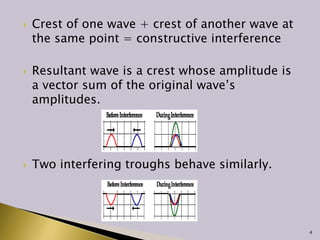
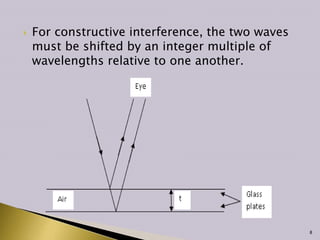
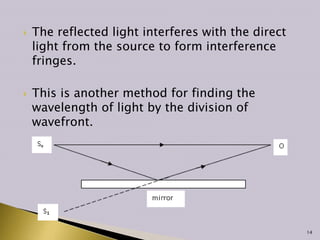
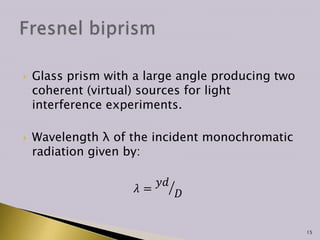
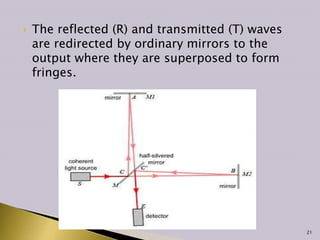
Interference occurs when two waves superimpose to form a resultant wave of greater or lower amplitude. There are two main types of interference: constructive and destructive. Constructive interference occurs when wave crests or troughs overlap, increasing amplitude, while destructive interference occurs when a crest and trough overlap, decreasing amplitude. Thin film interference is studied using thin films that reflect light, which can interfere and be analyzed to determine properties like film thickness. Interferometers exploit the interference of light to make extremely precise measurements of distance and other values.