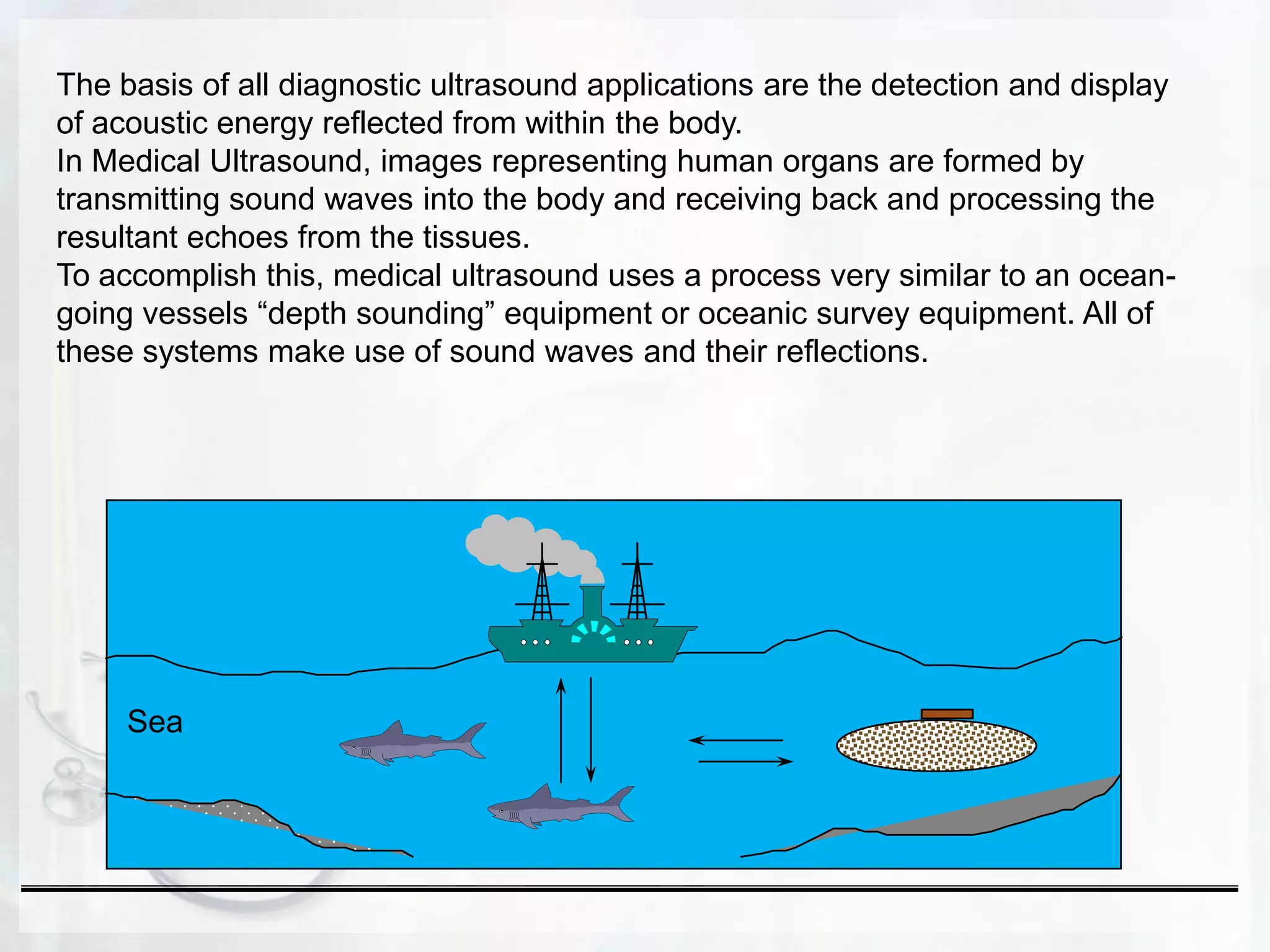
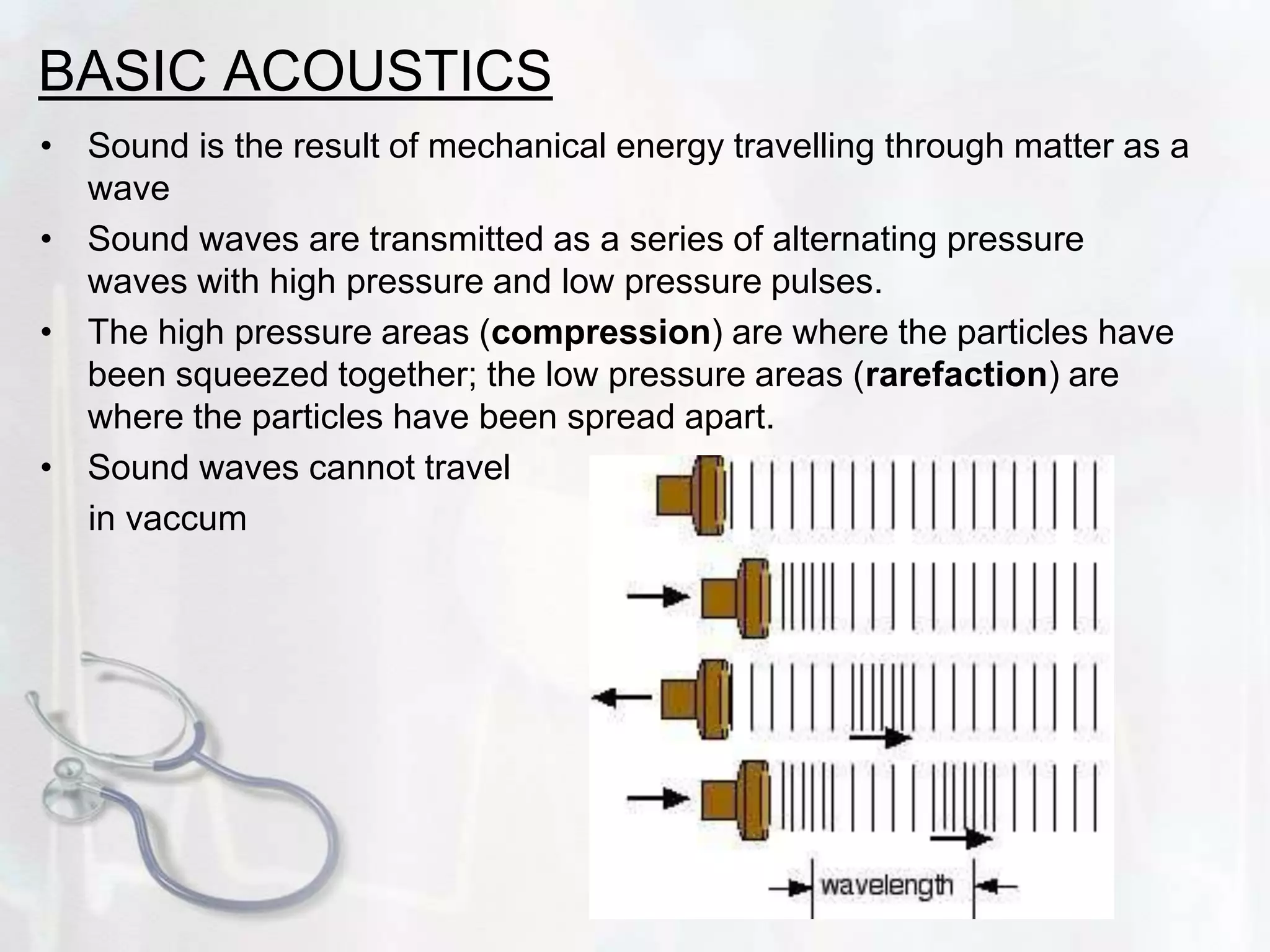
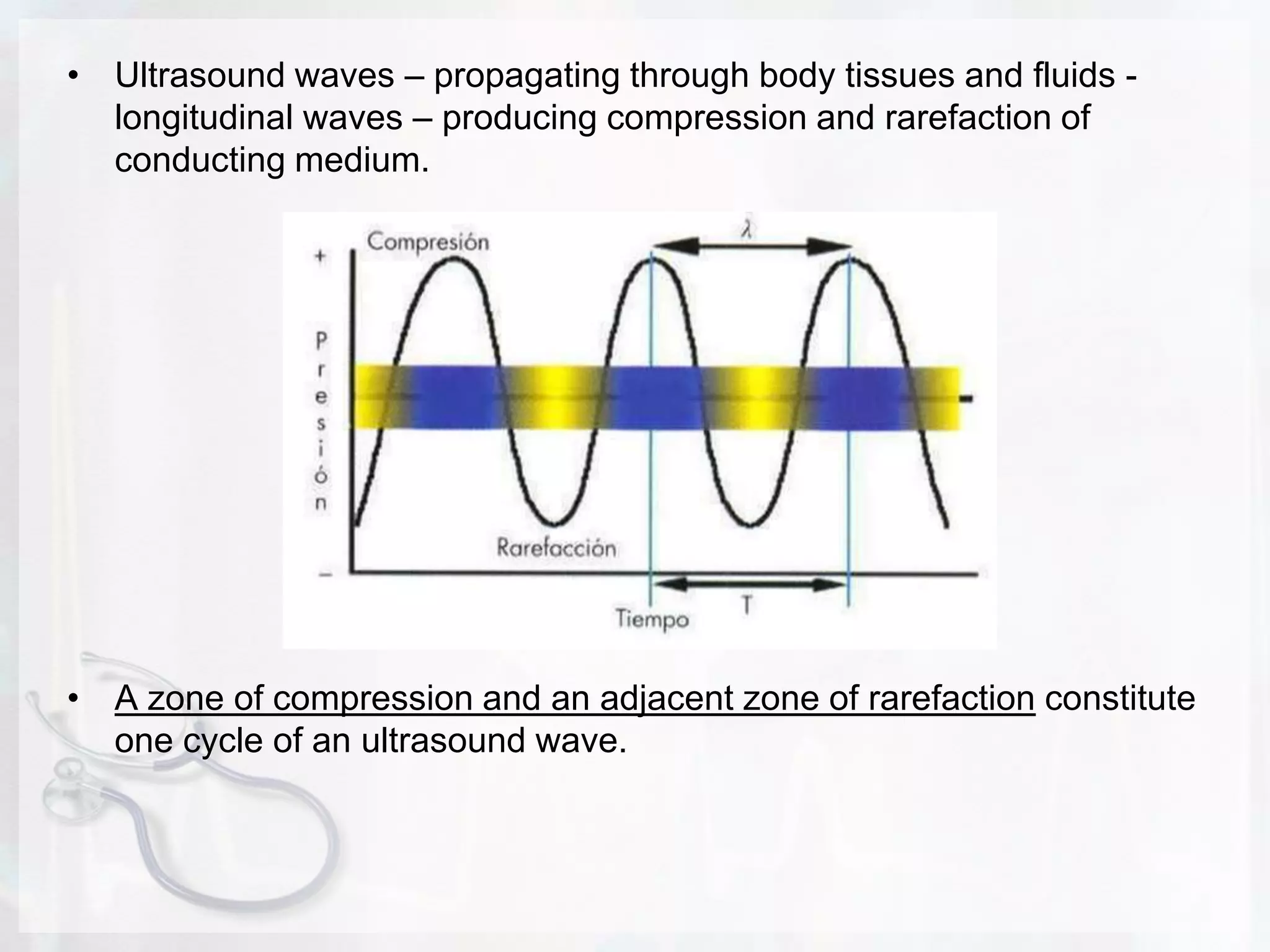
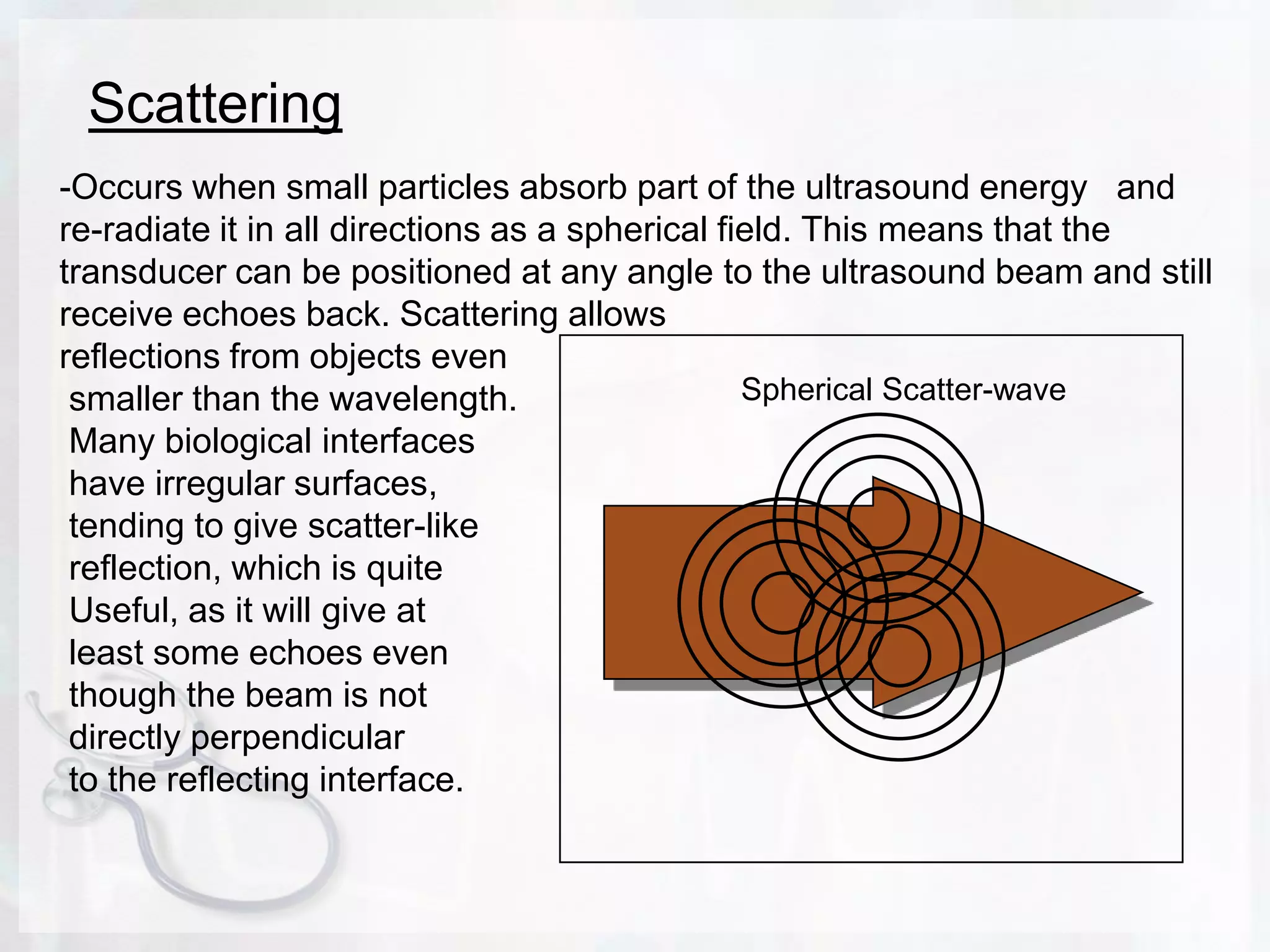
Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of internal organs and tissues. Sound waves are transmitted into the body and the echoes produced by reflections from structures and tissues are detected. Three key points:
1) Ultrasound transducers convert electrical pulses into sound waves which penetrate the body and receive the echoes. Piezoelectric crystals in the transducer perform this function.
2) Reflected sound waves are displayed as images on screen to visualize internal structures. The brightness of each pixel depends on the strength of reflection.
3) Different transducer designs like linear arrays and curved arrays allow imaging of different body regions. Imaging modes like B-mode show anatomical structures while M-mode depicts motion.