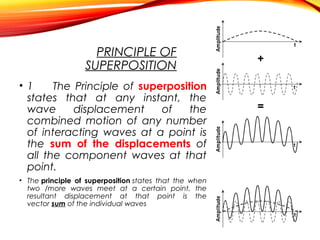
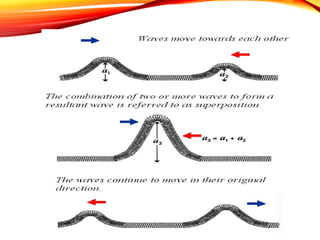
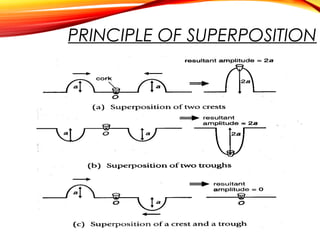
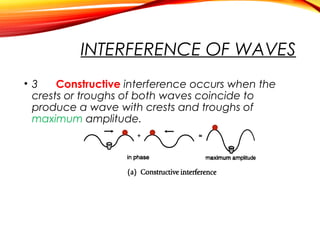
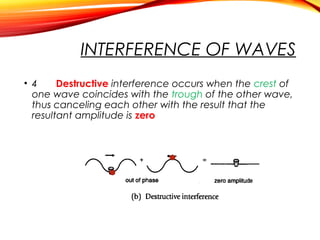
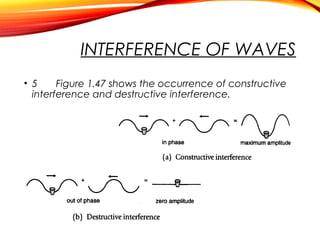
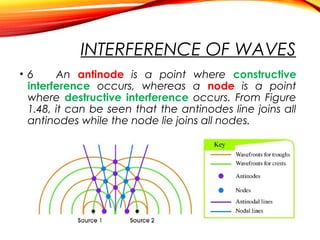
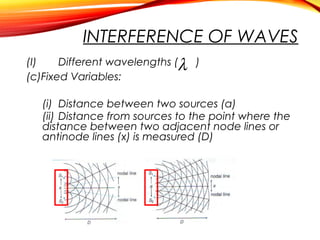
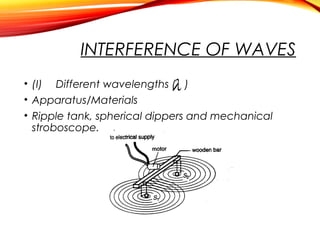
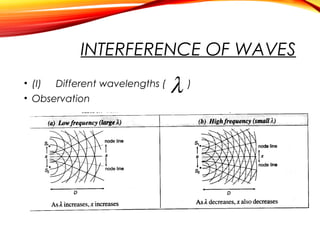
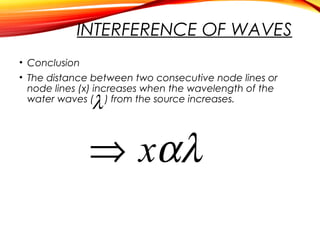
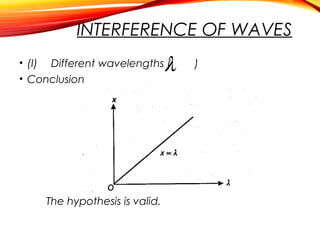
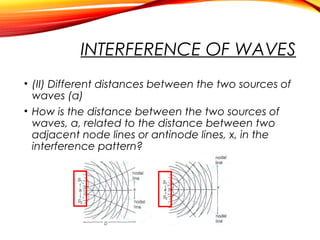
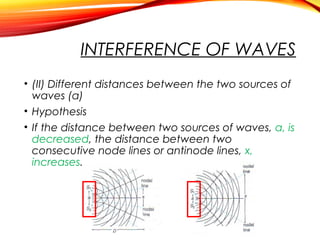
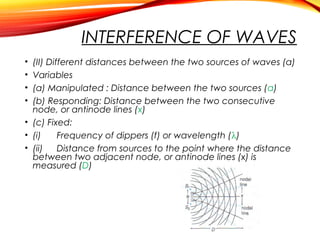
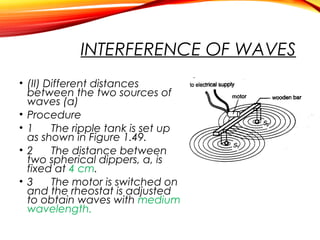
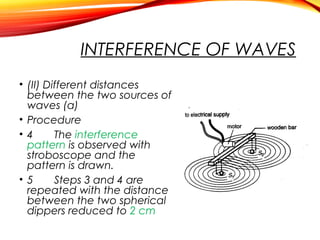
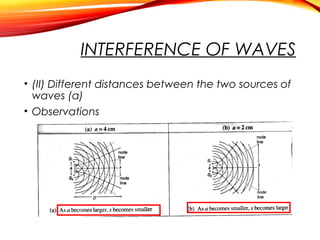
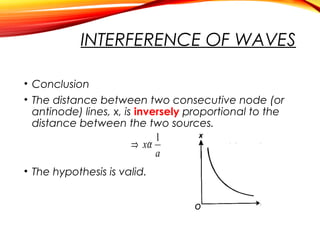
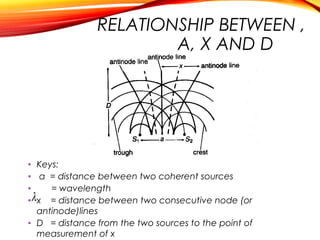
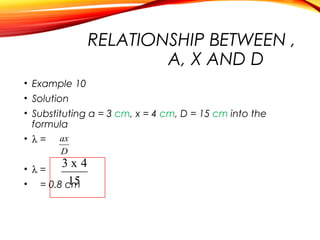
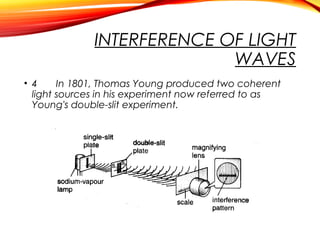
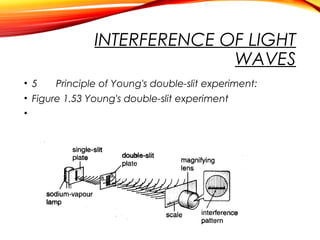
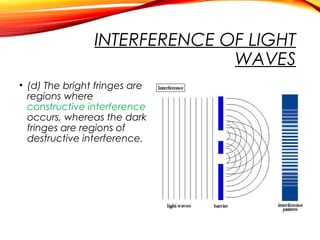
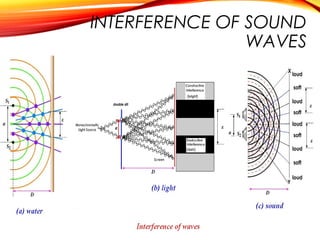
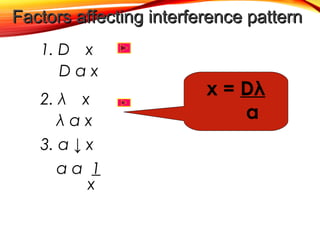
The document discusses the principles of interference and superposition of waves. It begins by explaining that when two or more waves meet at a point, the resultant displacement is the sum of the individual wave displacements. It then describes experiments investigating the interference patterns produced by water waves with varying wavelengths and distances between sources. The key findings are that the distance between nodes/antinodes increases with wavelength and decreases with source separation. The document concludes by explaining Young's double-slit experiment, which demonstrated interference of light waves.