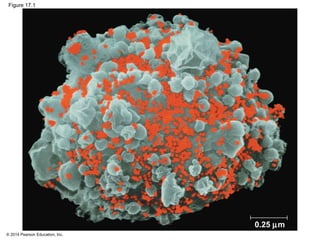
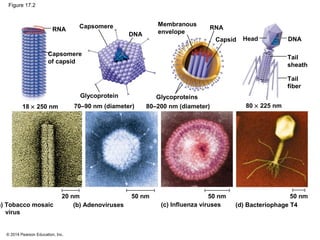
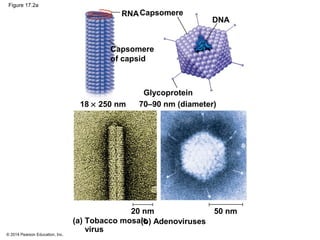
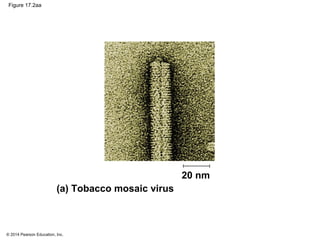
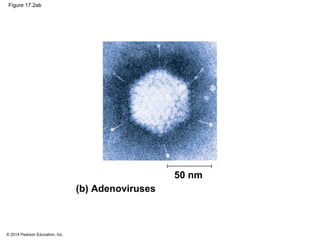
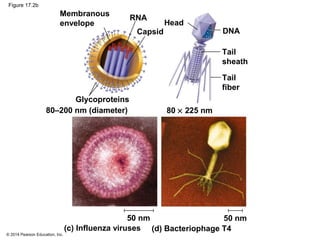
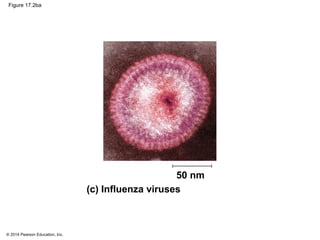
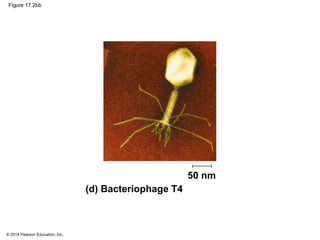
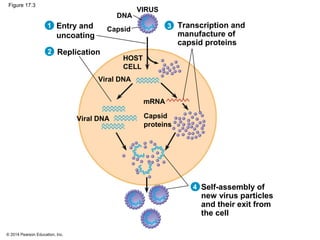
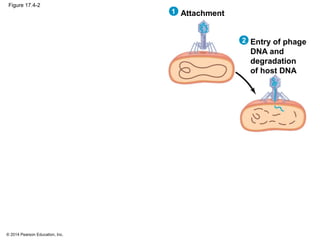
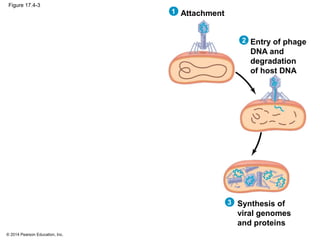
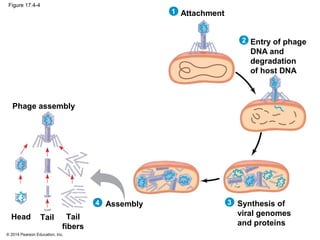
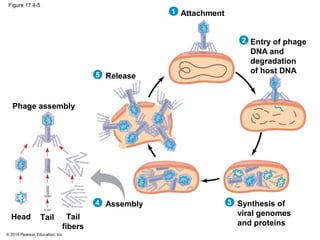
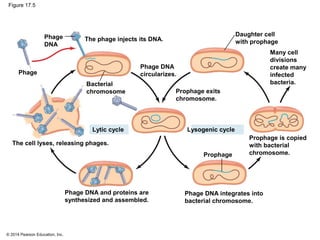
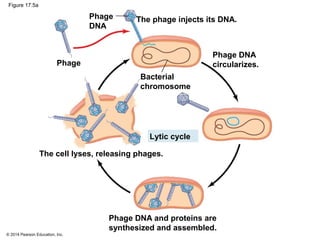
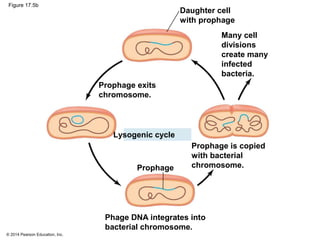
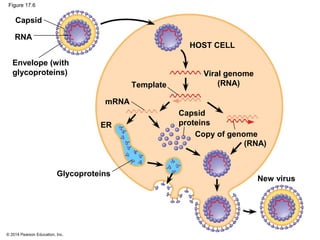
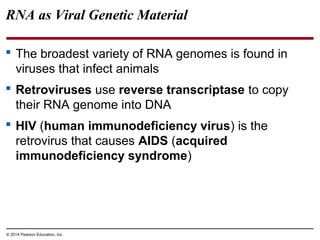
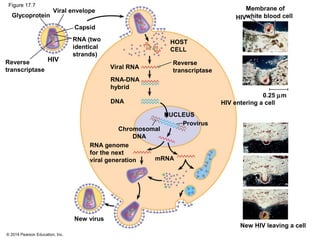
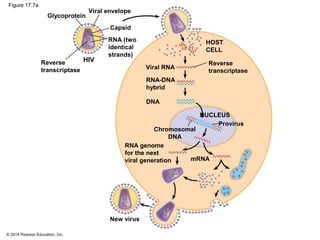
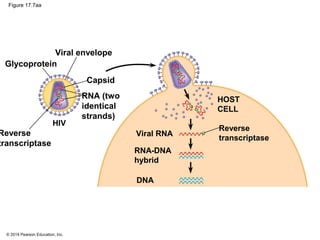
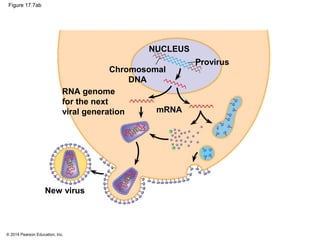
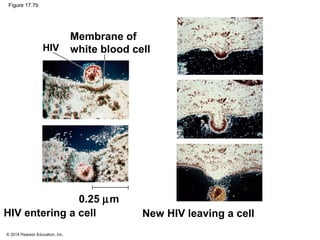
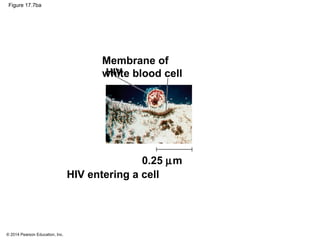
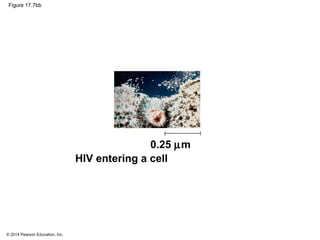
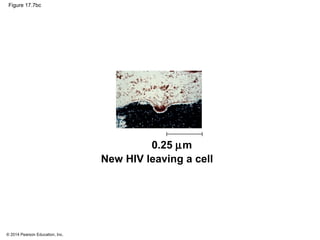
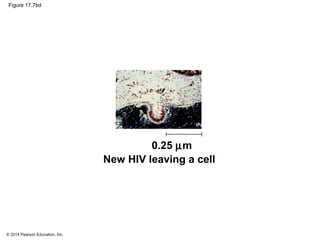
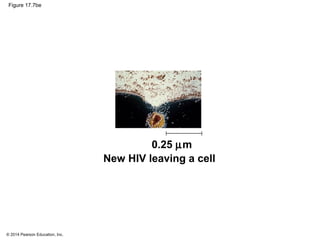
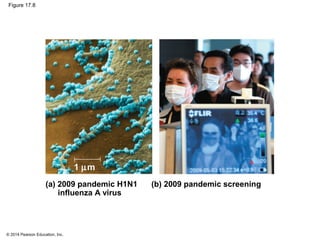
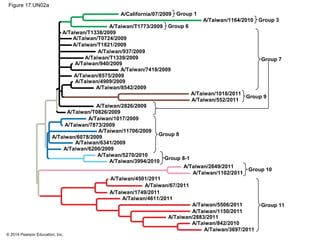
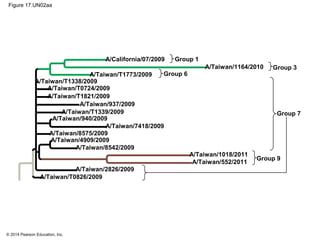
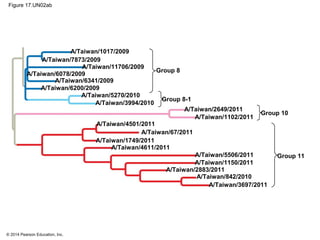
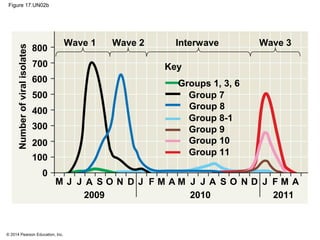
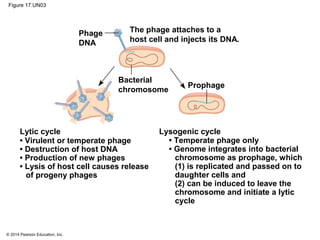
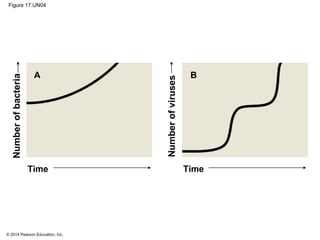
Viruses consist of either DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat. They can only replicate inside of host cells by using the host's cellular machinery. Viruses have a variety of structures depending on whether they have an envelope derived from the host cell membrane and the structure of their protein coat. They use different replication cycles like the lytic cycle which destroys the host cell or the lysogenic cycle where the viral DNA is incorporated into the host genome. Retroviruses like HIV replicate through reverse transcribing their RNA into DNA which then integrates into the host cell genome.