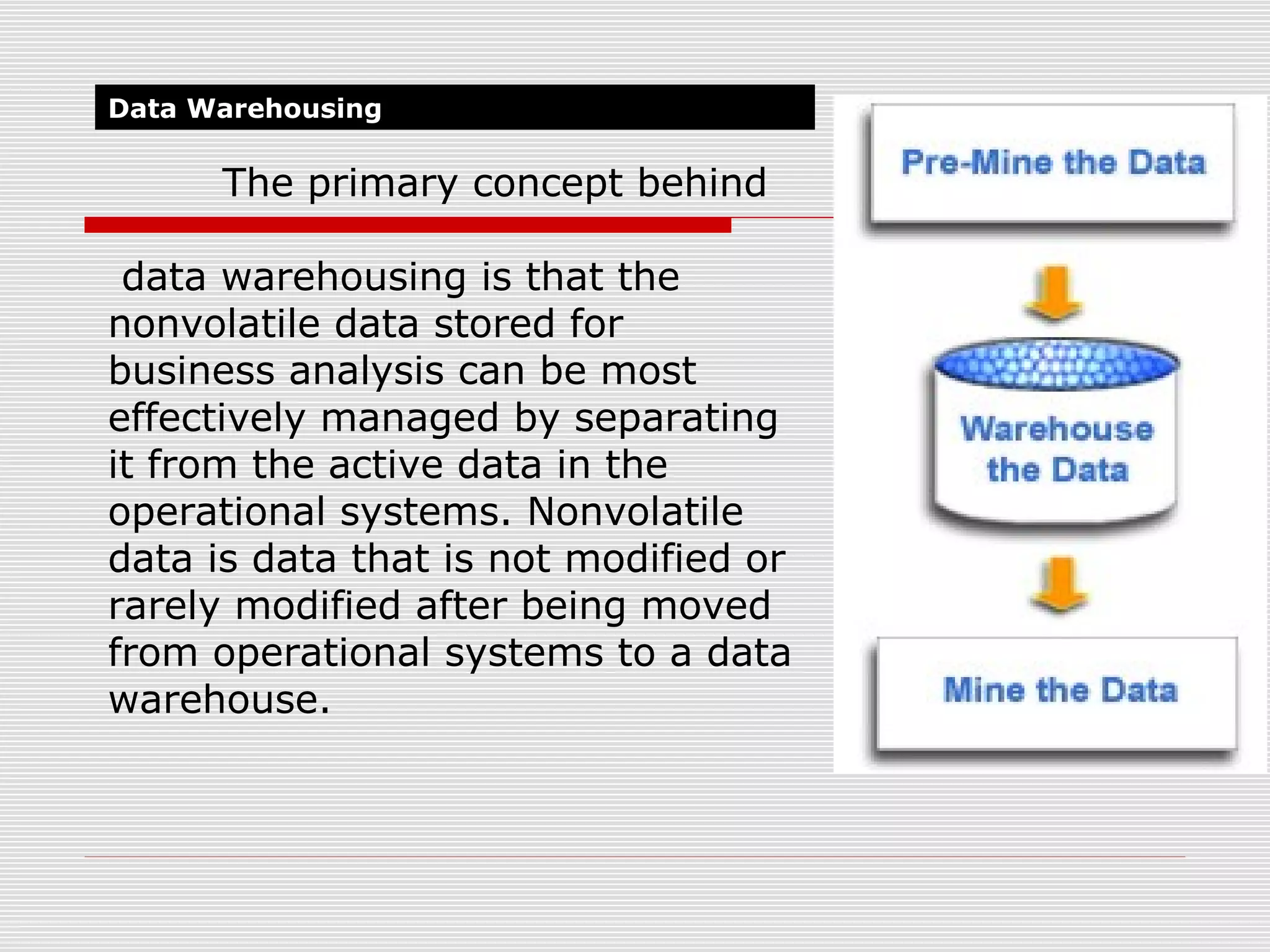
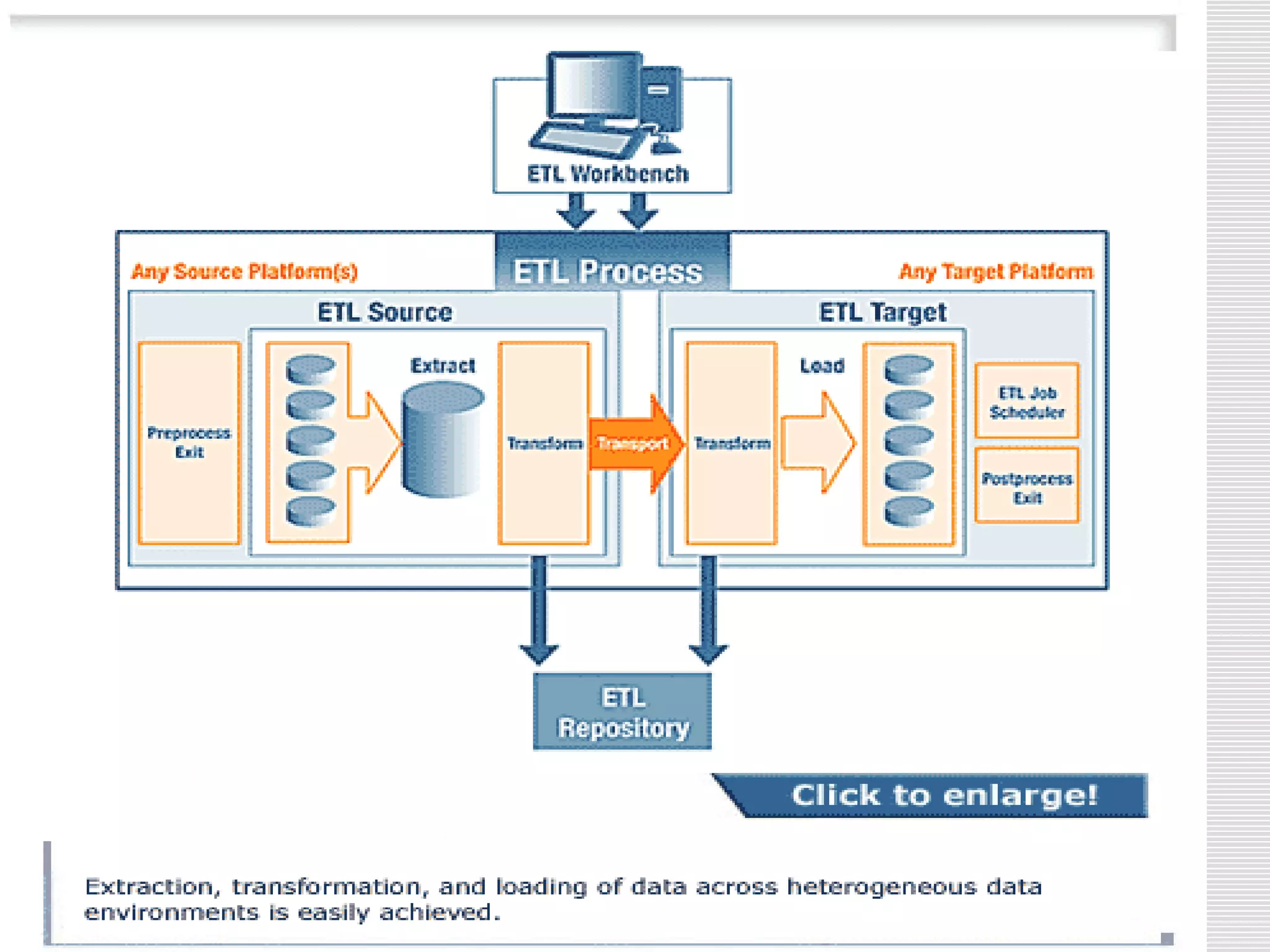
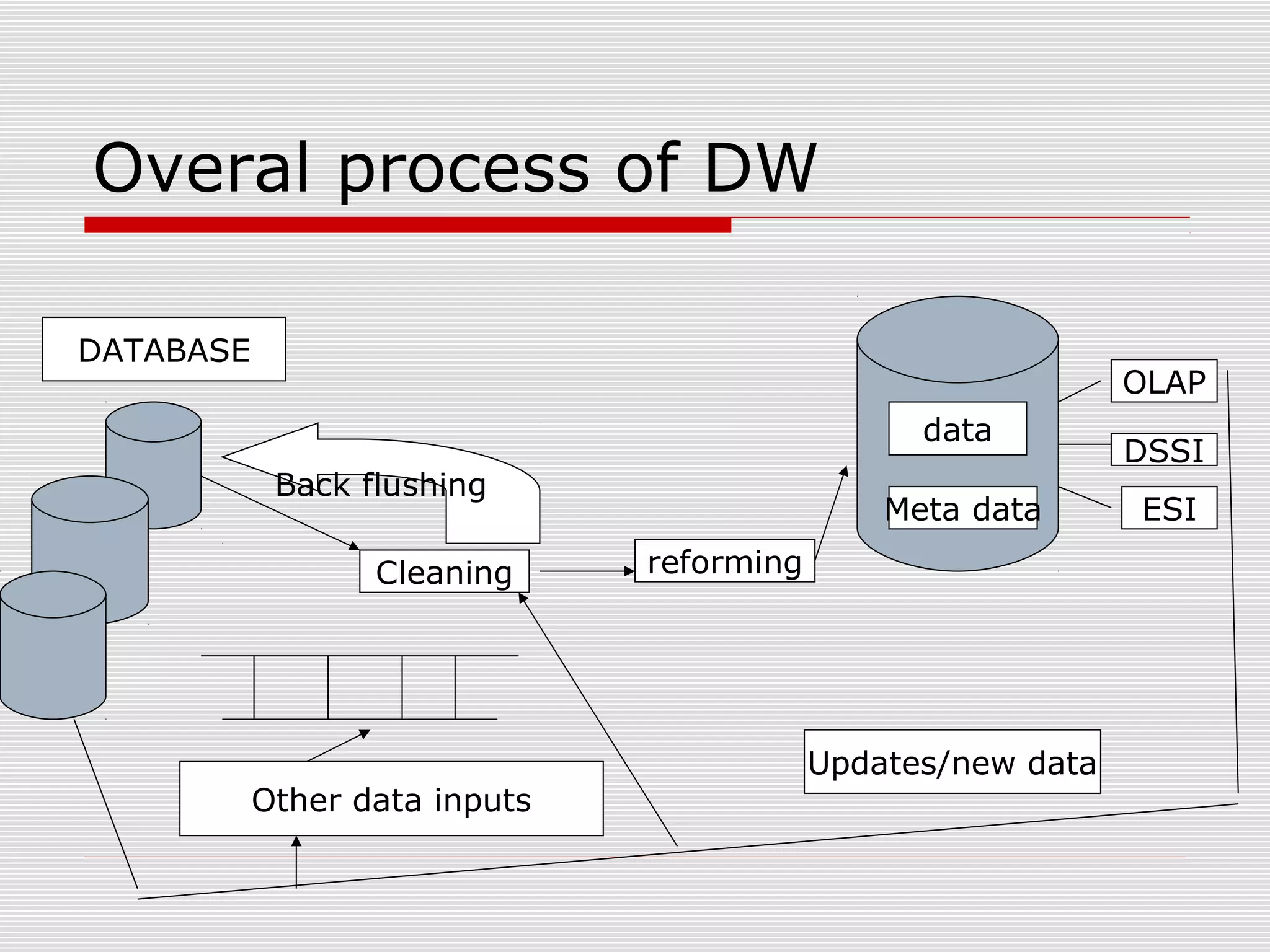
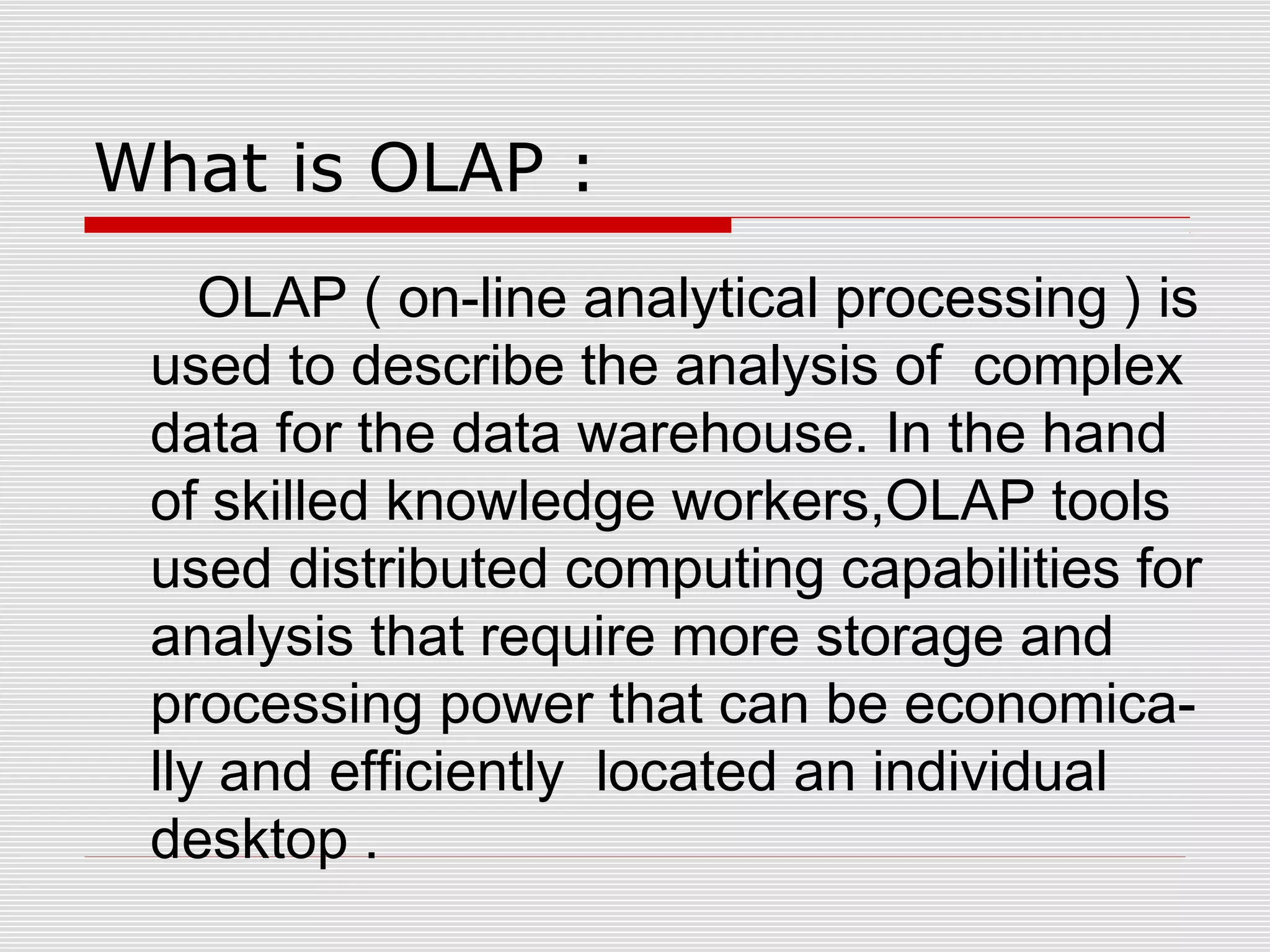
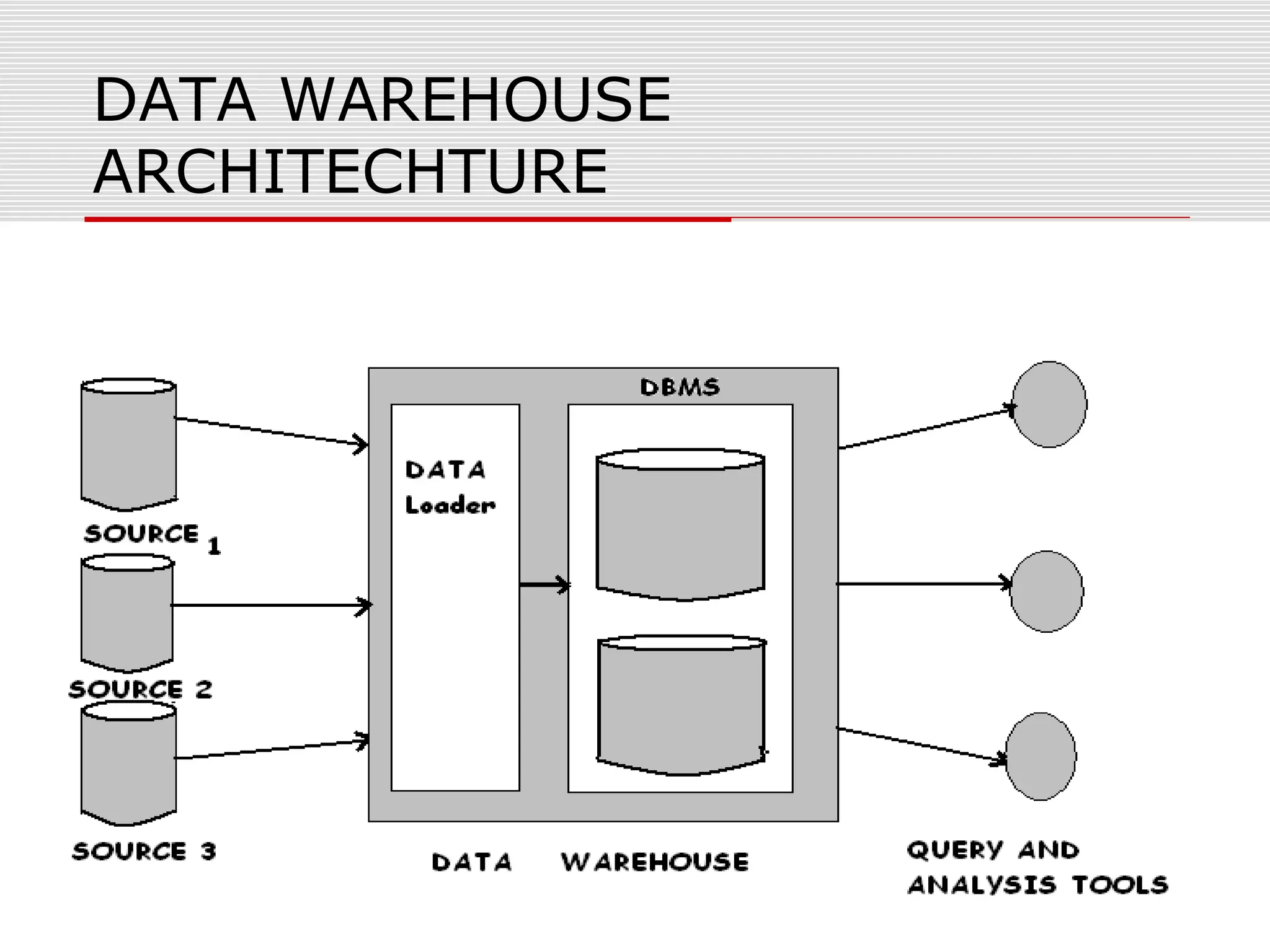
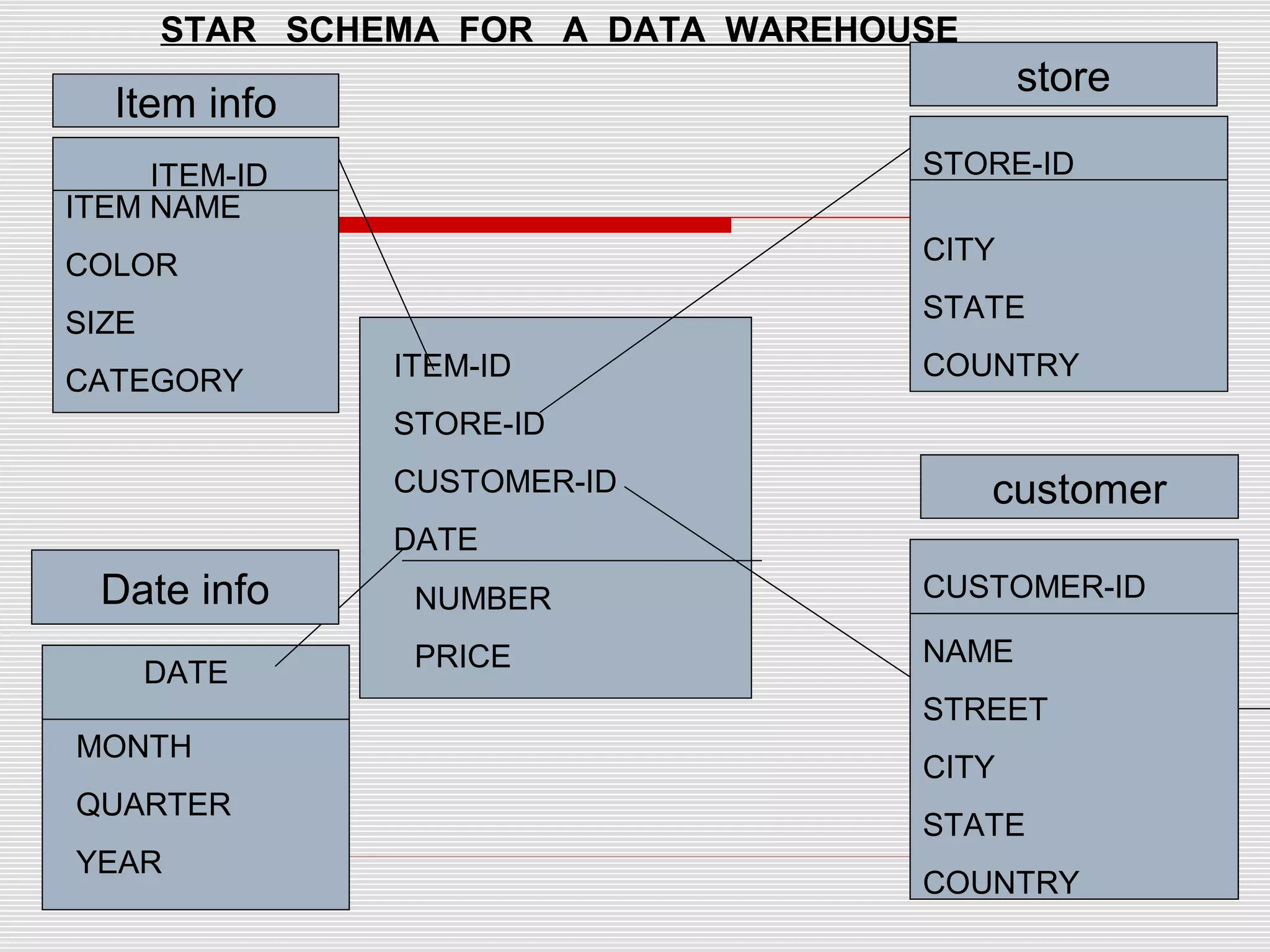
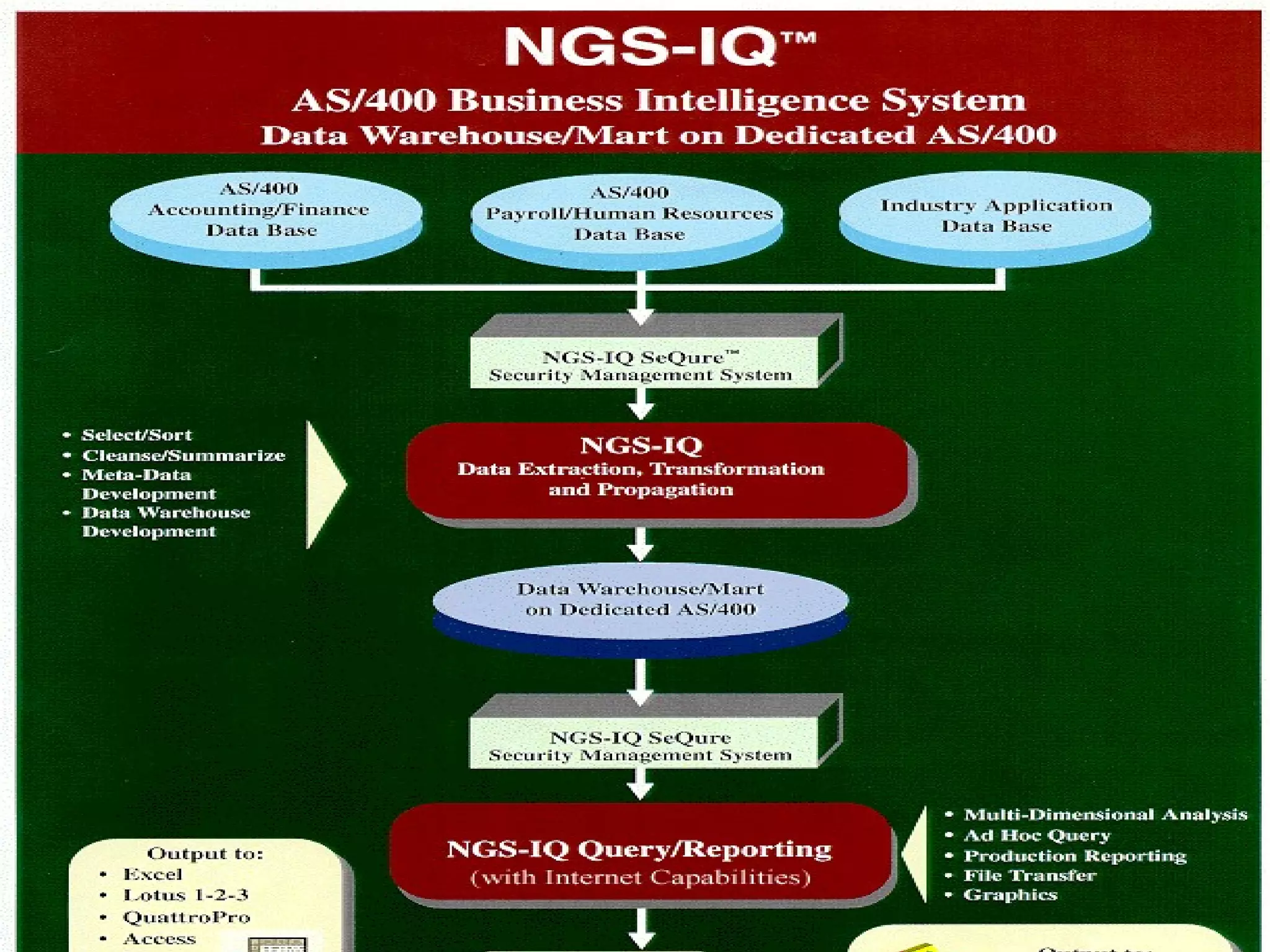
The document discusses a seminar on data warehousing presented by Sangram Keshari Swain. It defines a data warehouse as a subject-oriented, integrated, non-volatile collection of data used to support management decision making. The primary concept is separating nonvolatile data for analysis from operational systems. A data warehouse provides a single view of enterprise data optimized for reporting and analysis through extracting and integrating data from different sources.