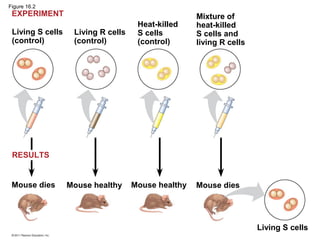
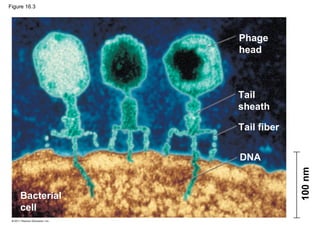
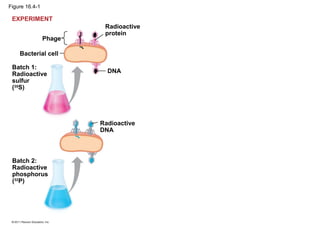
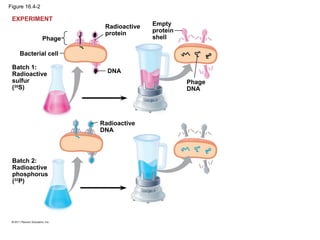
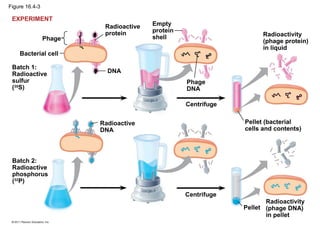
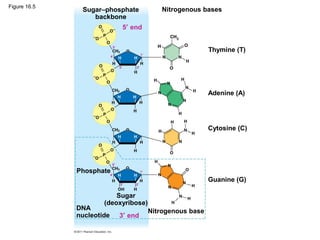
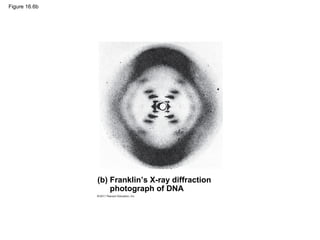
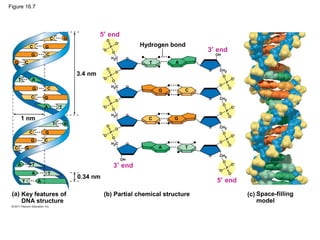
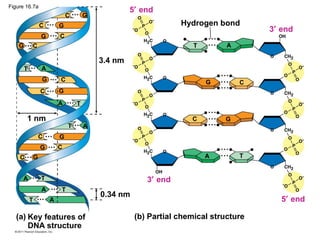
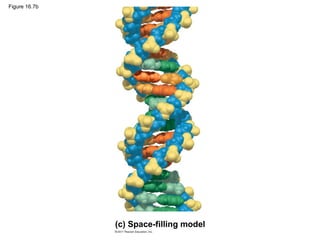
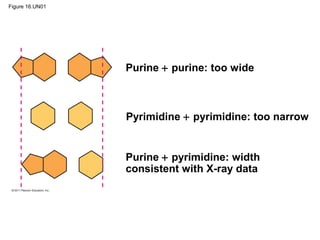
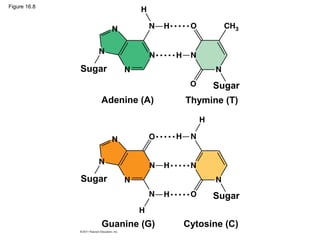
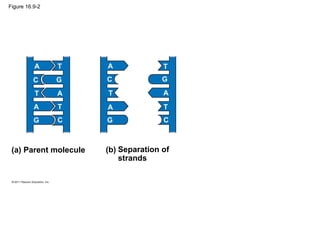
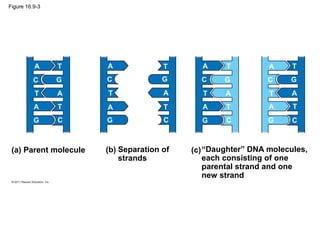
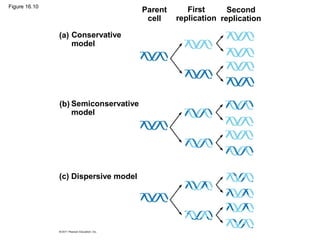
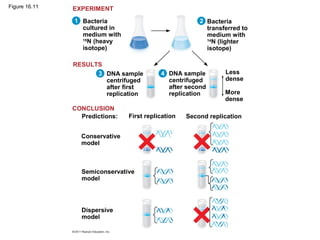
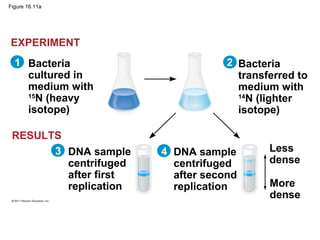
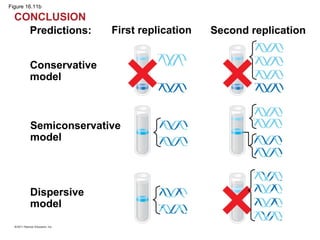
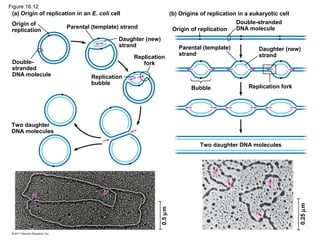
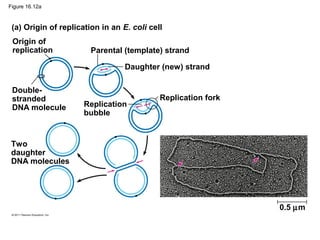
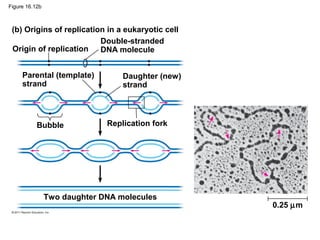
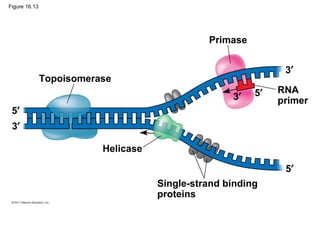
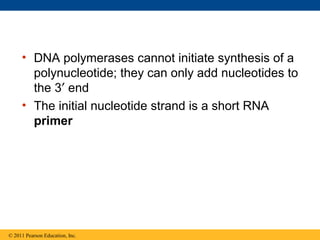
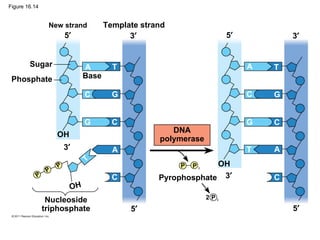
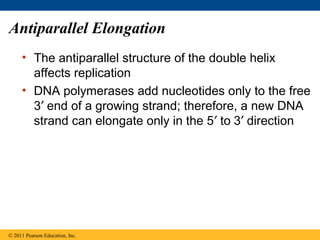
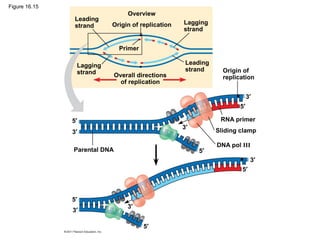
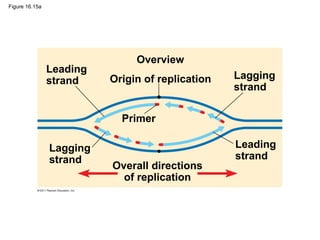
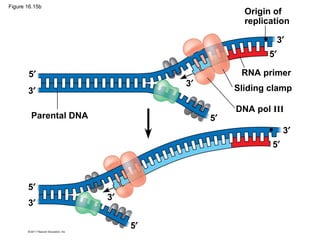
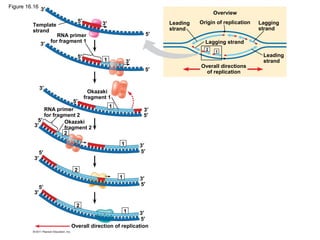
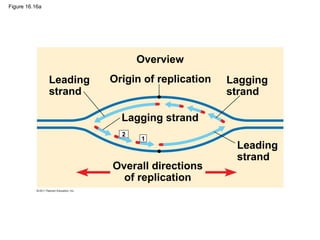
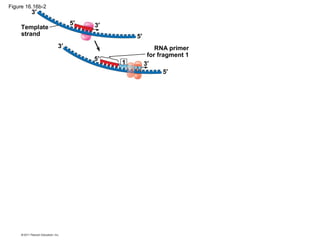
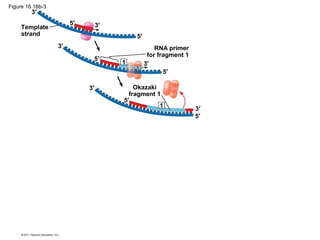
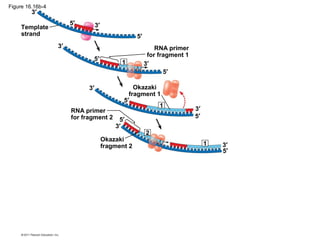
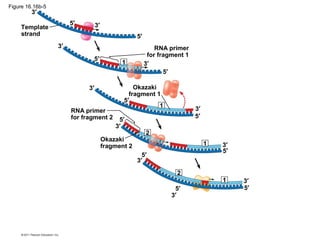
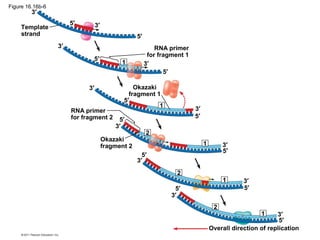
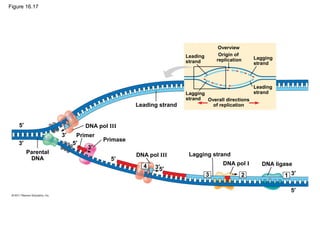
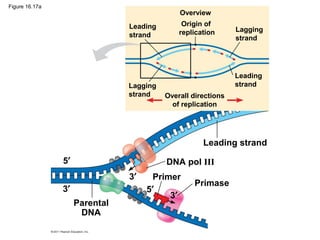
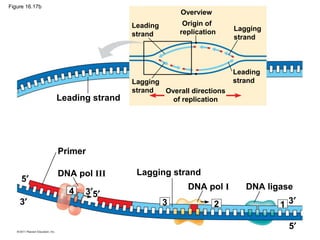
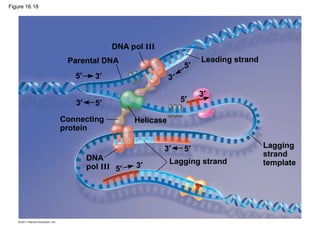
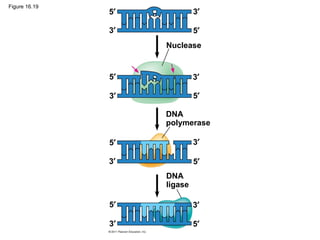
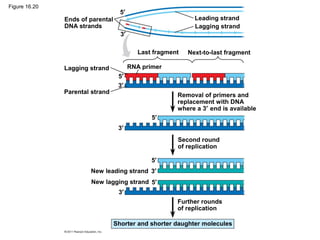
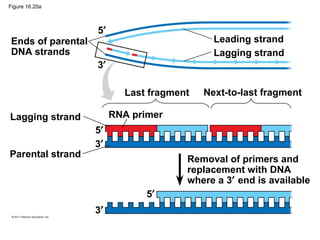
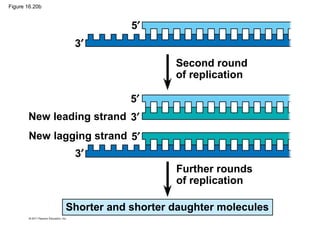
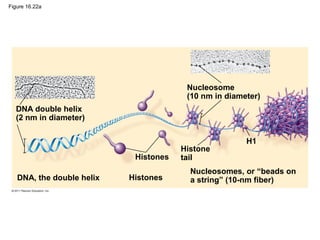
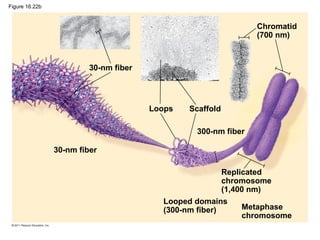
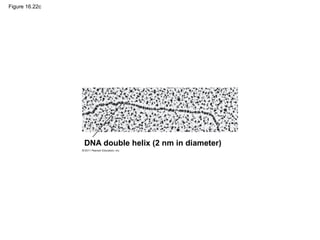
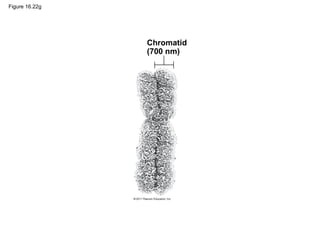
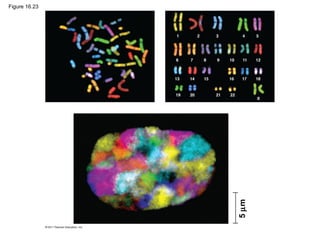
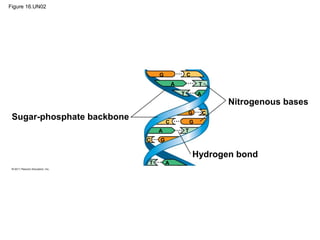
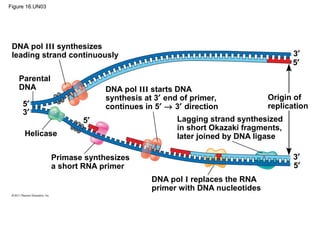
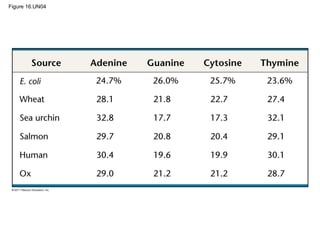
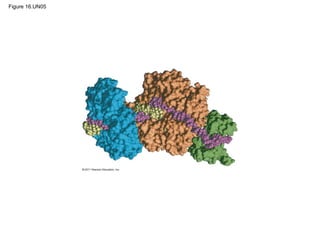
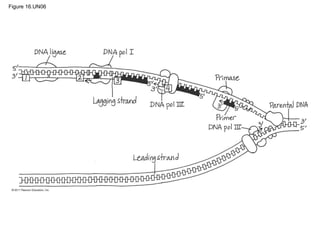
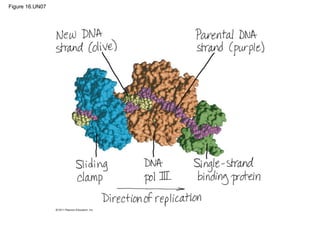
DNA is the genetic material that is faithfully replicated and passed from parents to offspring. James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the double helix structure of DNA in 1953, which explained how DNA could store and replicate the instructions for making organisms. Their model showed that DNA consists of two strands coiled around each other, with nucleotides on the strands bonded together through base pairing with adenine bonding only to thymine and guanine only to cytosine. This allows each strand to serve as a template for duplicating the other, explaining DNA's role in inheritance and allowing organisms to pass genetic information between generations.