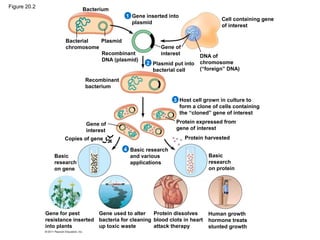
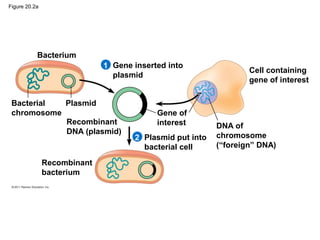
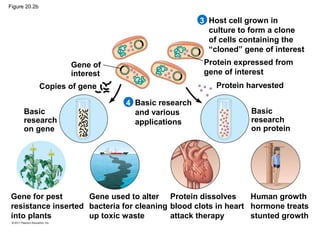
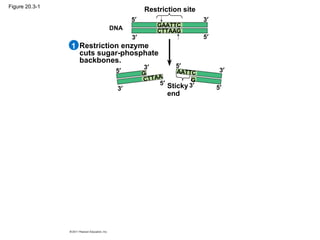
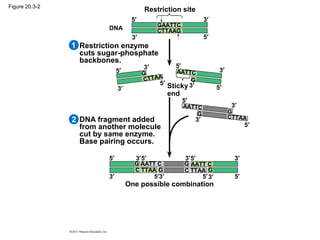
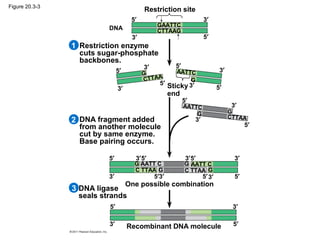
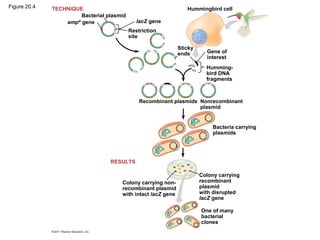
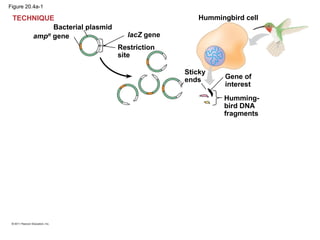
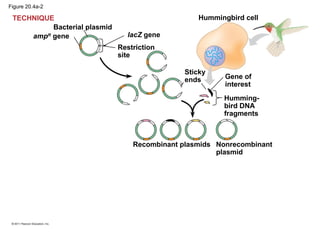
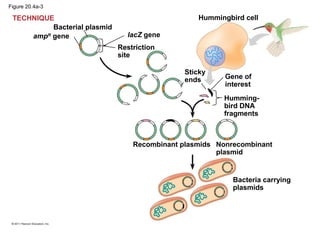
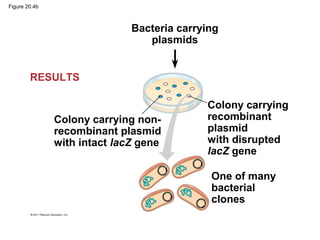
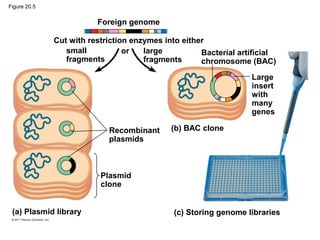
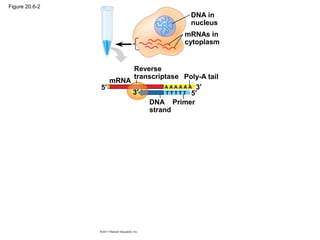
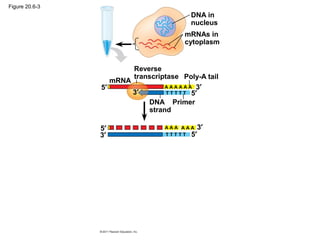
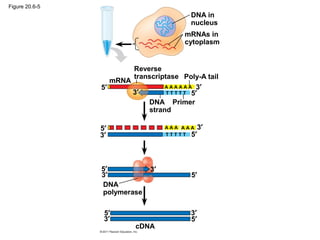
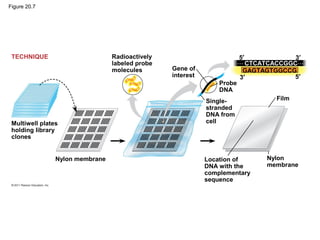
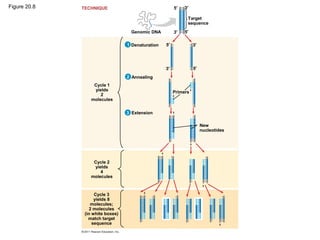
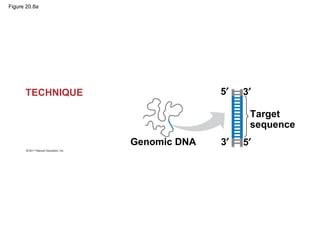
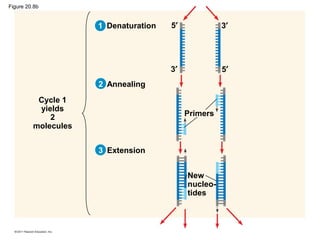
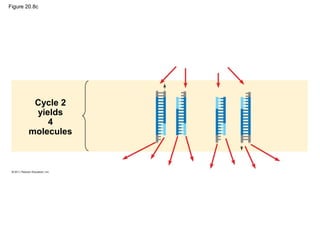
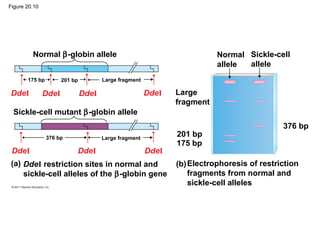
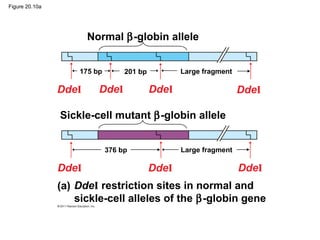
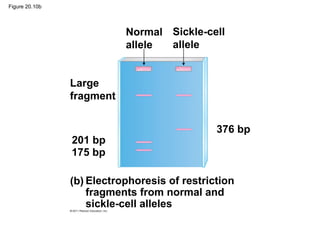
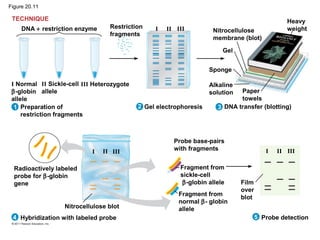
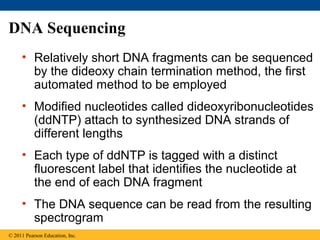
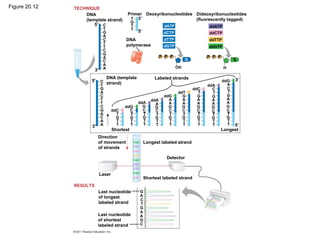
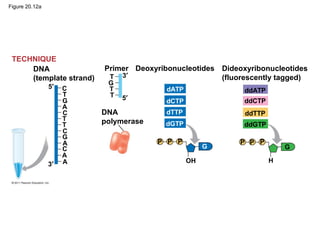
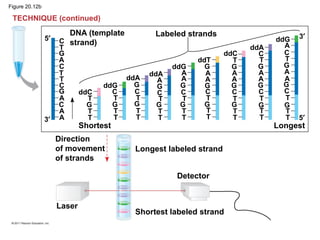
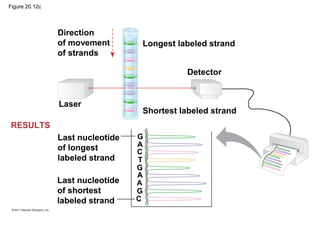
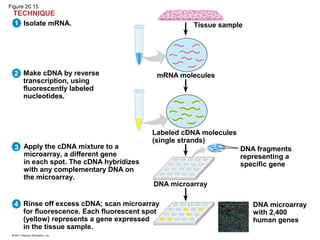
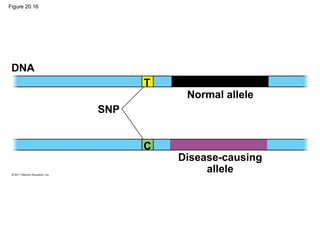
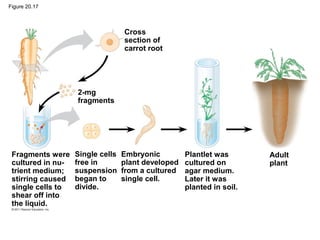
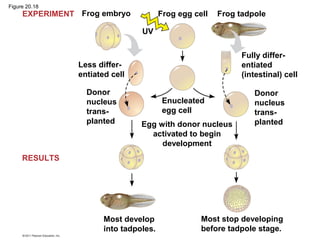
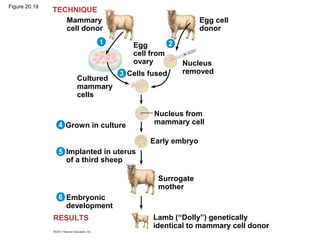
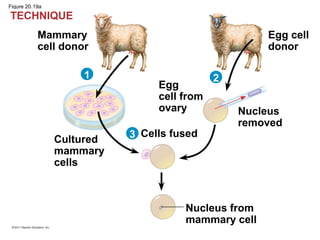
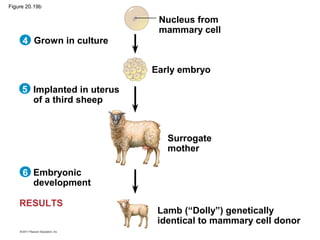
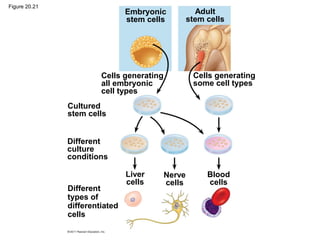
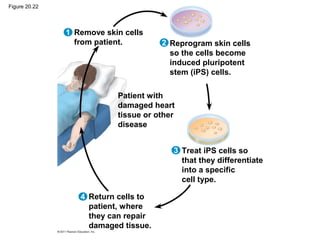
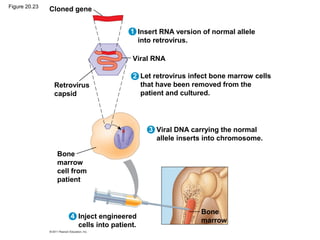
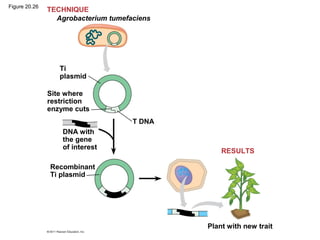
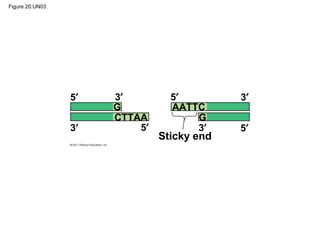
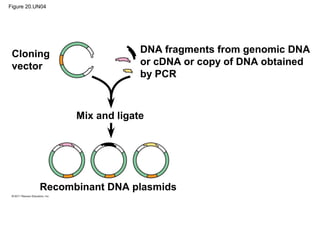
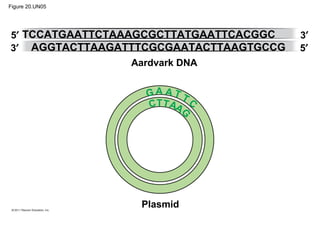
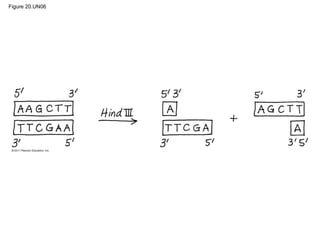
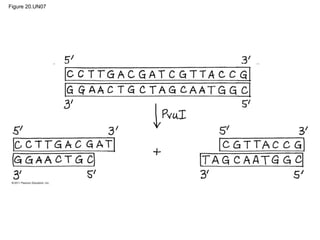
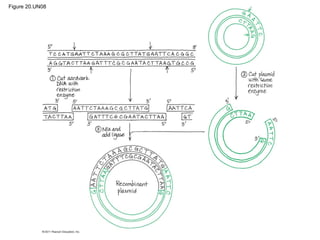
Gene cloning involves inserting DNA fragments from one source into plasmids or bacteria. This allows for the production of multiple copies of the gene. Restriction enzymes and DNA ligase are used to cut and paste DNA fragments into plasmids. The plasmids are then inserted into bacteria which replicate, producing many copies of the gene. Libraries of cloned DNA fragments can be stored in bacteria or plasmids. The library can be screened to identify clones containing genes of interest using probes complementary to the target gene. Expressed genes can be studied by producing their protein products in bacterial or eukaryotic cells.