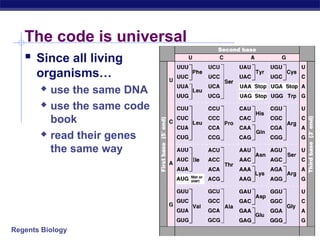
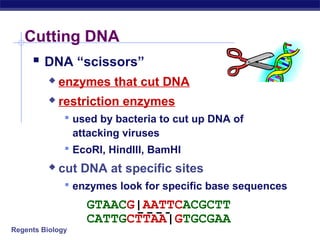
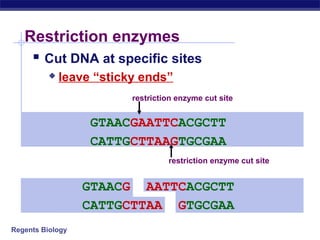
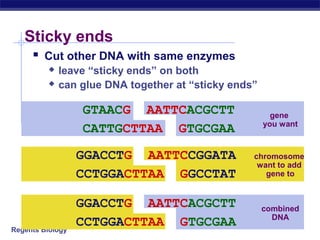
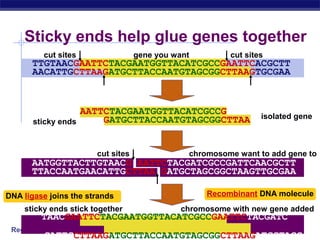
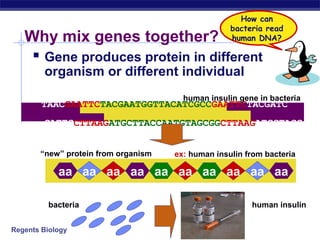
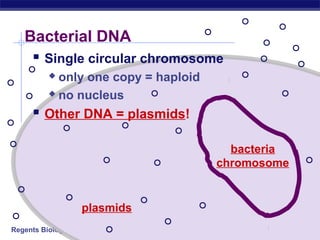
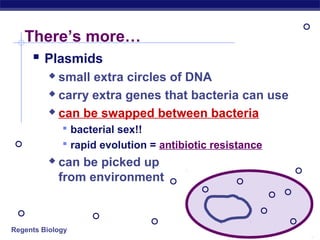
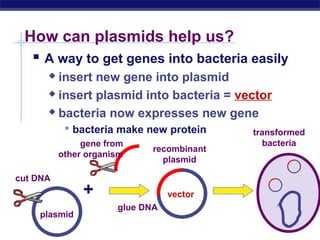
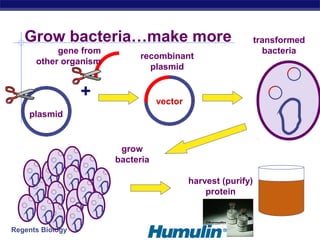
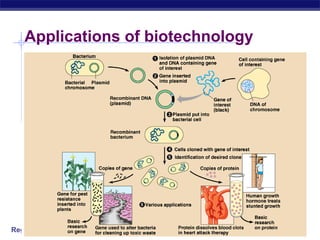
This document discusses genetic engineering and biotechnology. It begins by explaining how artificial breeding has been used for generations to create new breeds of animals and crop plants. It then discusses how genetic engineering works, including cutting DNA with restriction enzymes, joining DNA segments through complementary "sticky ends," and inserting new genes into organisms. Examples are given of genetically modified crops and organisms created for various purposes, such as producing human insulin or creating disease-resistant plants. The role of bacteria and plasmids in genetic engineering is also described.