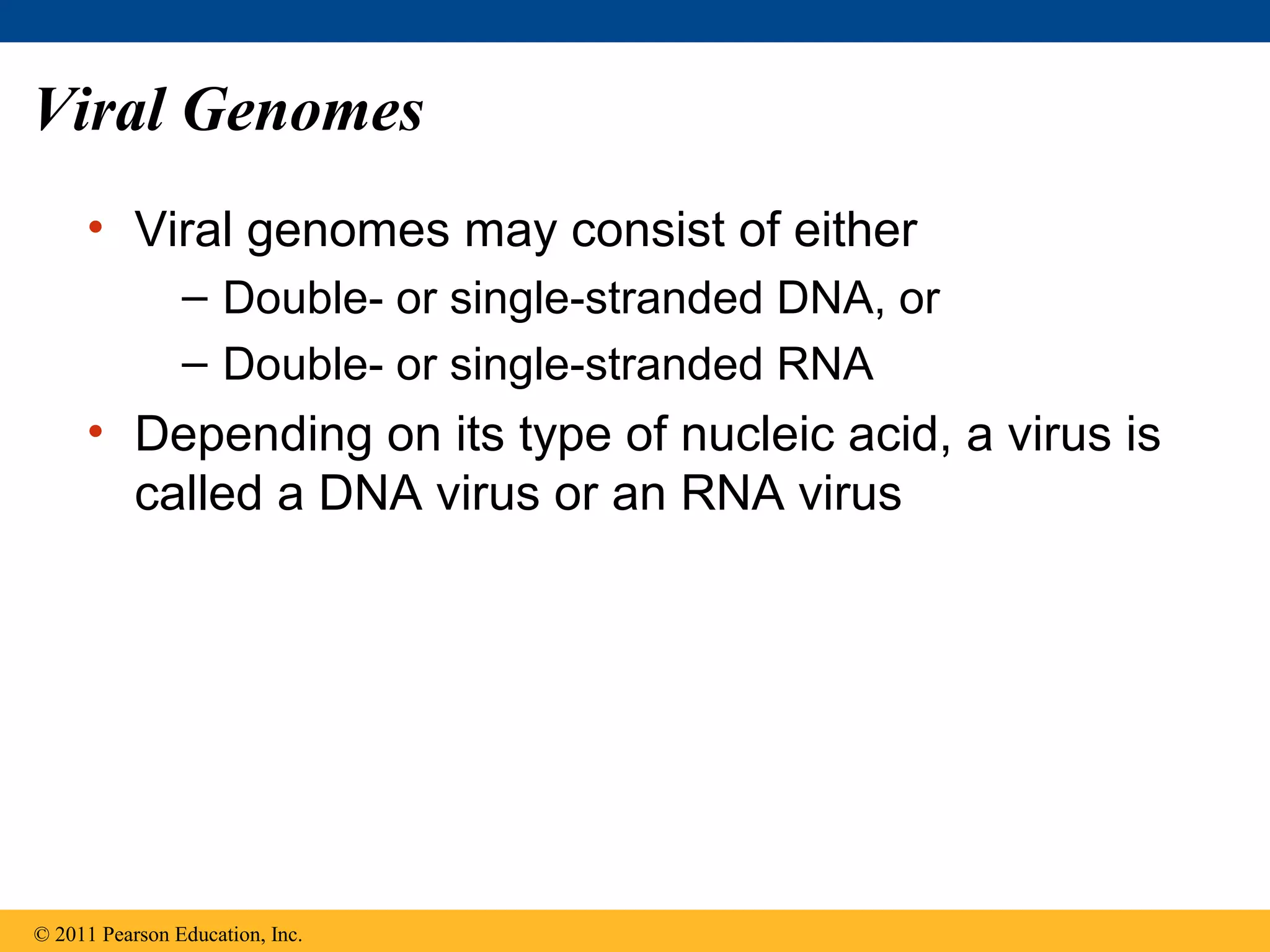
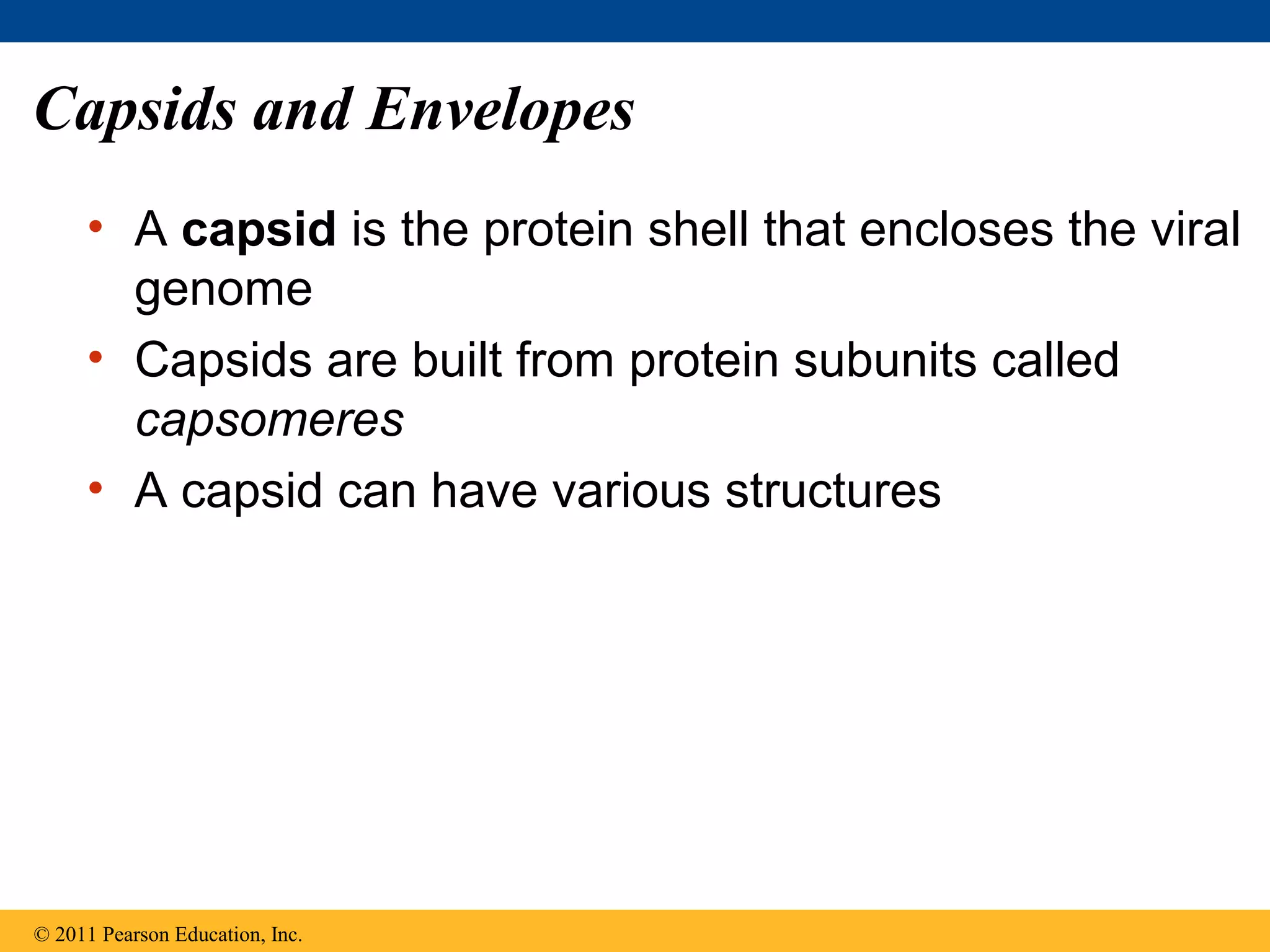
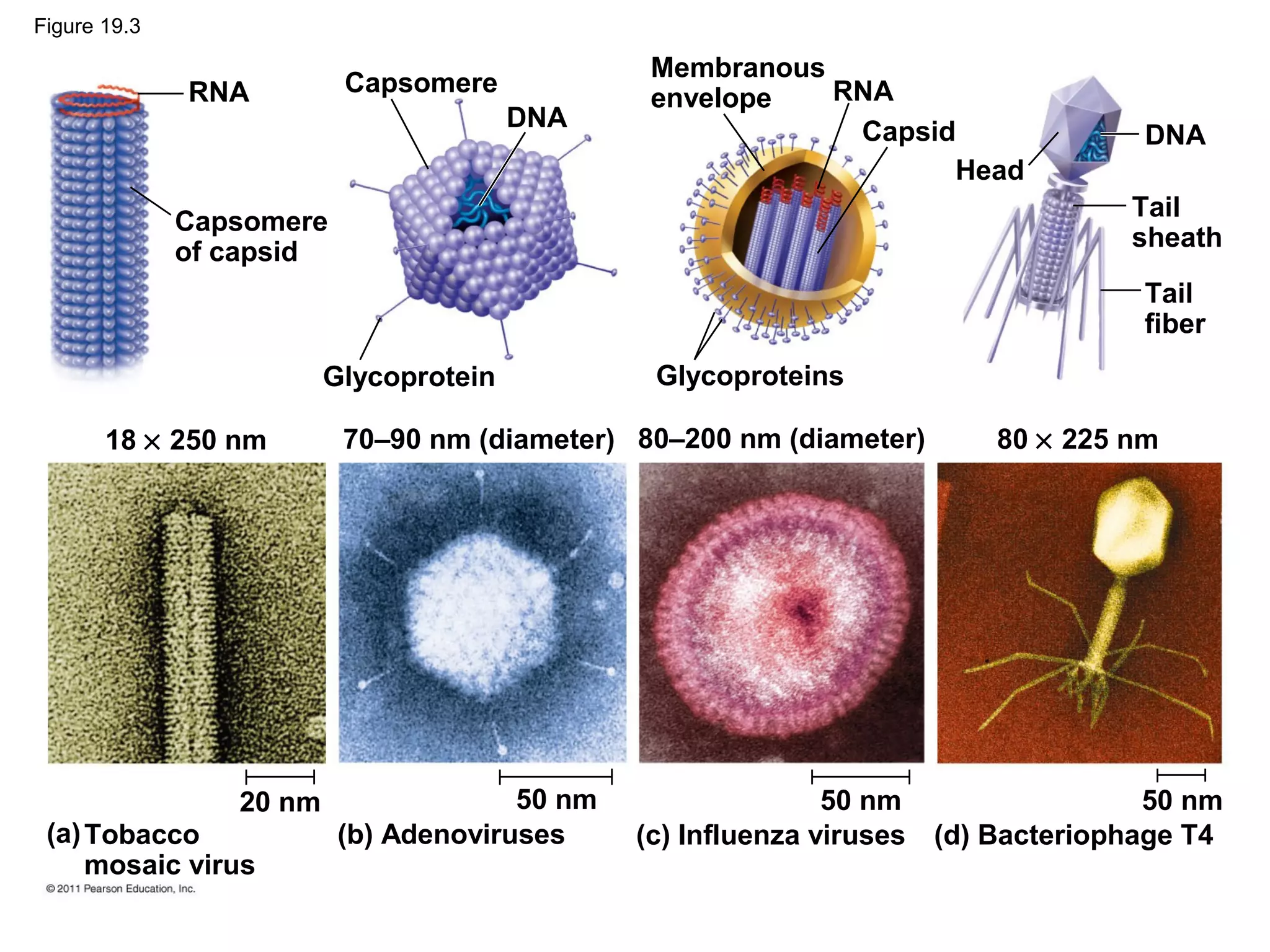
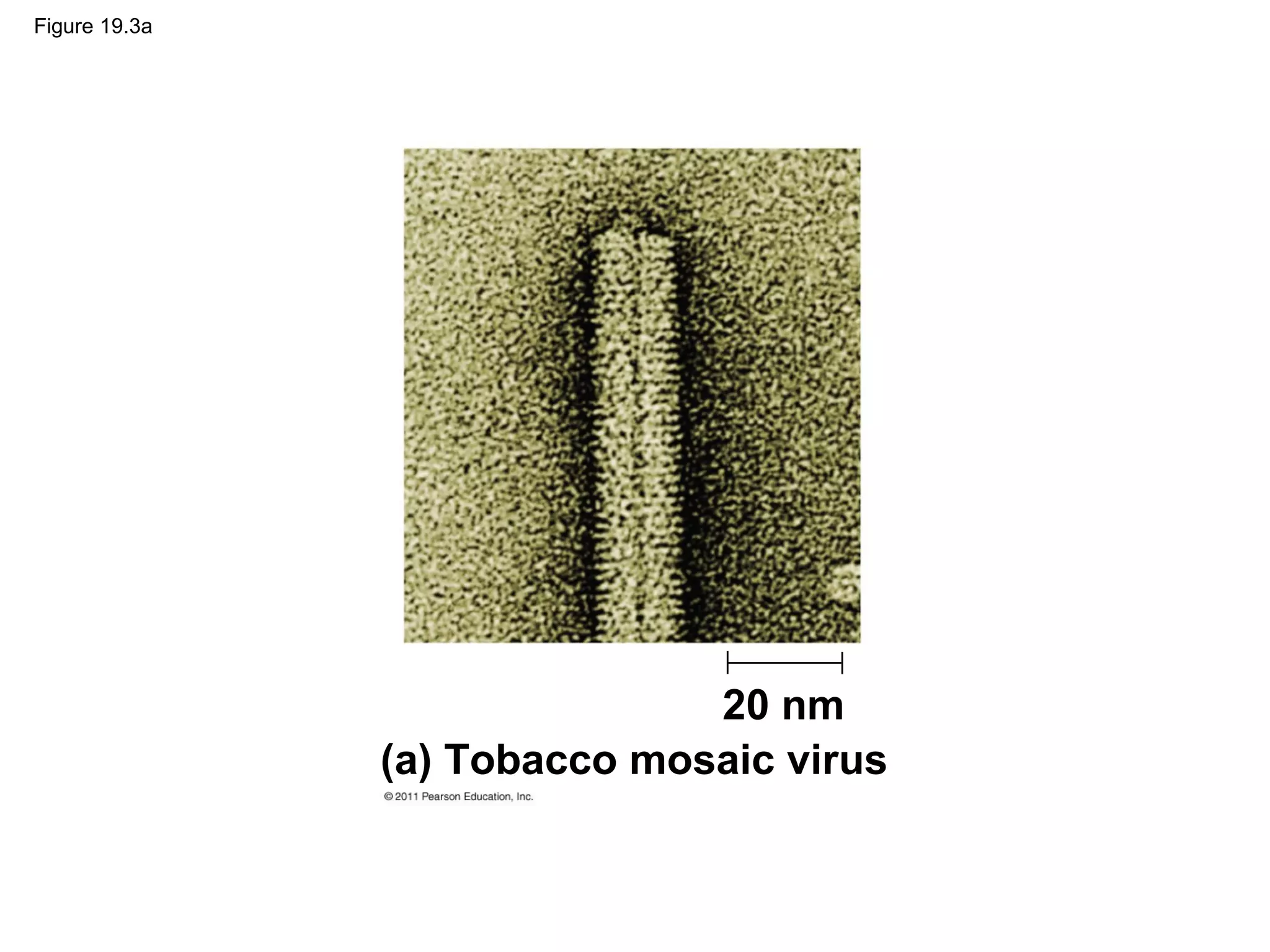
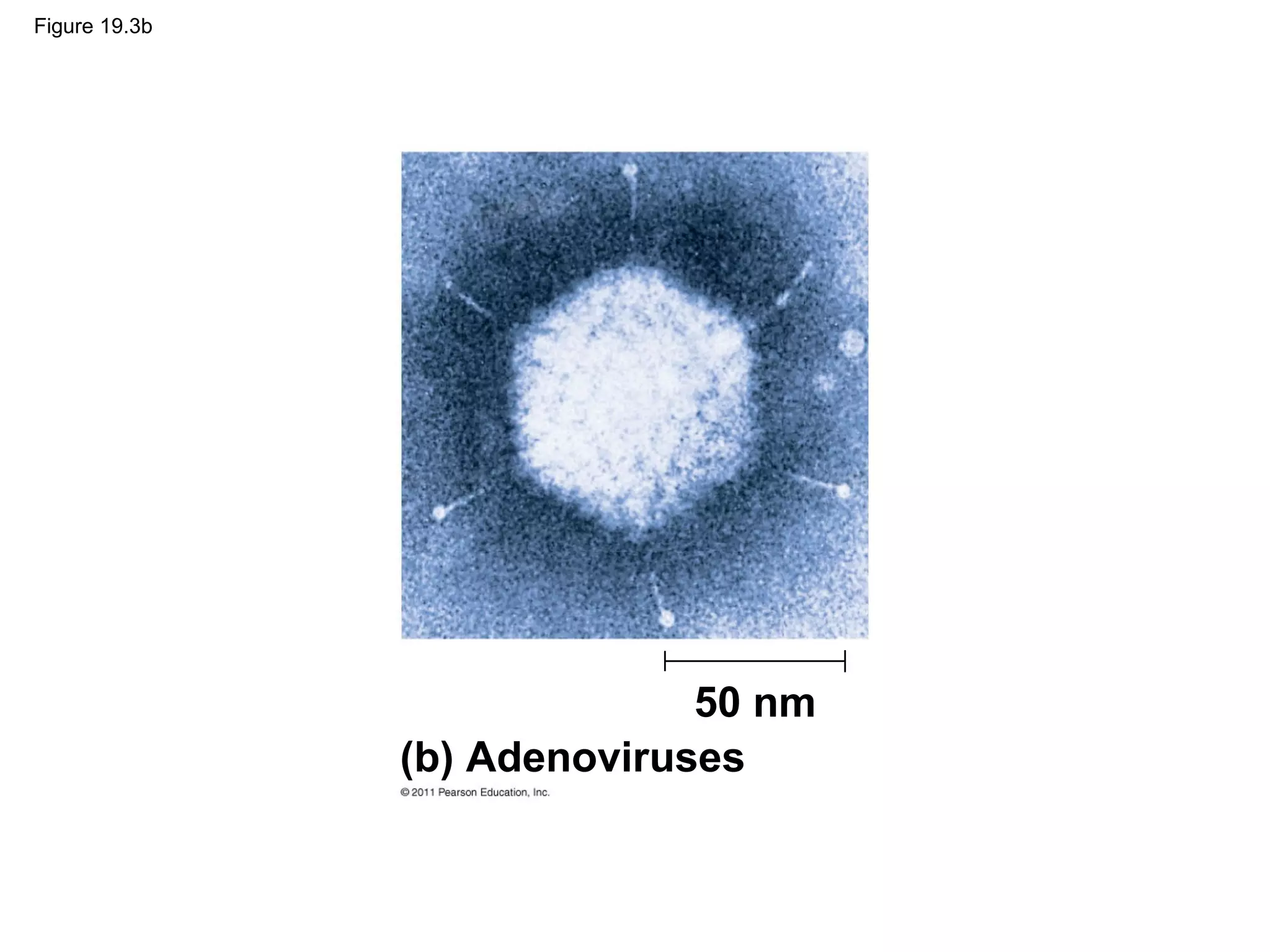
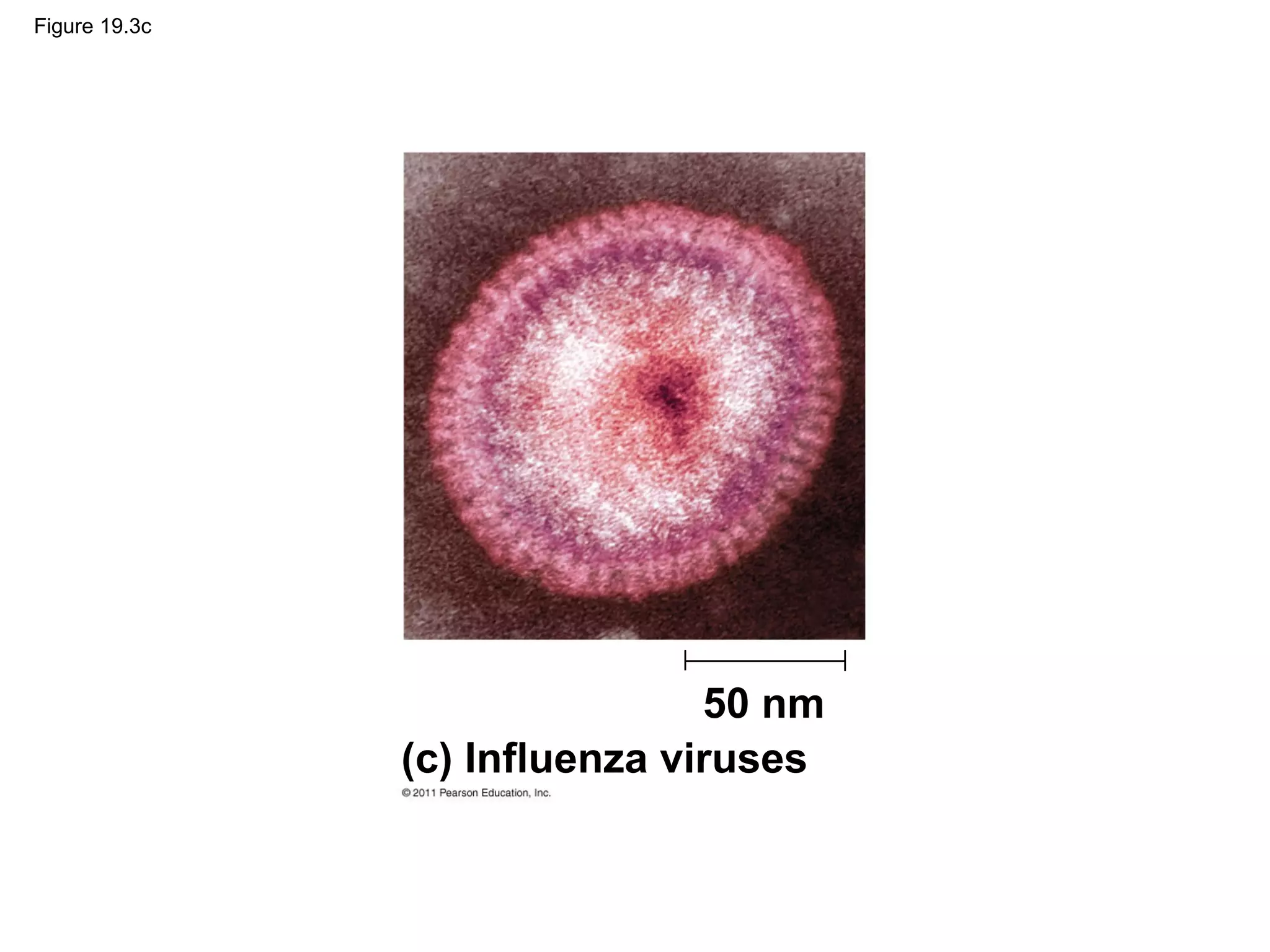
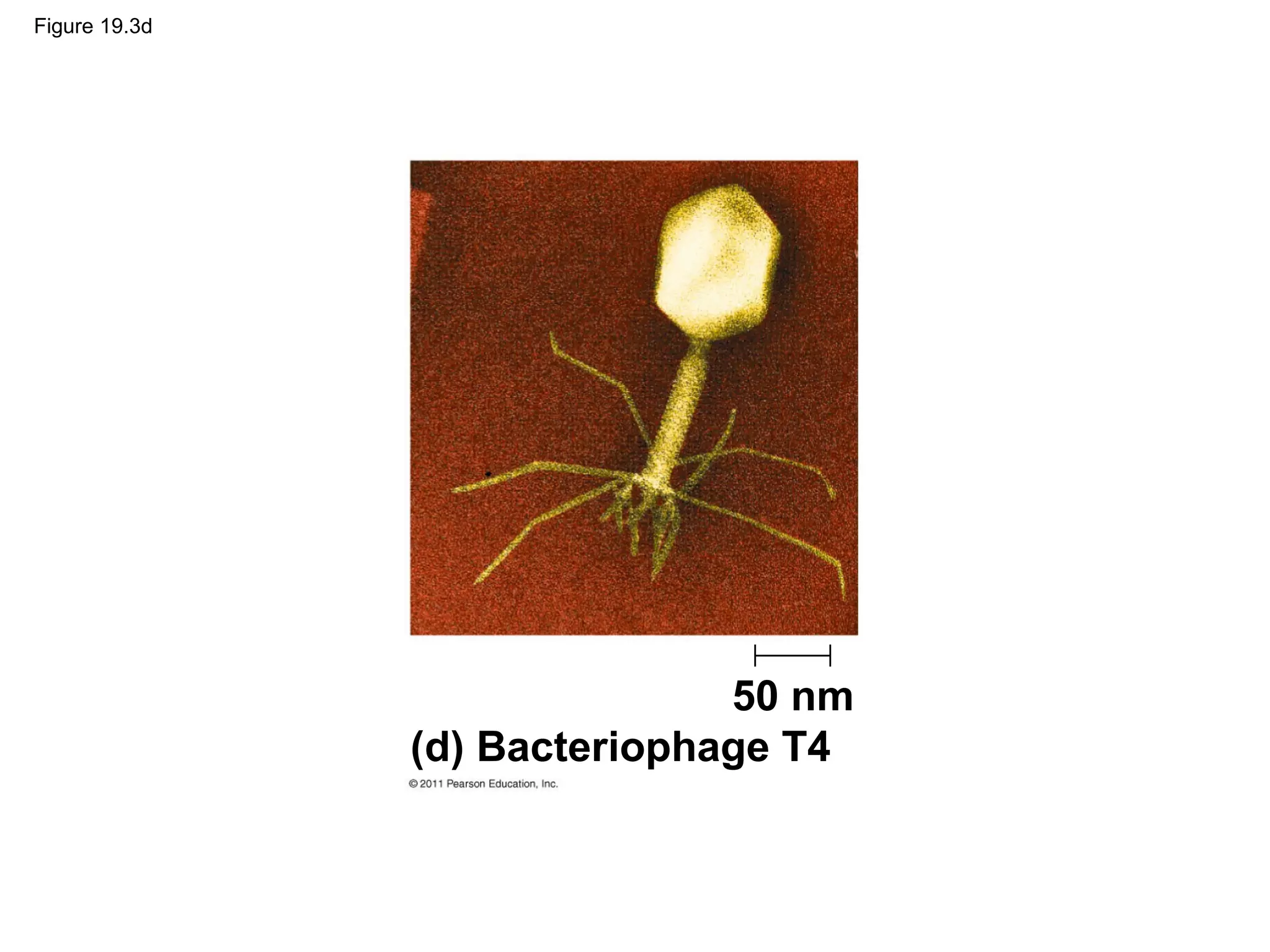
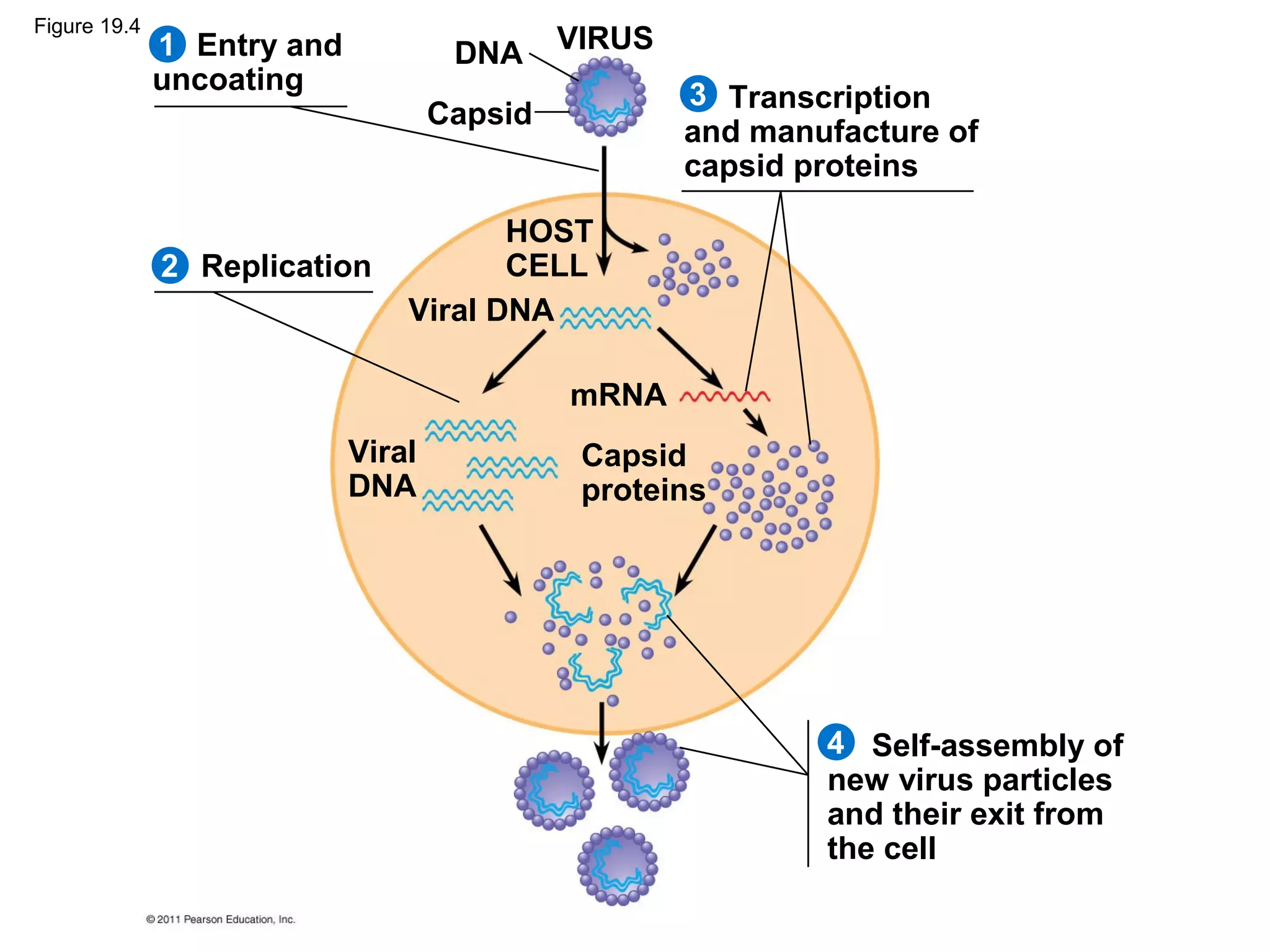
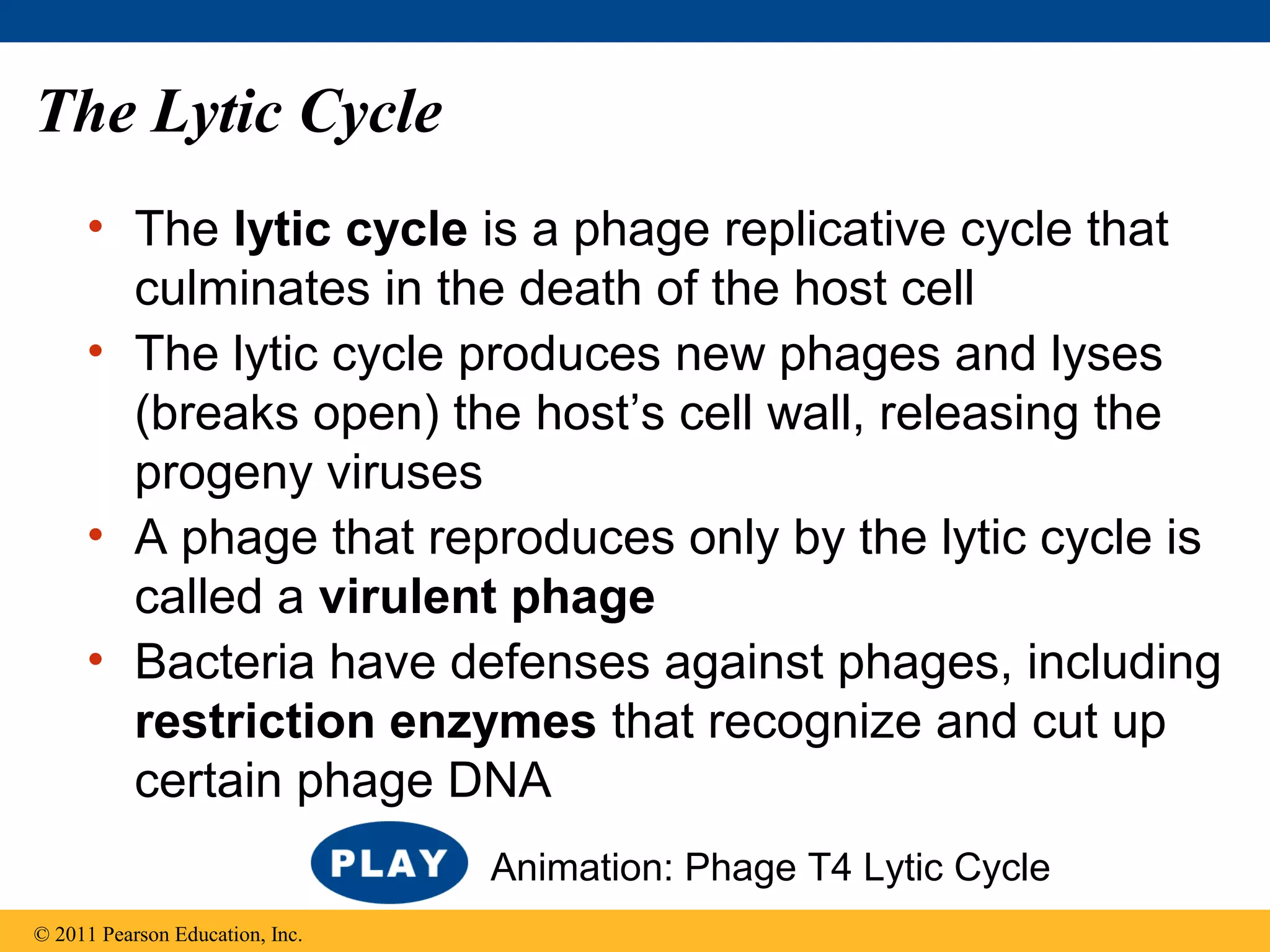
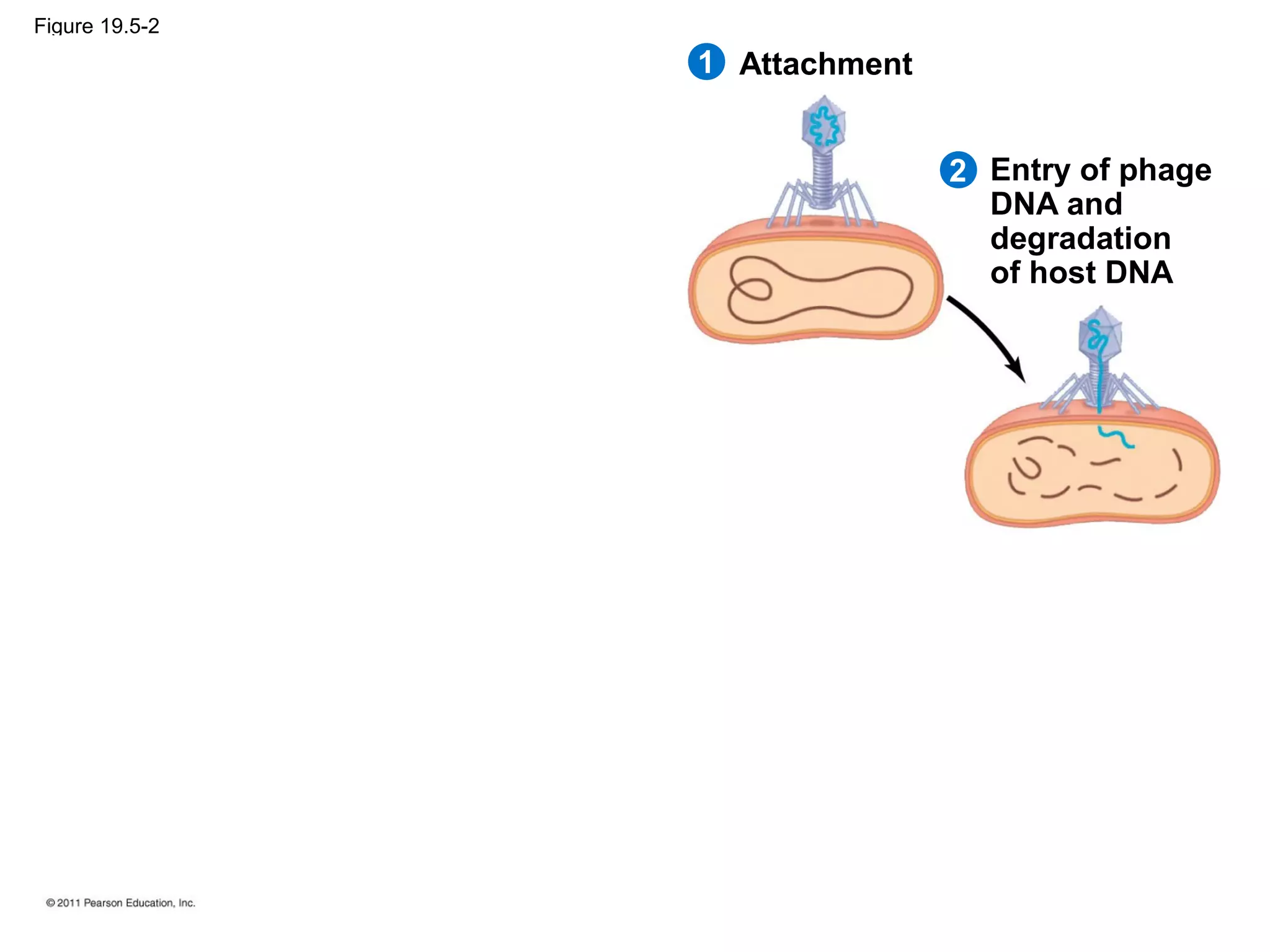
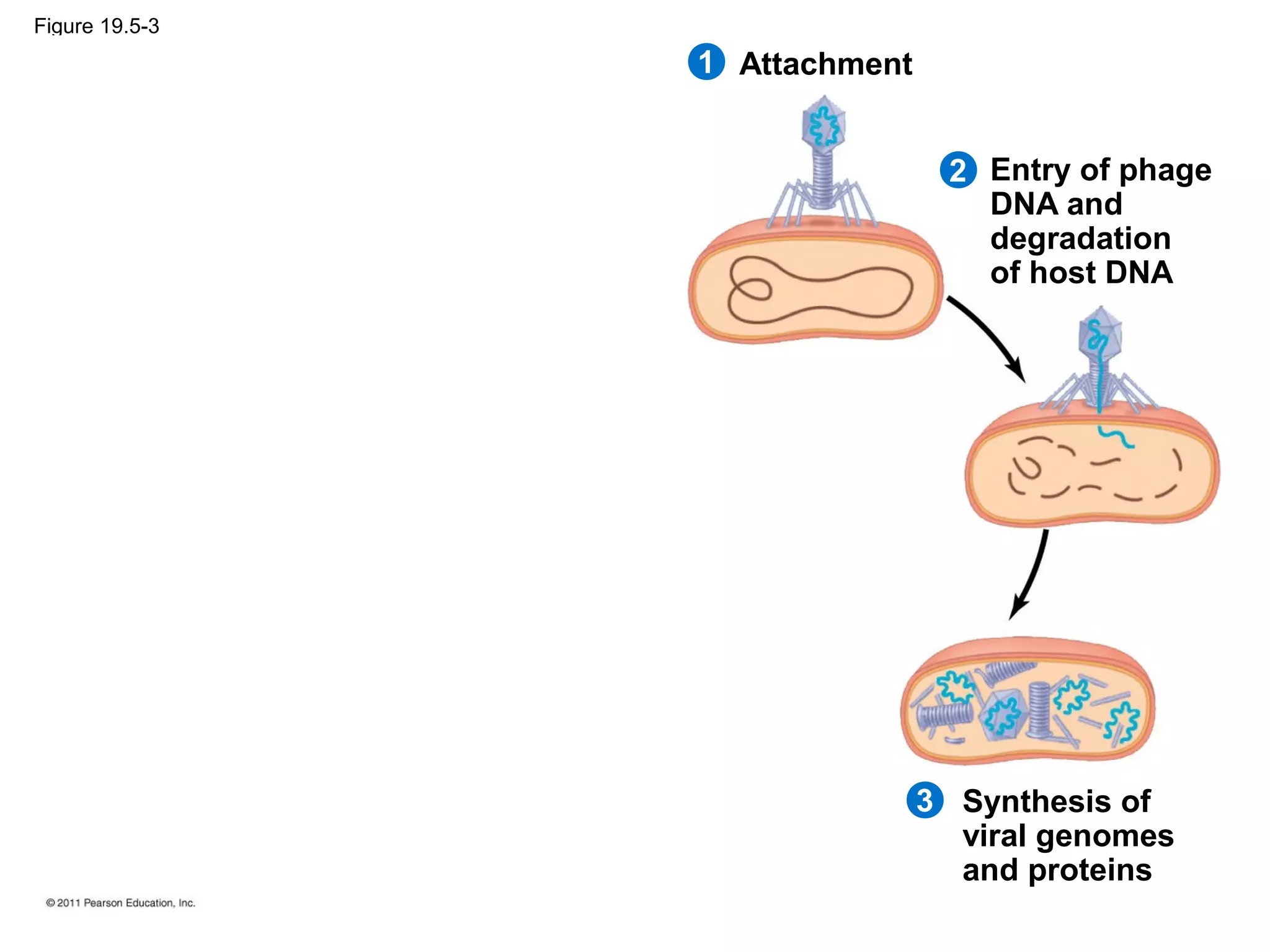
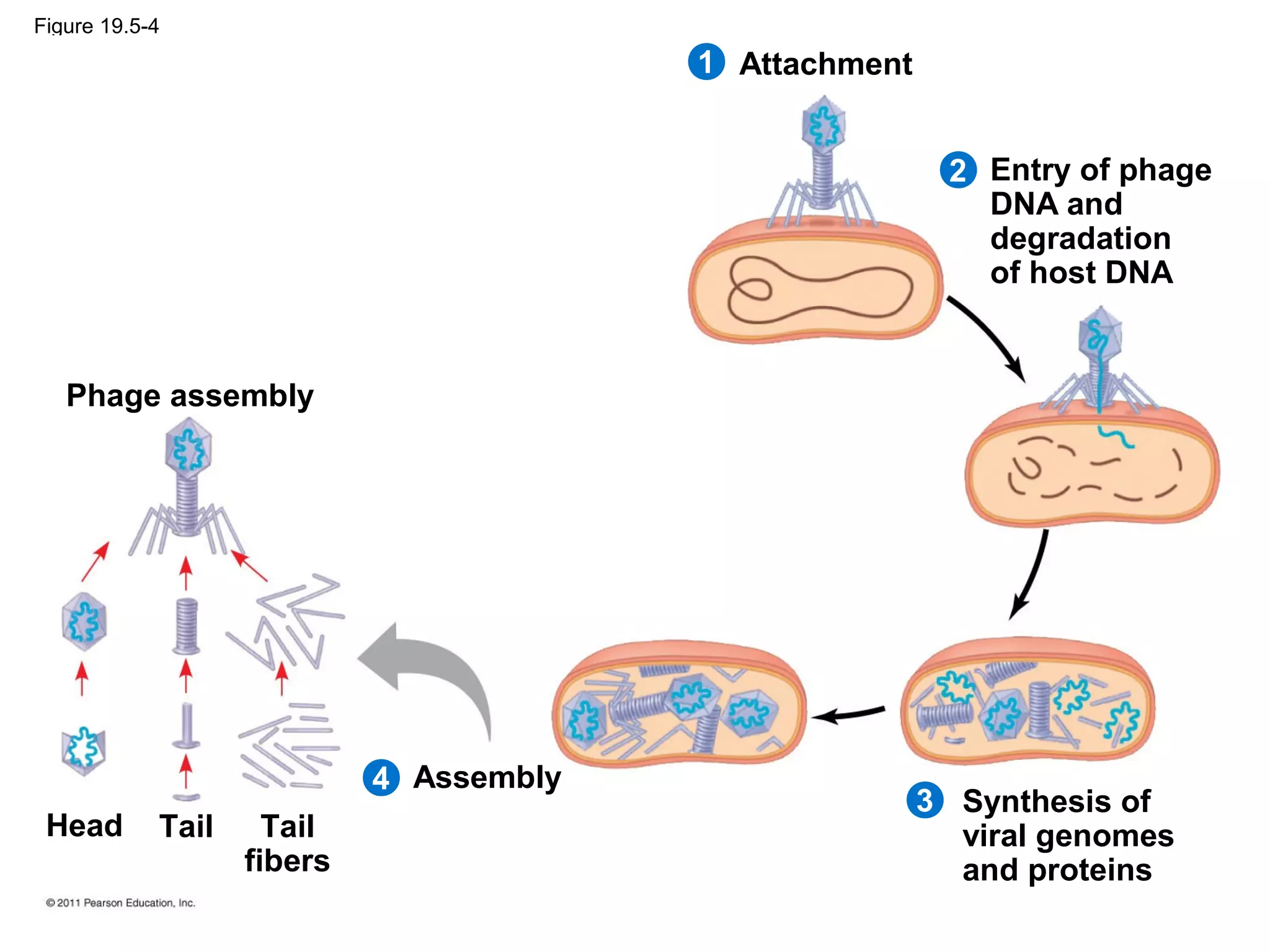
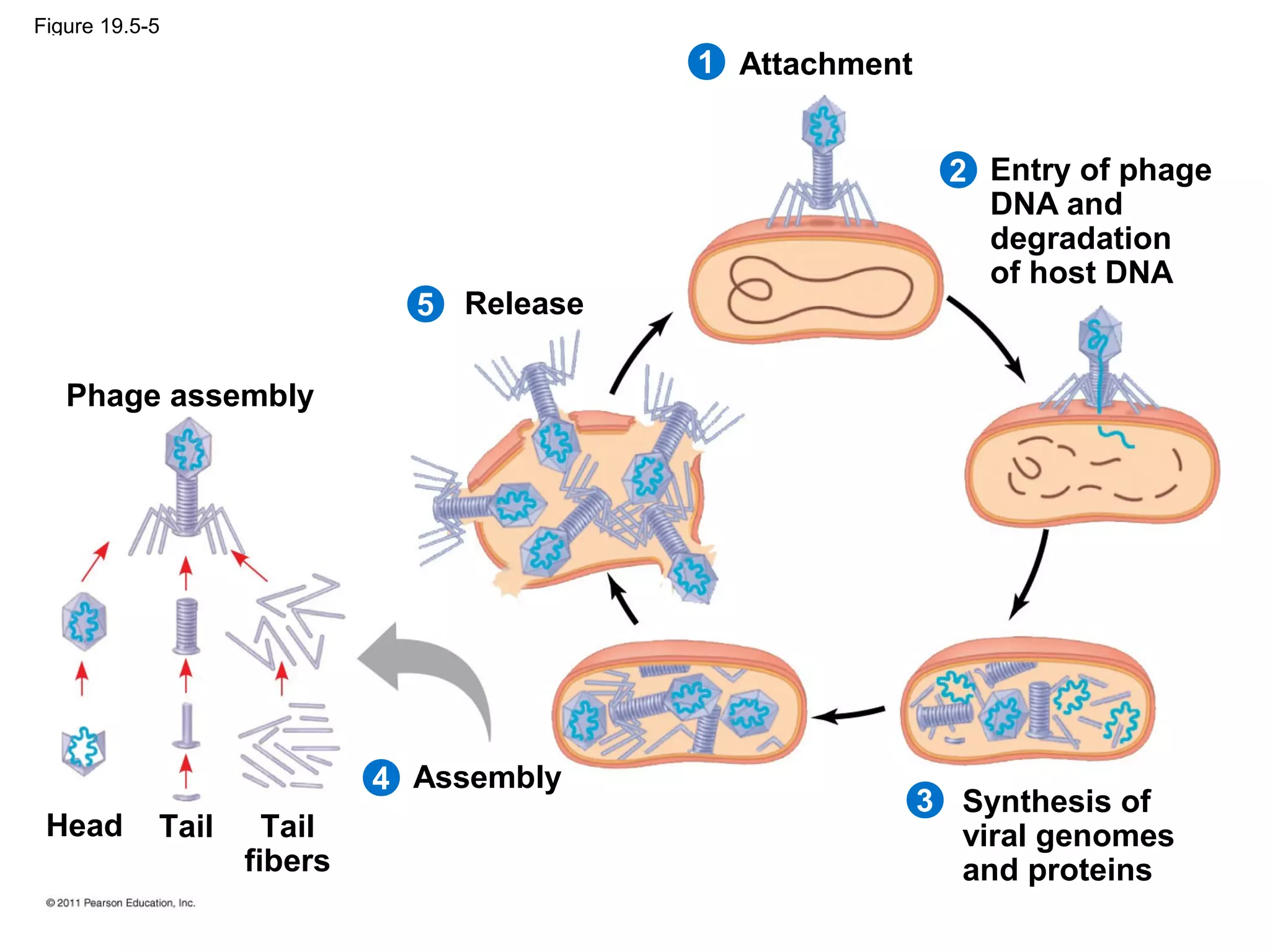
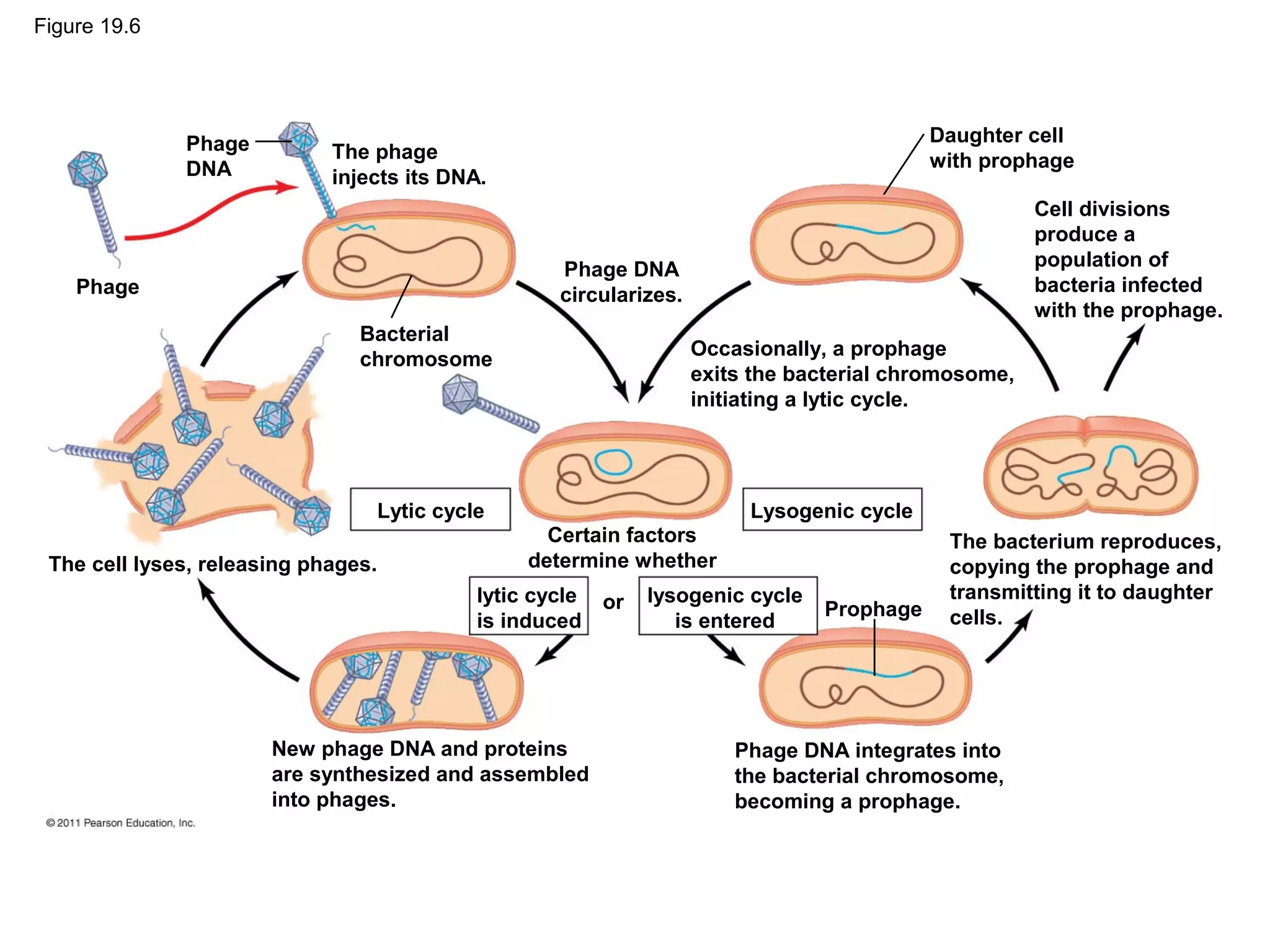
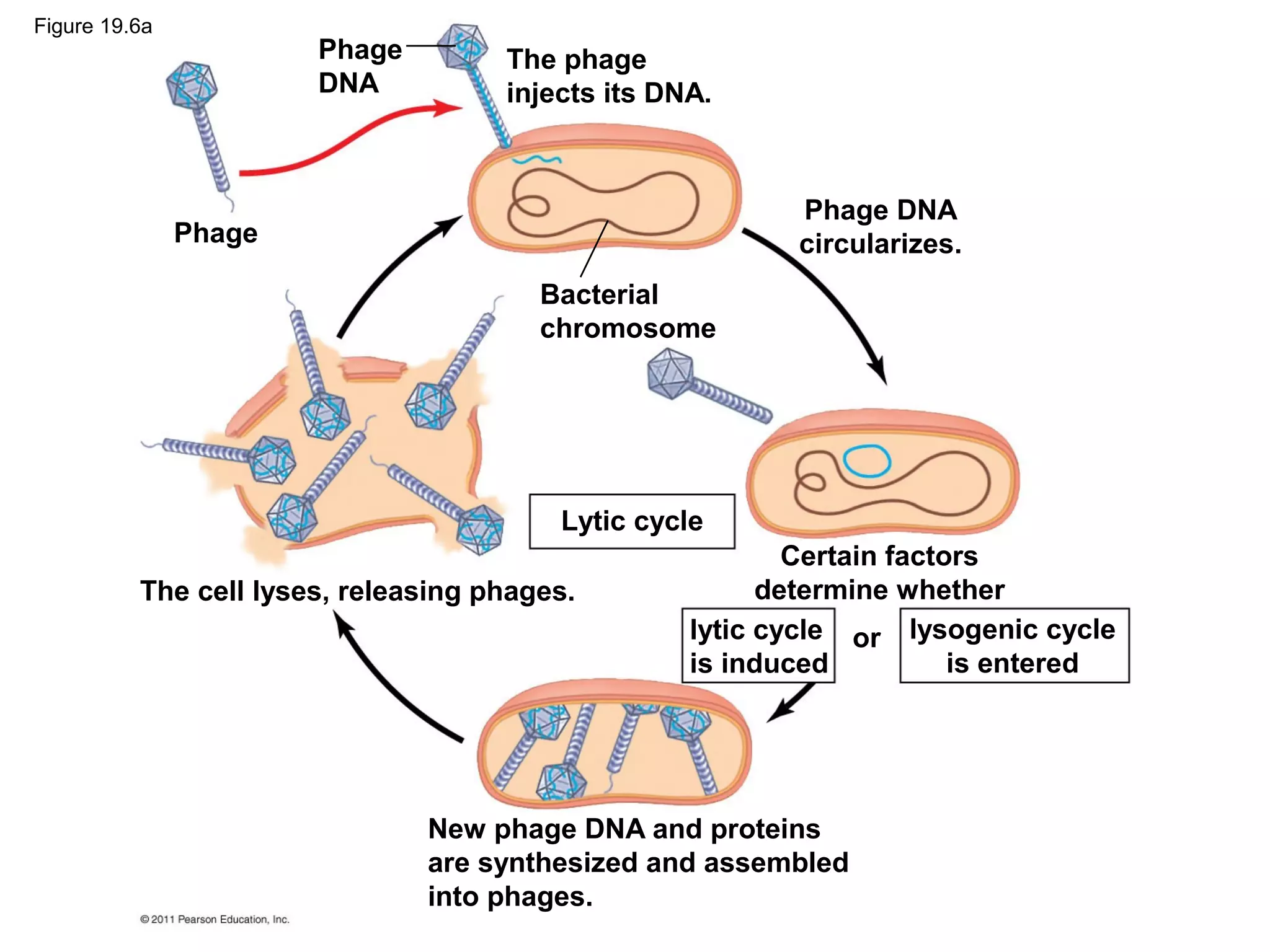
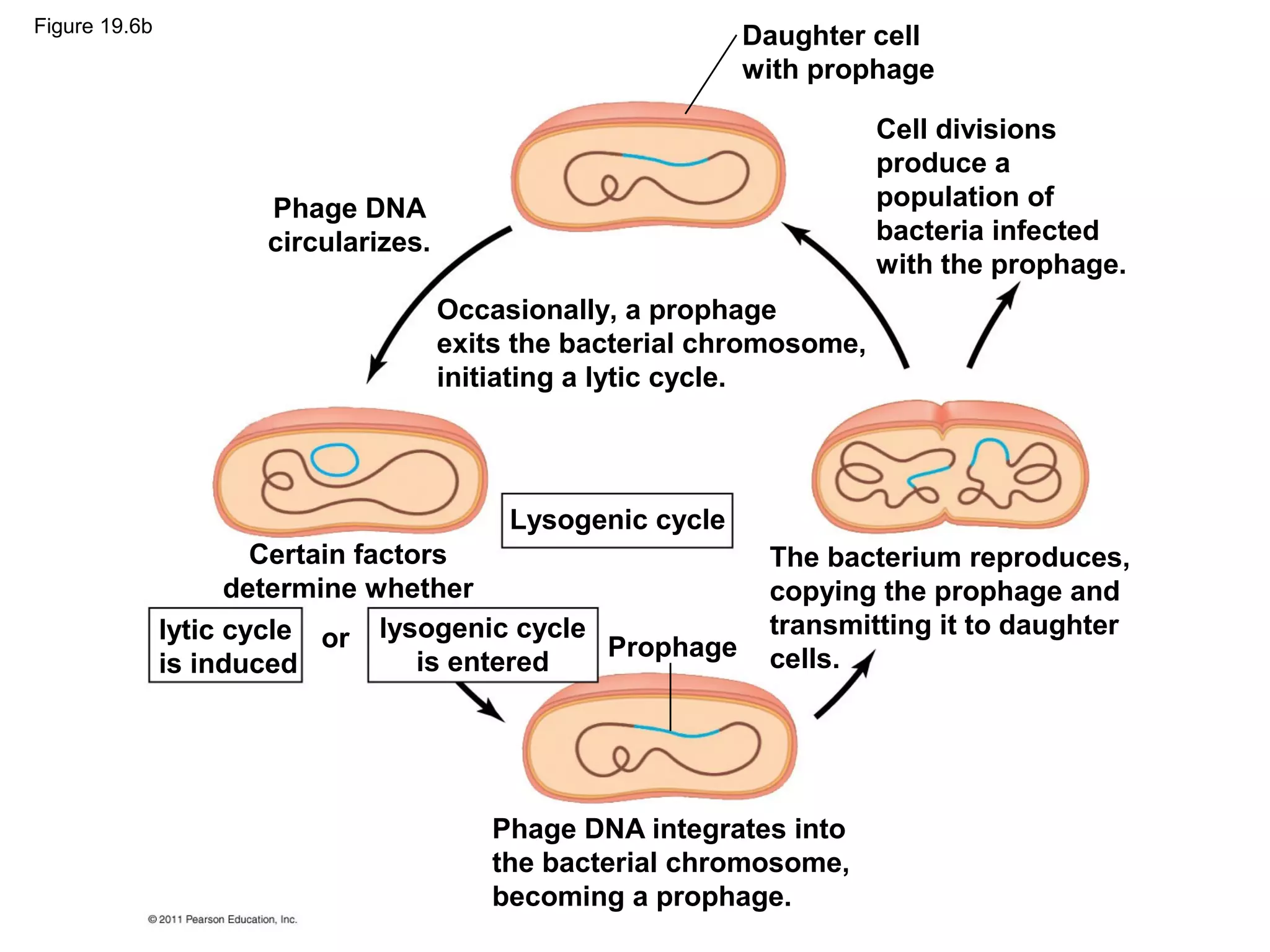
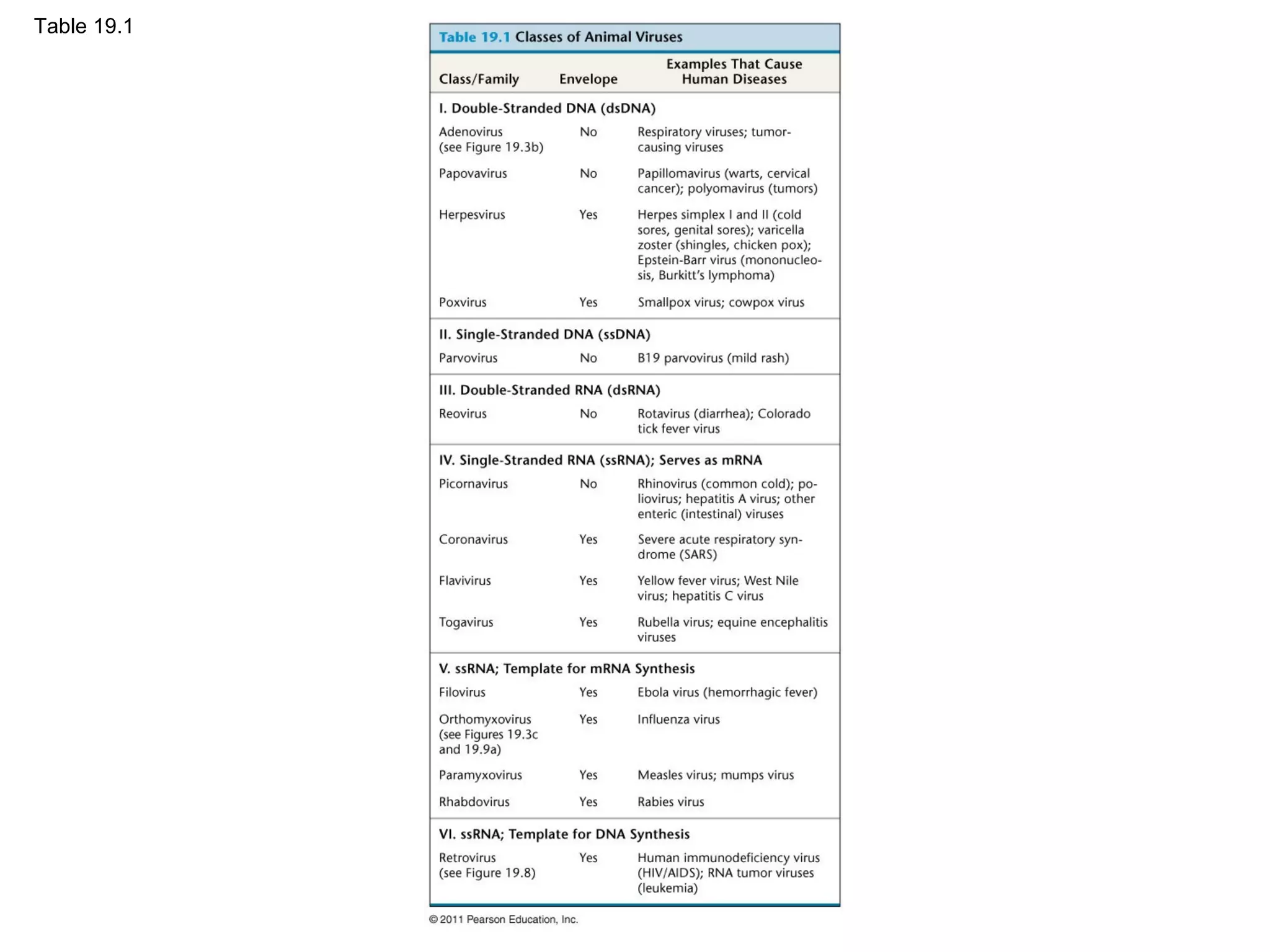
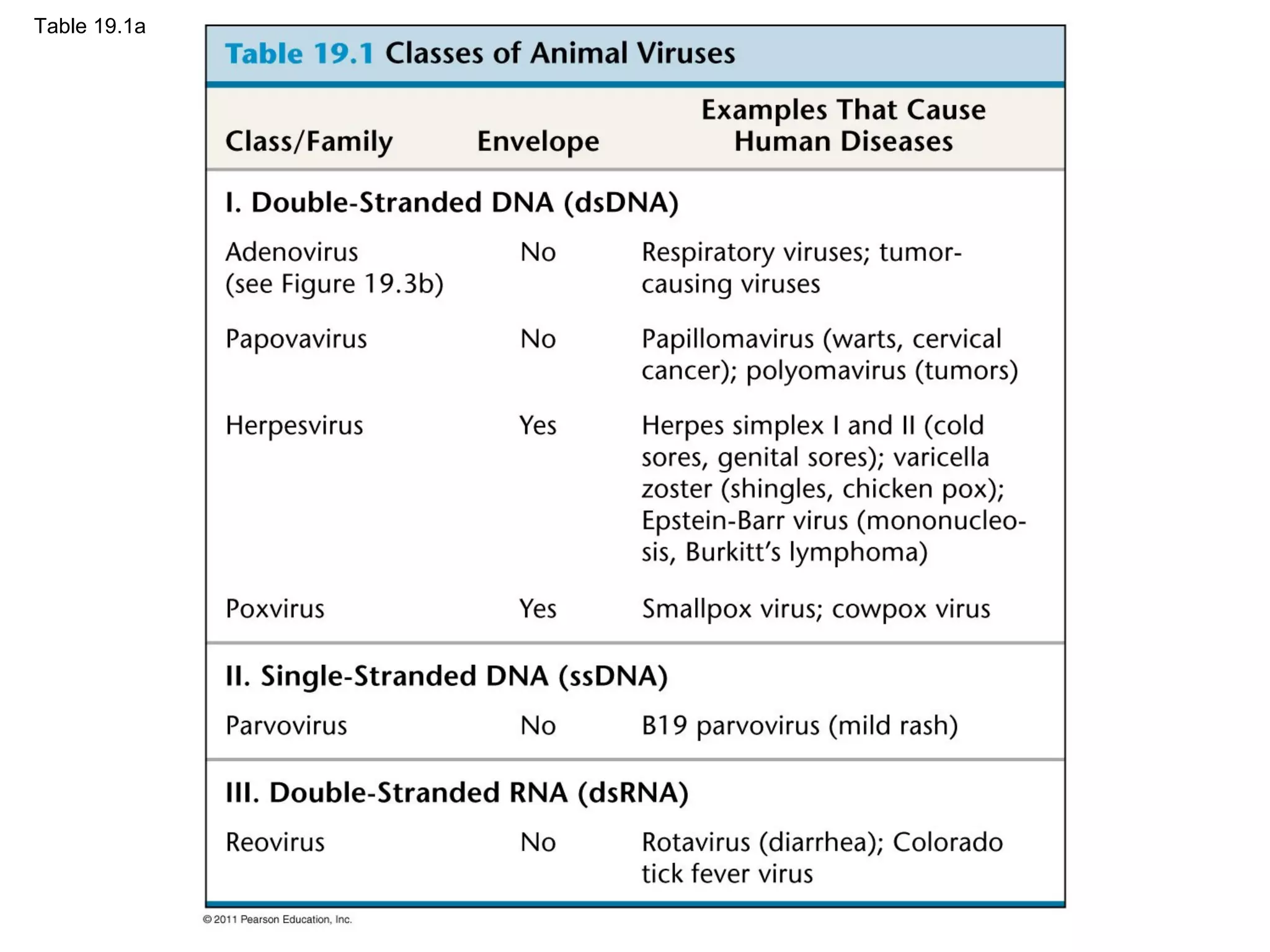
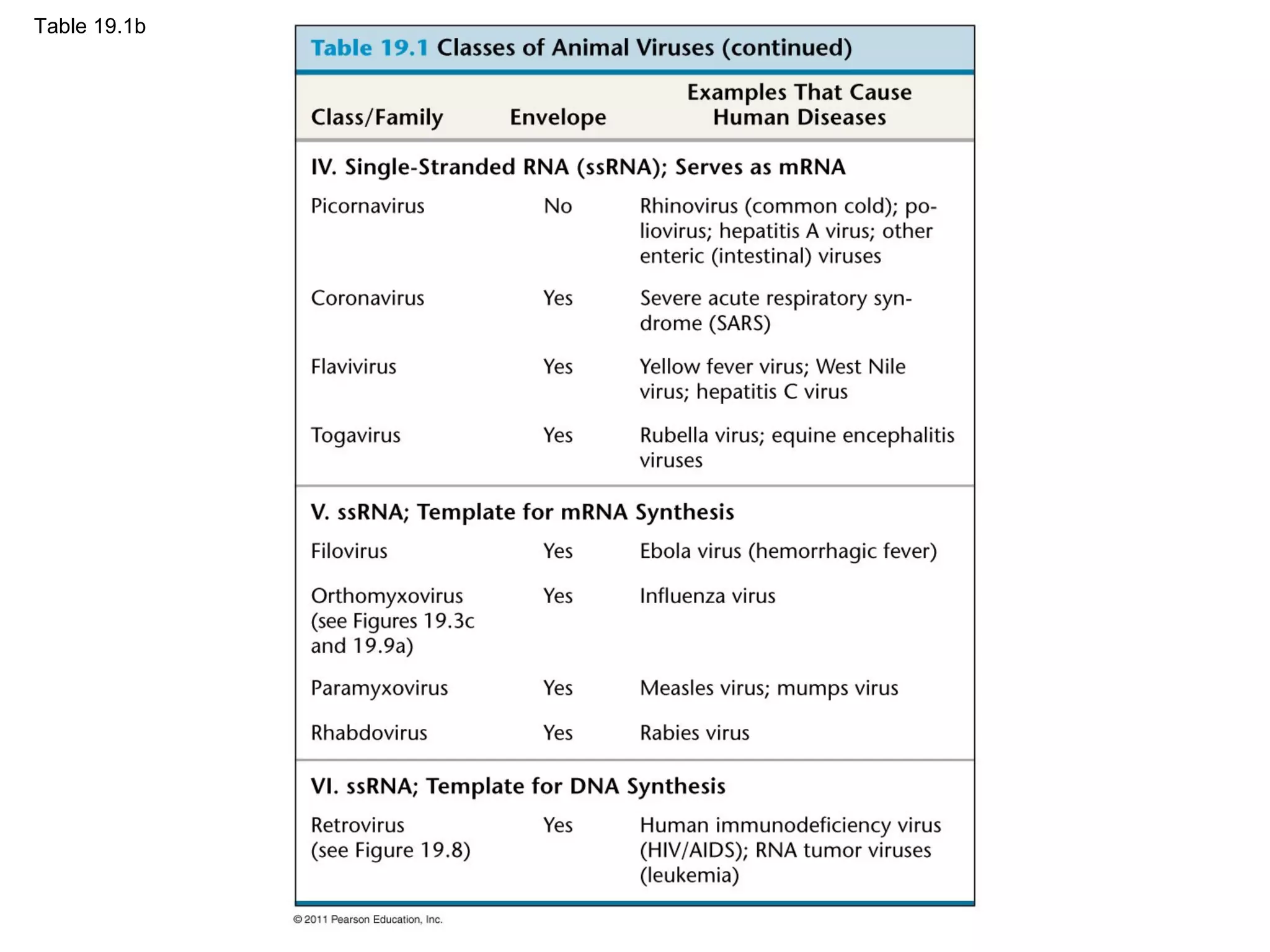
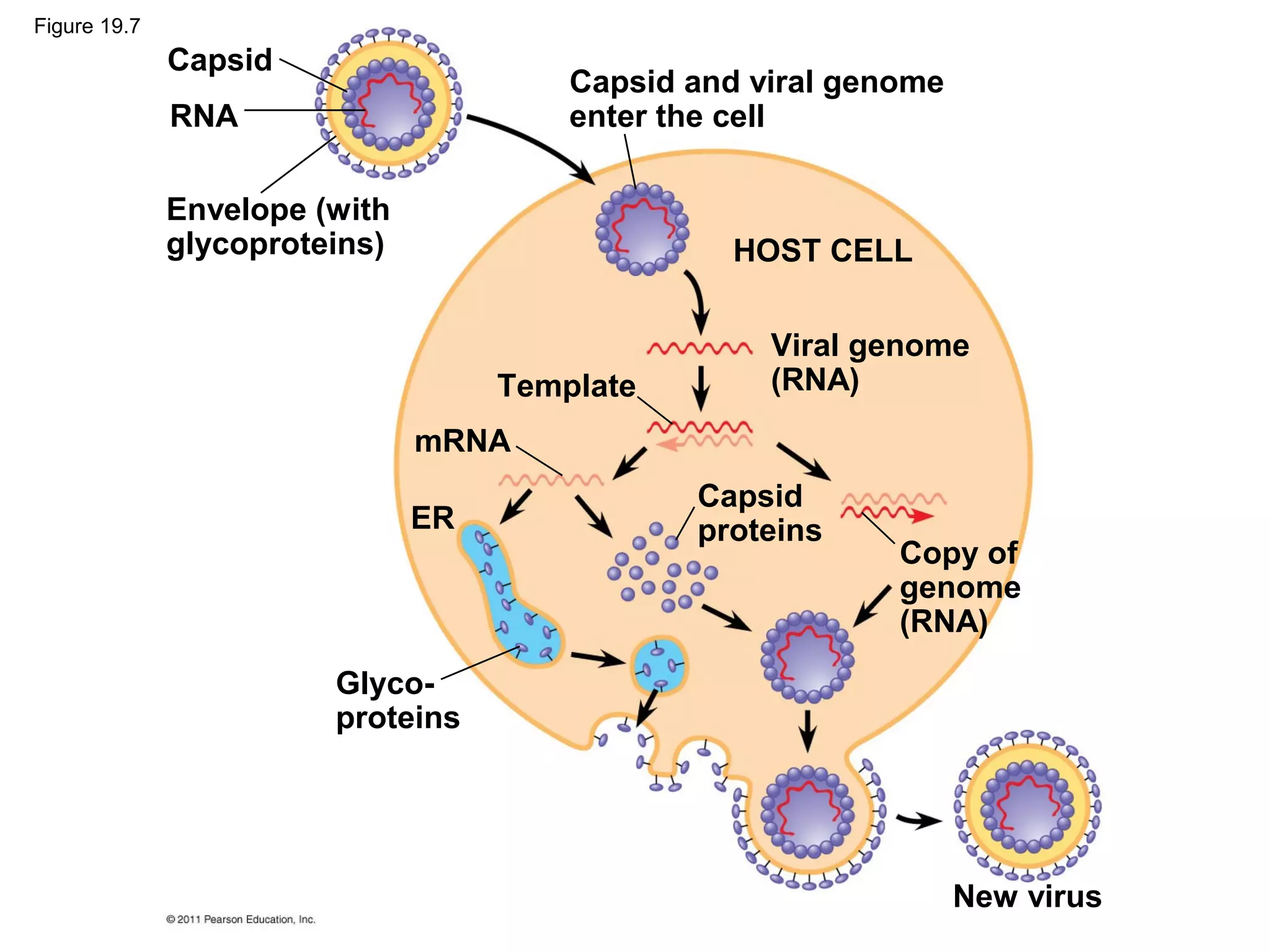
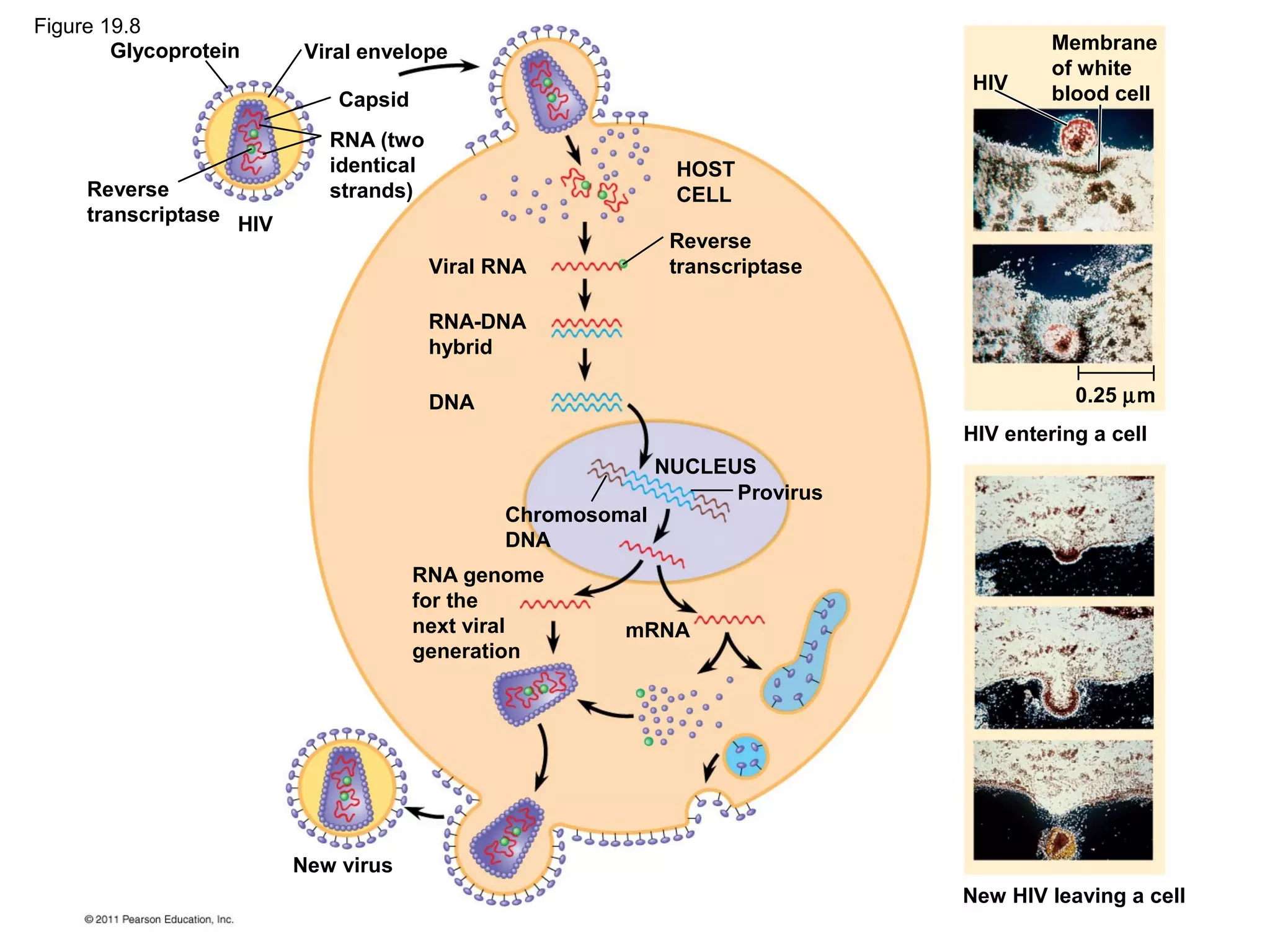
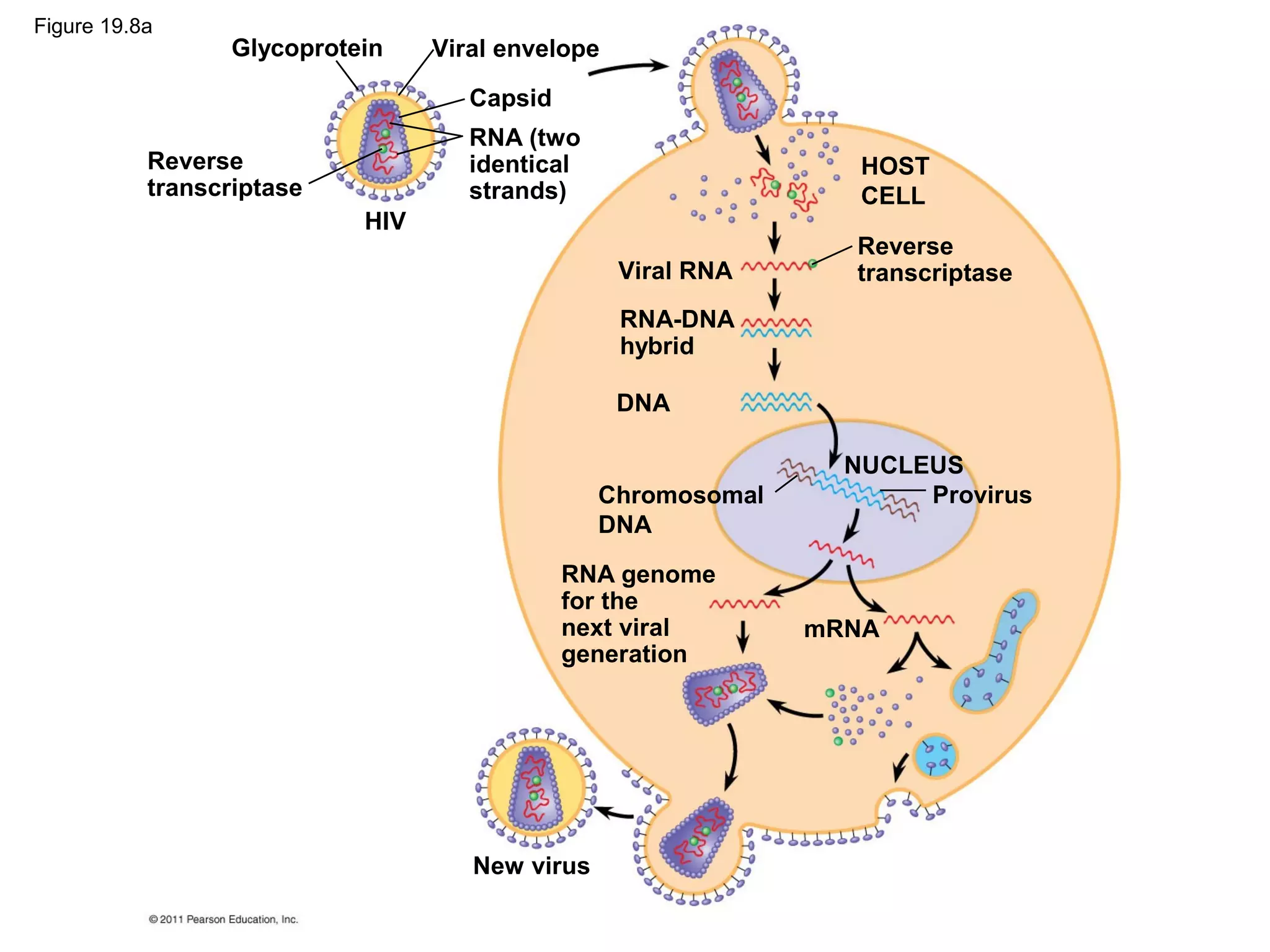
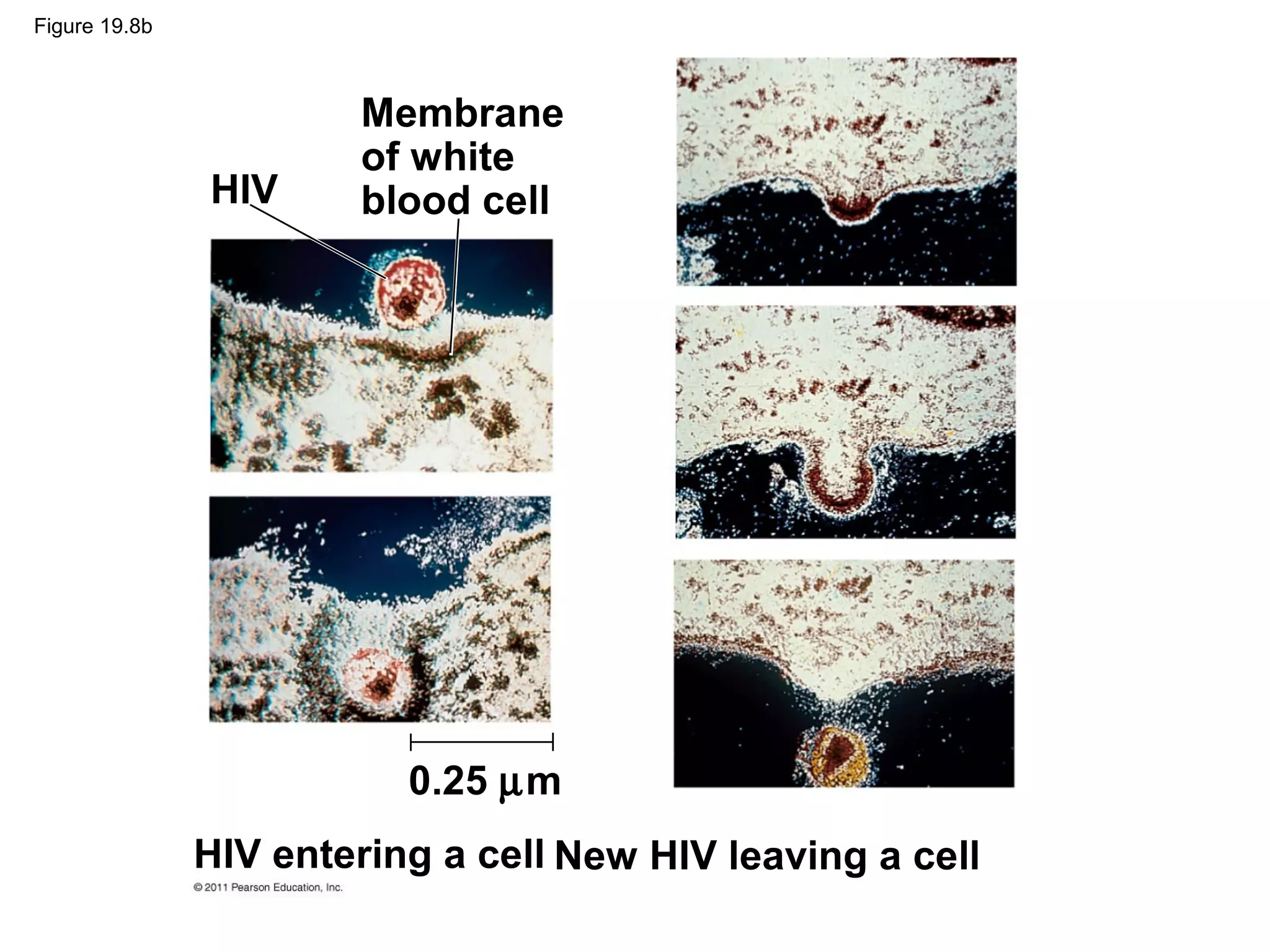
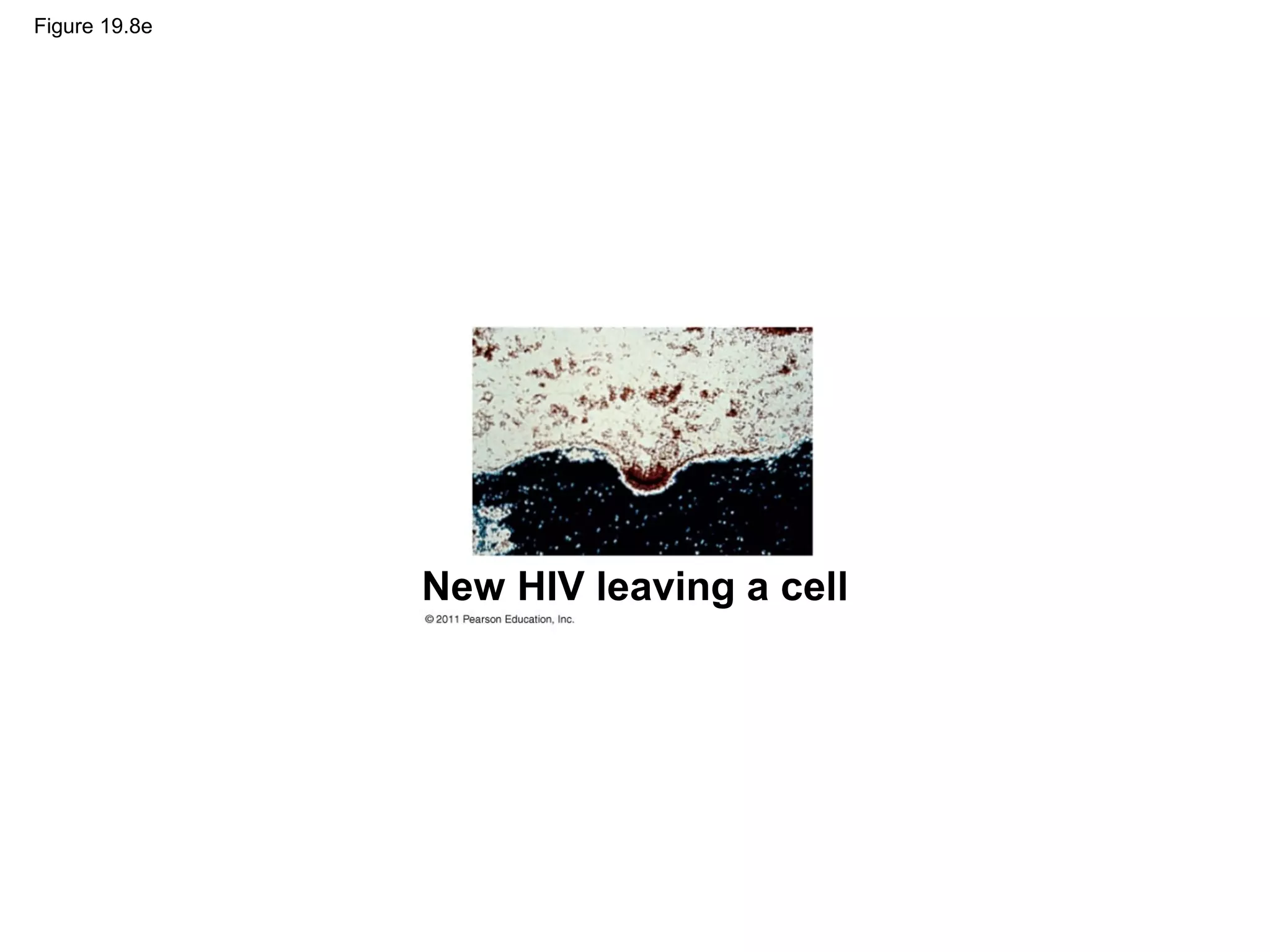
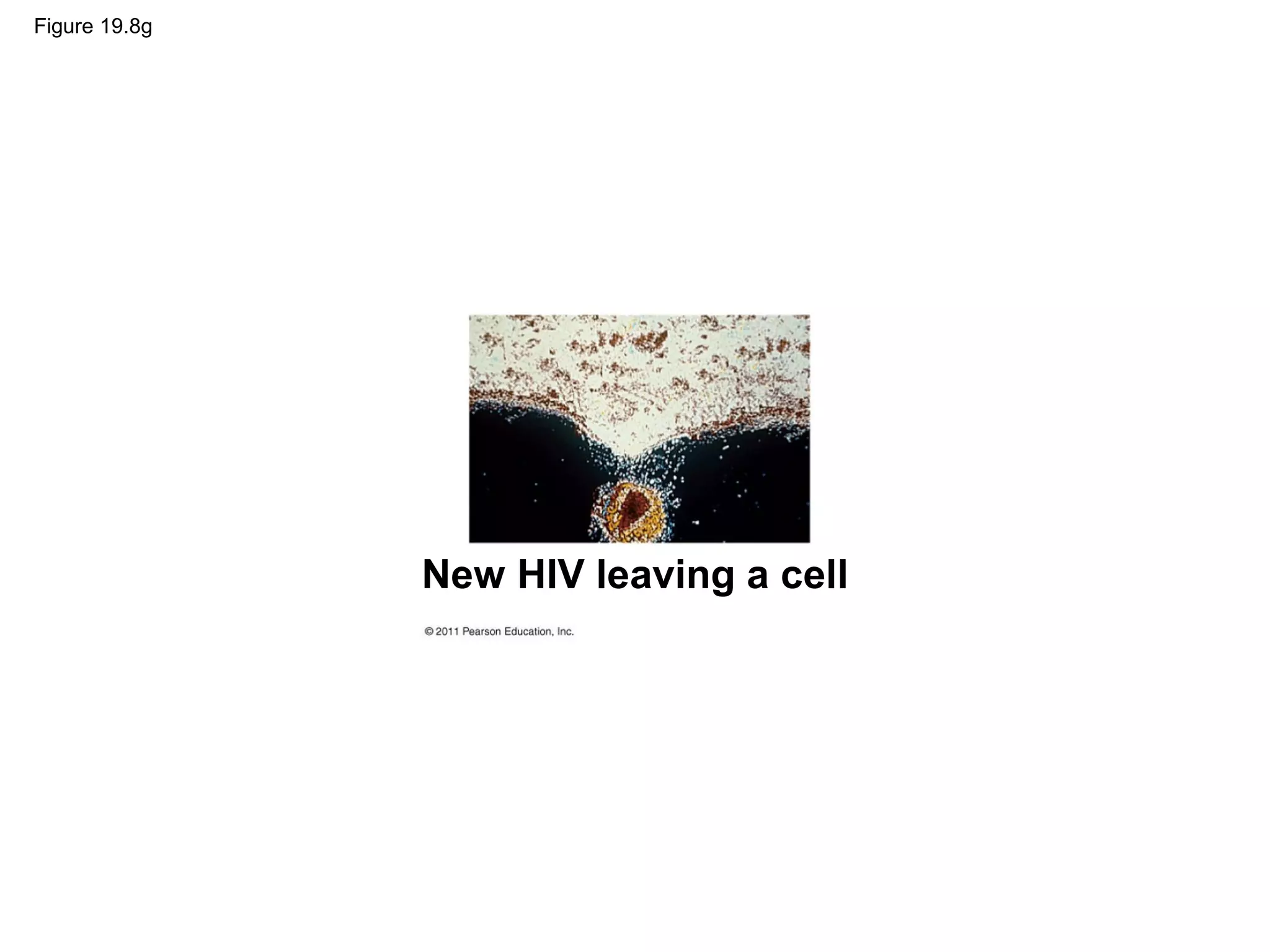
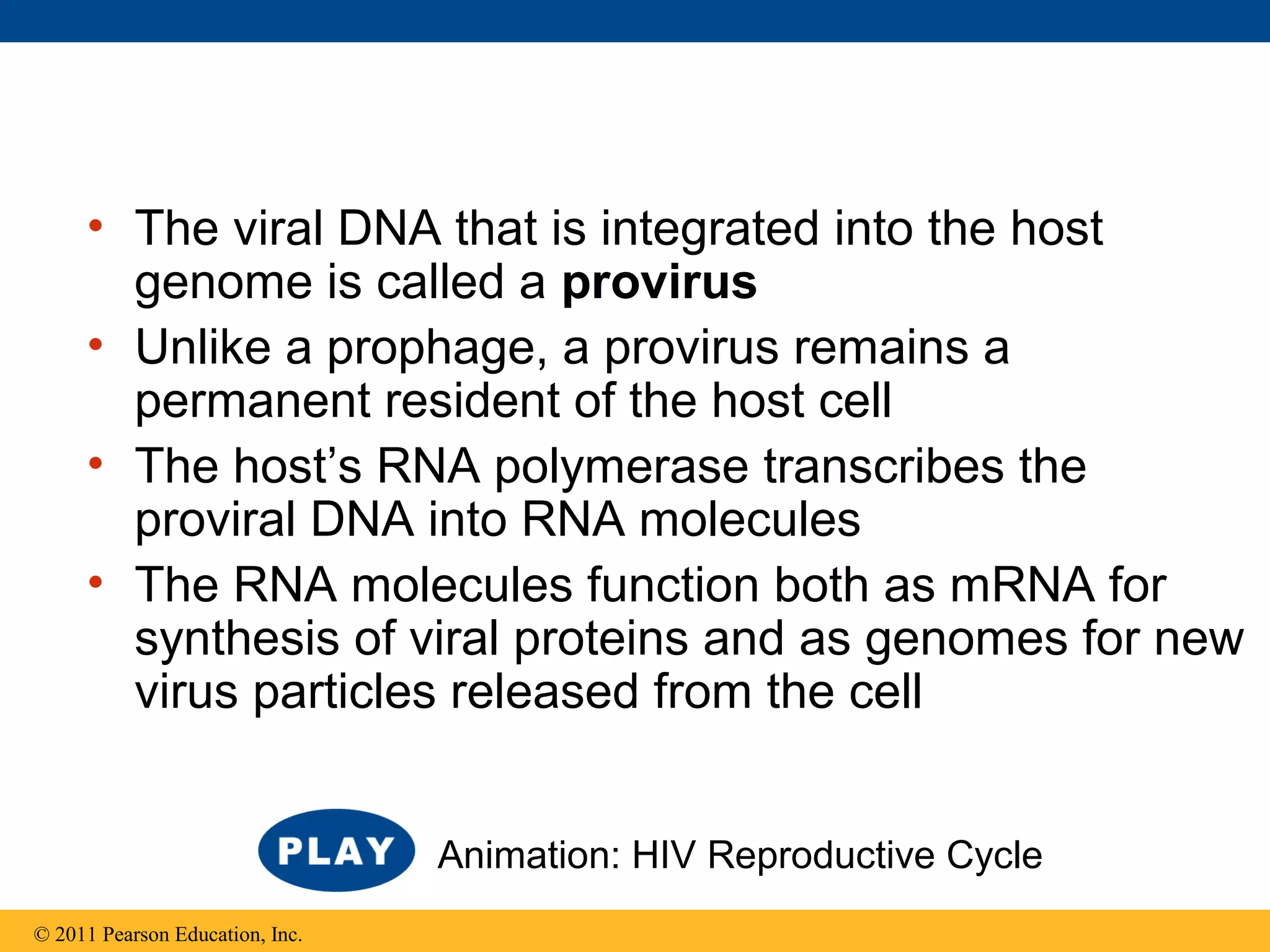
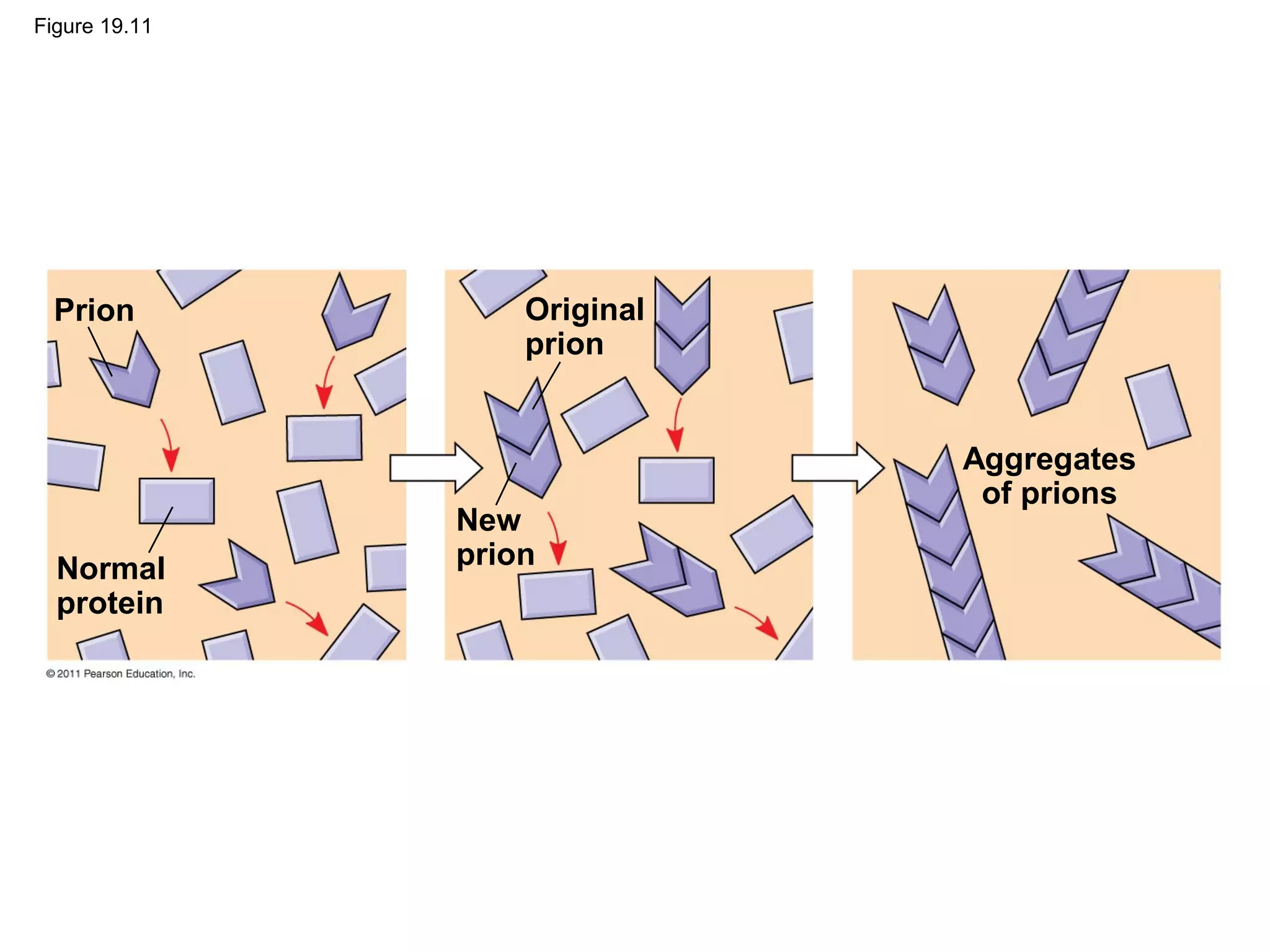
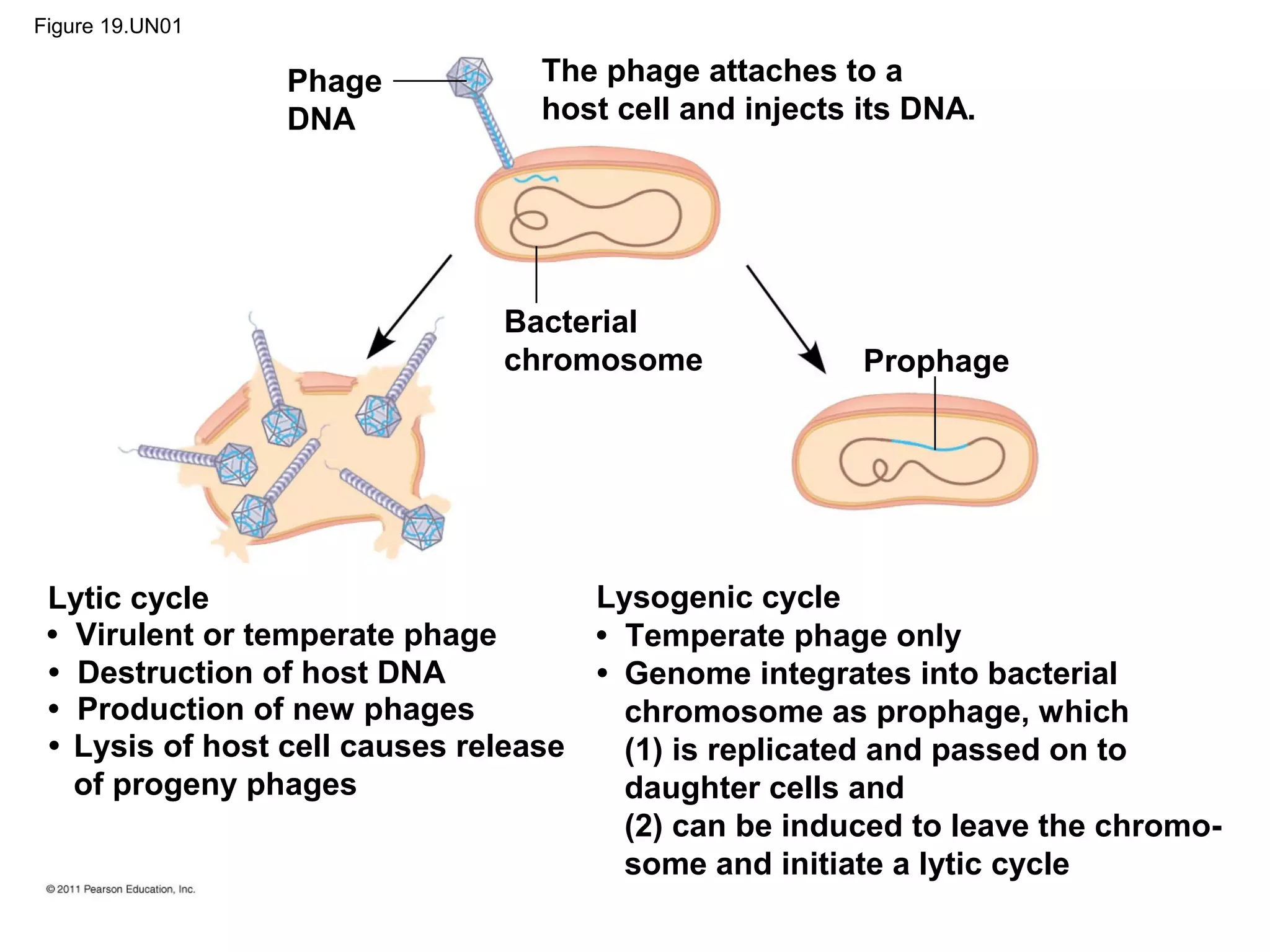
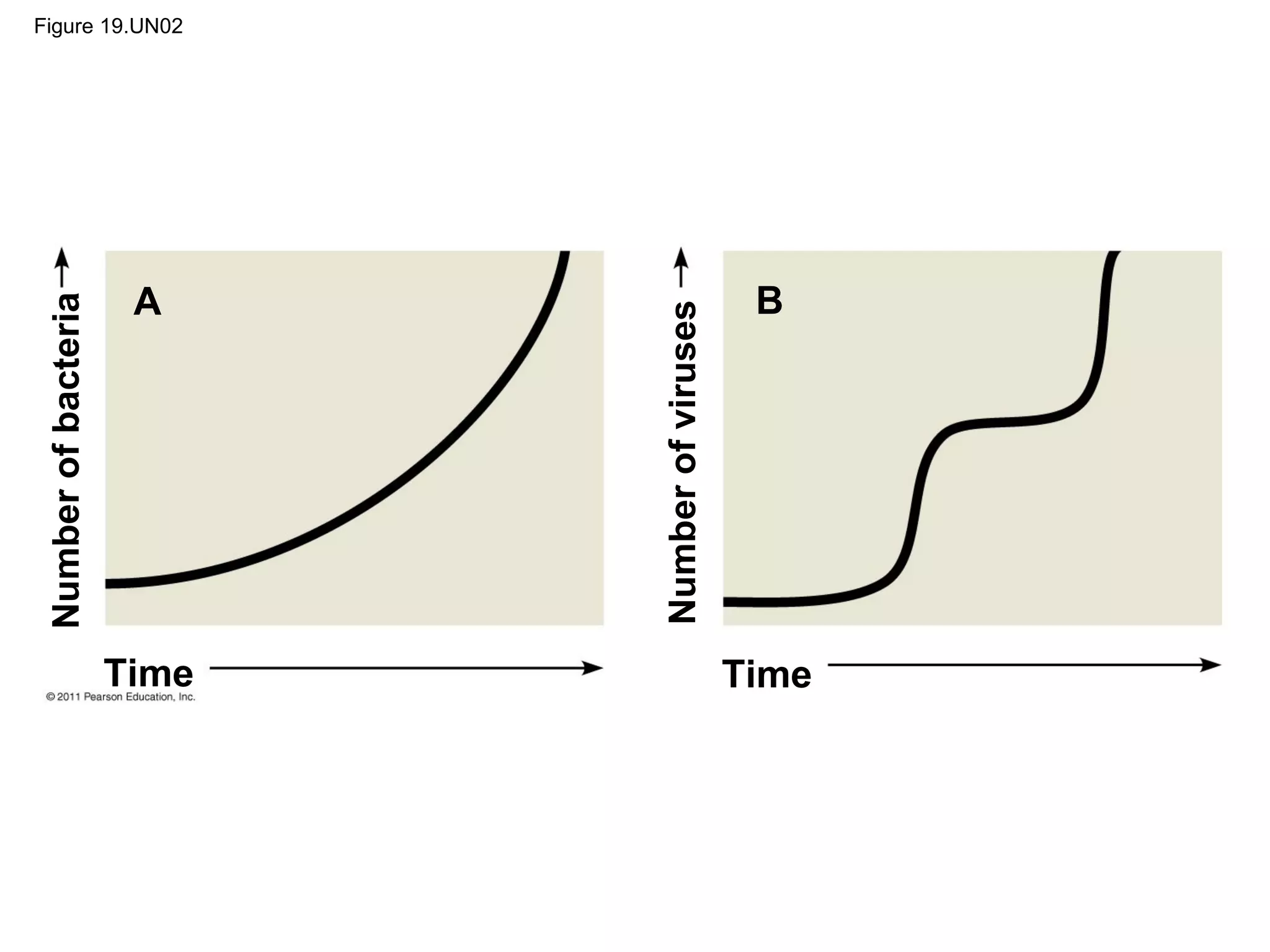
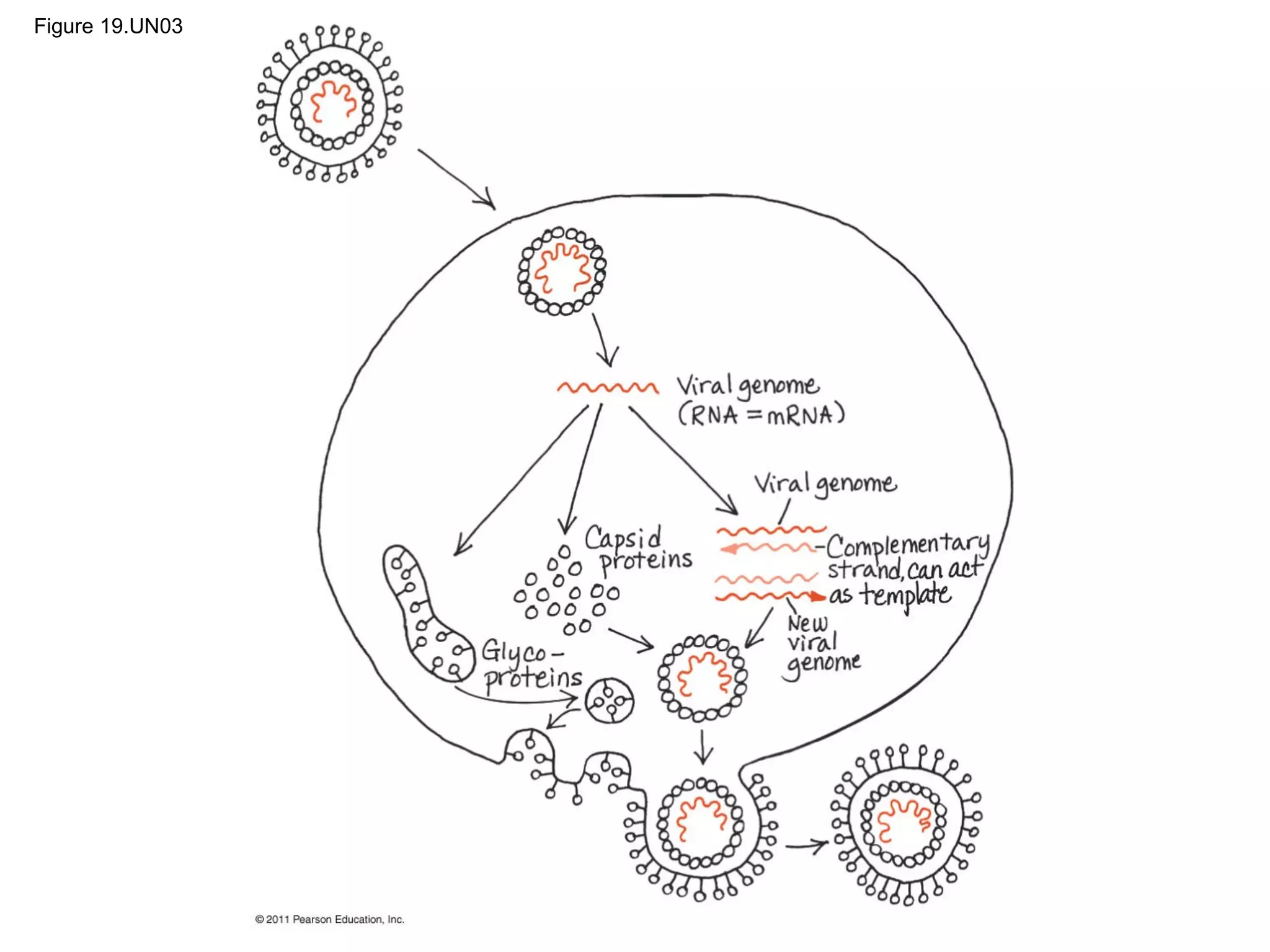
Viruses consist of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat. They can only replicate inside host cells by using the host's cellular machinery. There are two main cycles by which viruses replicate - the lytic cycle which results in host cell death and release of new virus particles, and the lysogenic cycle where the viral genome integrates into the host genome and is copied along with it until induced to enter the lytic cycle. Retroviruses like HIV are unique in that they reverse transcribe their RNA genome into DNA which then integrates into the host cell genome.