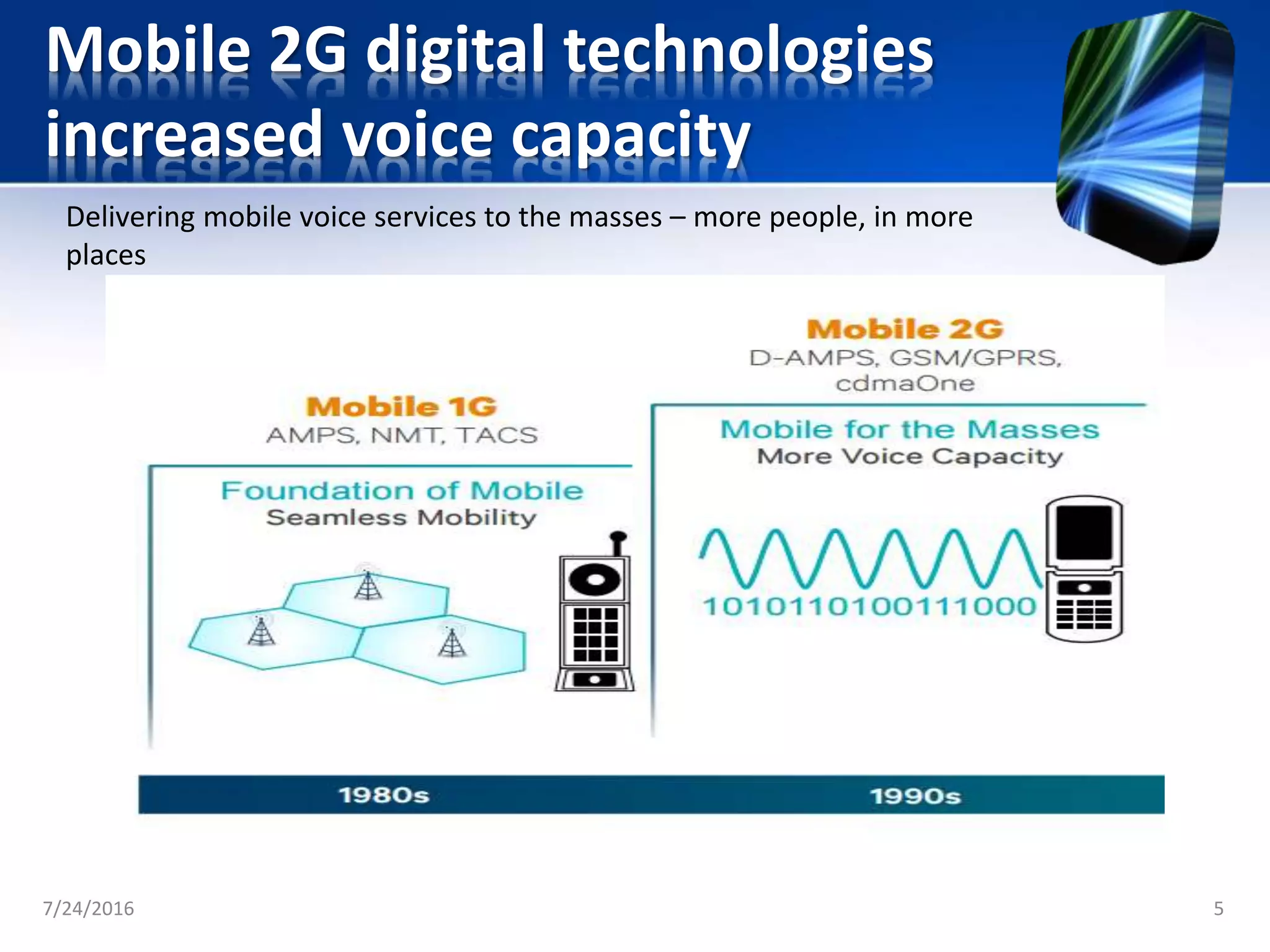
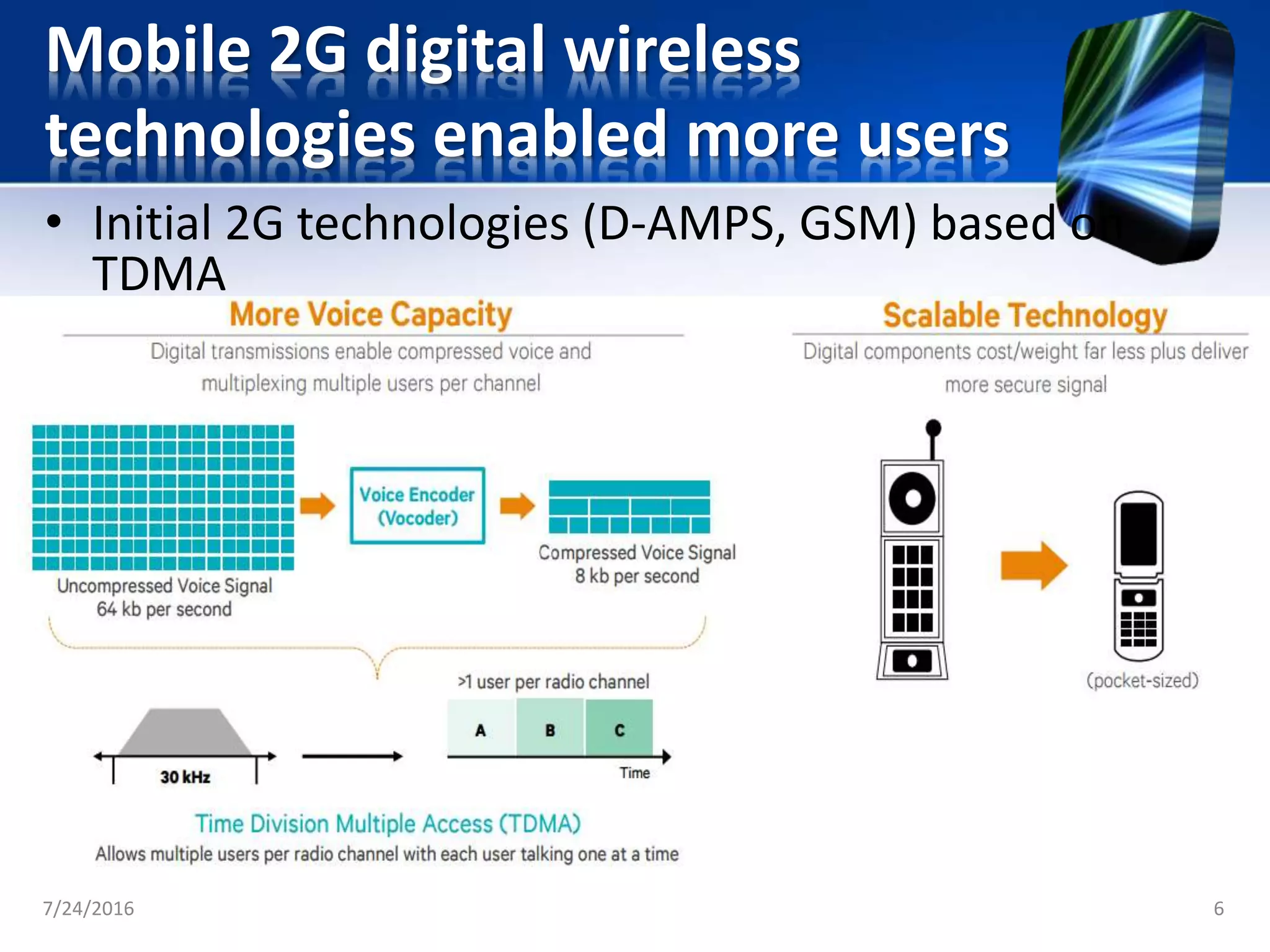
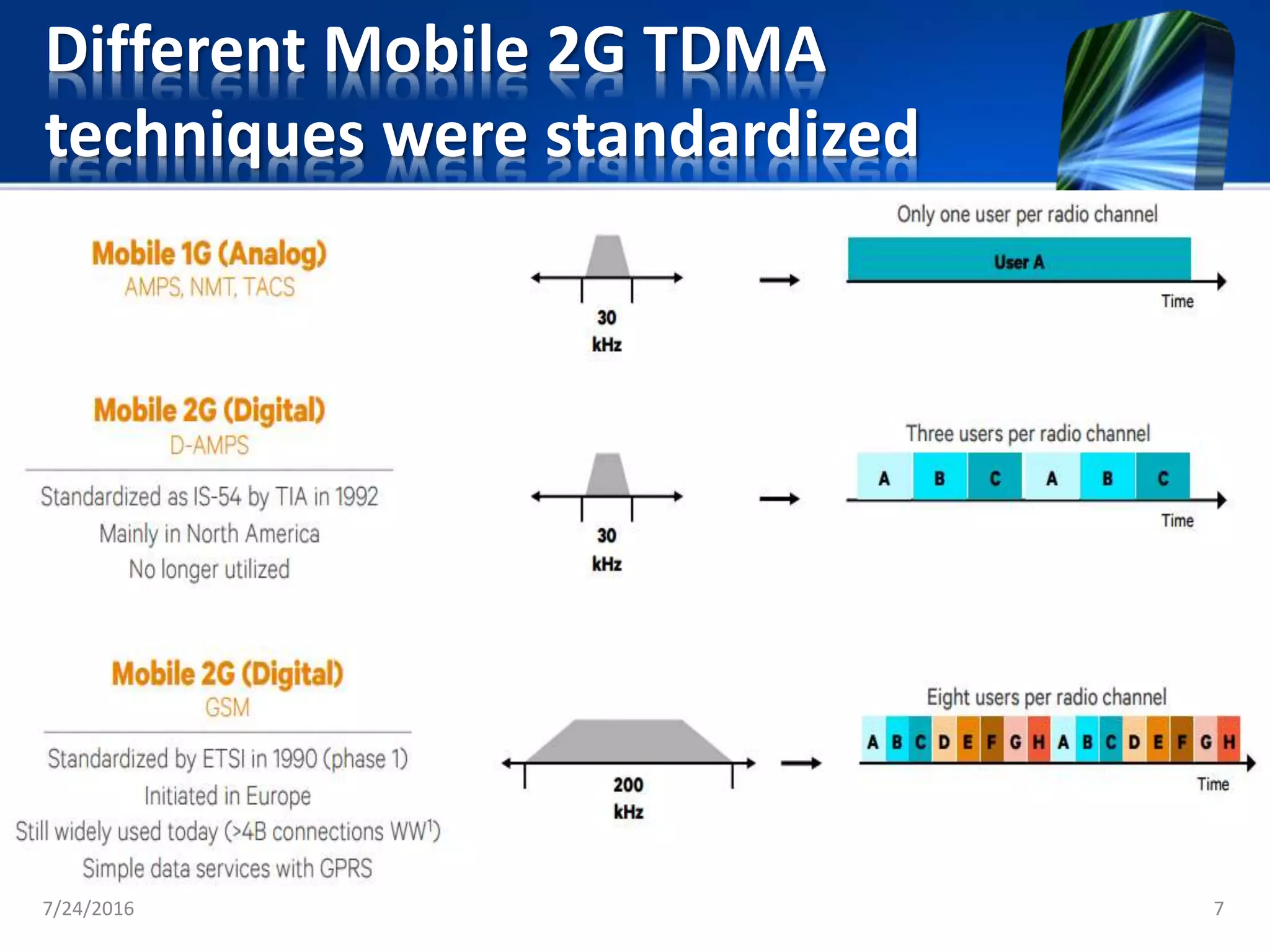
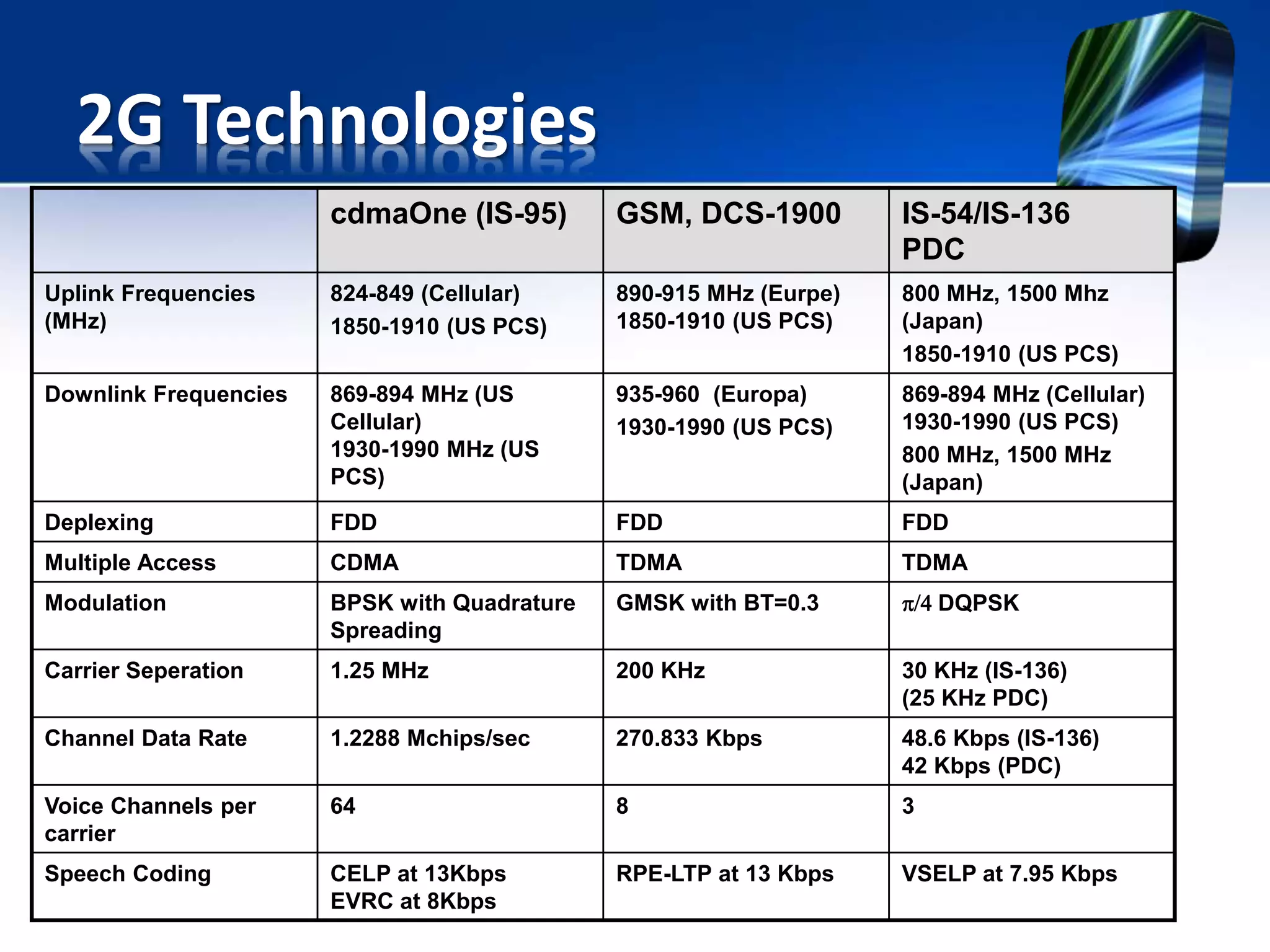
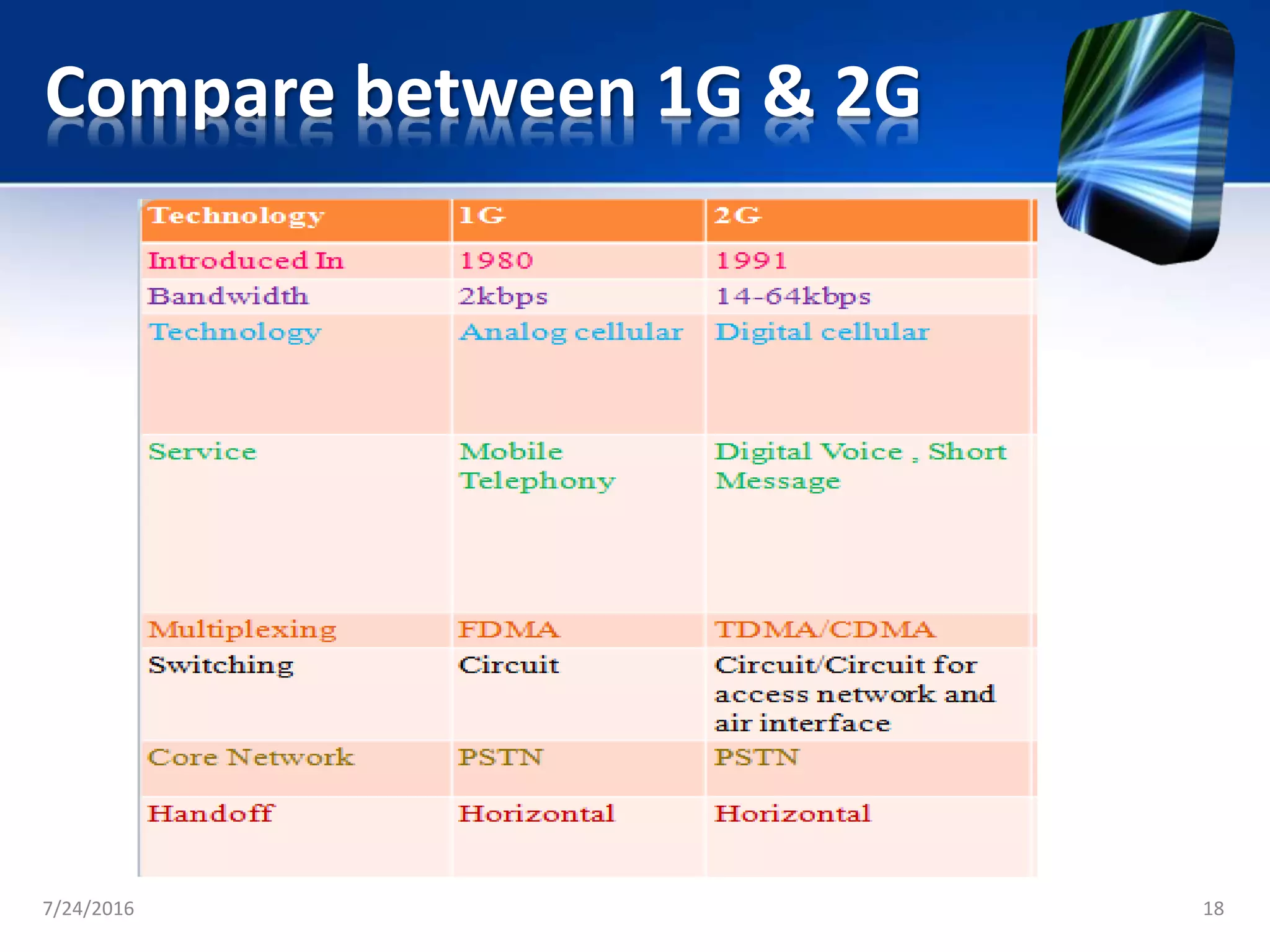
The document discusses the second generation (2G) of cellular telephone technology. 2G networks used digital signaling and enabled SMS and MMS messaging. It provided higher quality voice calls and increased network capacity compared to 1st generation analog networks. Popular 2G standards included GSM, CDMA, and TDMA-based systems. 2G networks supported data speeds up to 64 kbps and allowed basic mobile internet access through technologies like WAP. While 2G enhanced voice services and introduced data, it had limitations with bandwidth and was unable to support more complex data like videos.