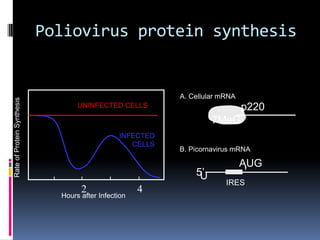
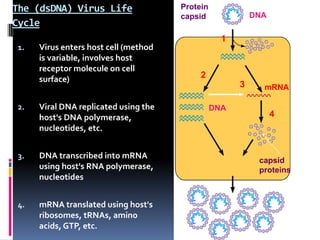
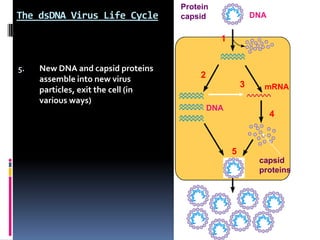
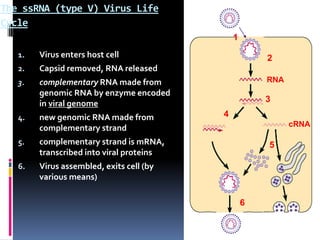
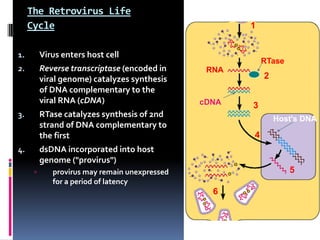
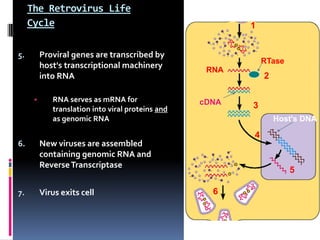
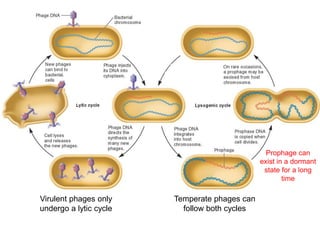
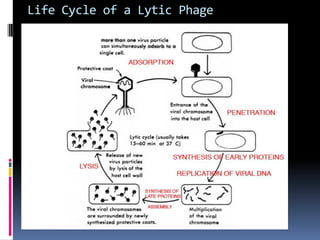
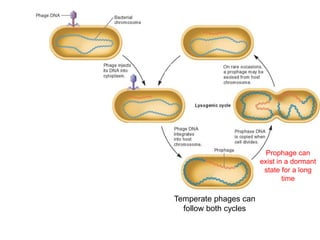
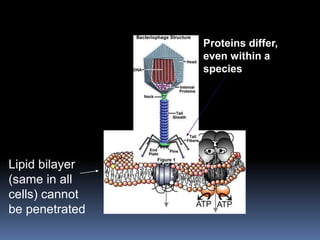
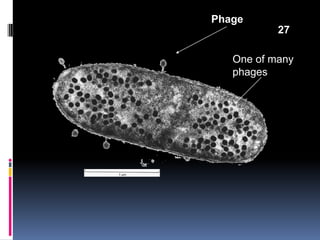
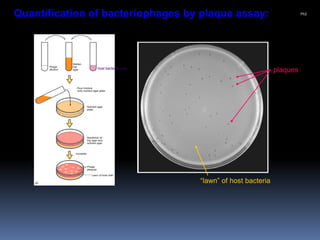
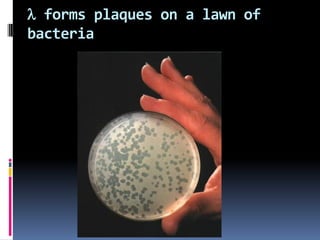
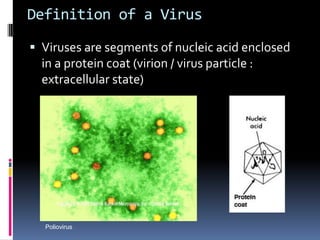
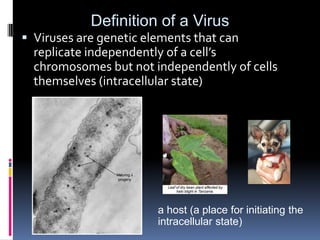
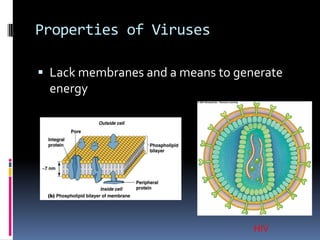
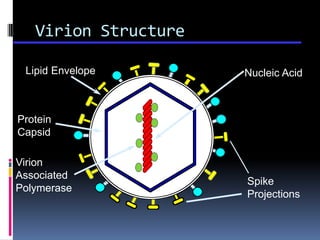
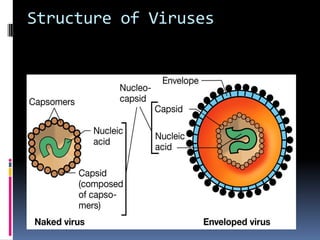
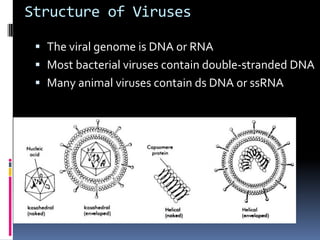
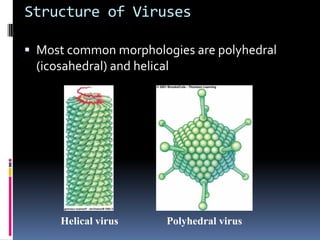
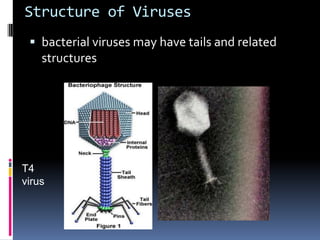
Viruses exhibit great diversity in their structures and genomes. They range in size from 0.02 to 0.3 micrometers and have various morphologies including helical, polyhedral, and filamentous shapes. All viruses are obligate intracellular parasites as they cannot reproduce outside of a living host cell. The viral genome is comprised of DNA or RNA and is enclosed in a protein coat called a capsid. Viruses infect bacteria, plants, and animals and are classified based on attributes like nucleic acid composition and host range. The life cycles of viruses vary depending on whether they contain DNA or RNA genomes and can involve the production of mRNA, reverse transcription, integration into the host genome, and assembly of new viral particles.









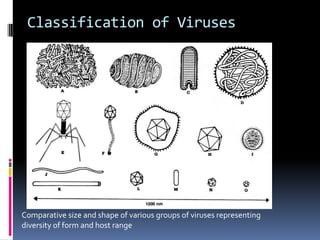


![Virus Groups
“Positive” RNA viruses - Genome RNA is of the same sense as mRNA and
can be infectious.
First stage in replication is the translation of the genome RNA with the
production of the virus polymerase.
“Negative” RNA viruses – Genome RNA is complementary to mRNA.
Virion-associated RNA-polymerase and first stage in replication is
mRNA transcription.
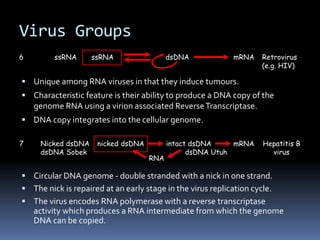
4 +ve ssRNA dsRNA +ve ssRNA [Acts as mRNA] Enterovirus
5 -ve ssRNA Influenza A
virus
dsRNA -ve ssRNA mRNA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virus-220807084633-ca9afd03/85/Virus-pdf-25-320.jpg)