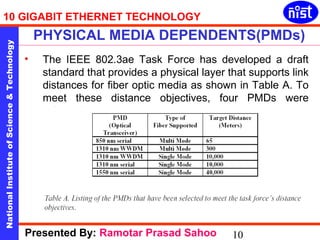
Ramotar Prasad Sahoo presented on 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology. The presentation discussed the history and development of 10 Gigabit Ethernet, its standards and architectures, and its applications in local, metropolitan, wide and storage area networks. It also covered fiber optic implementations and the future of 10 Gigabit Ethernet technology.