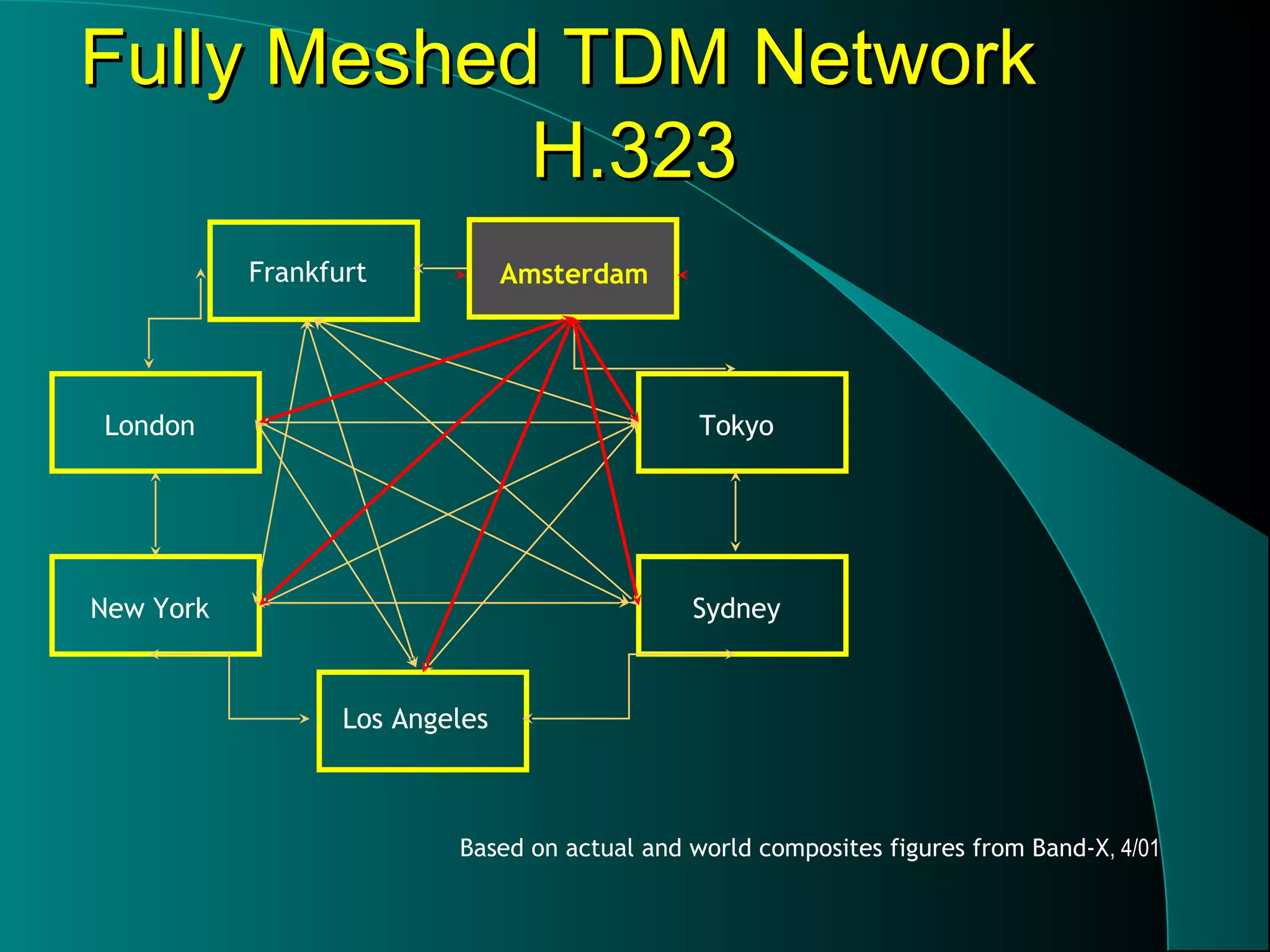
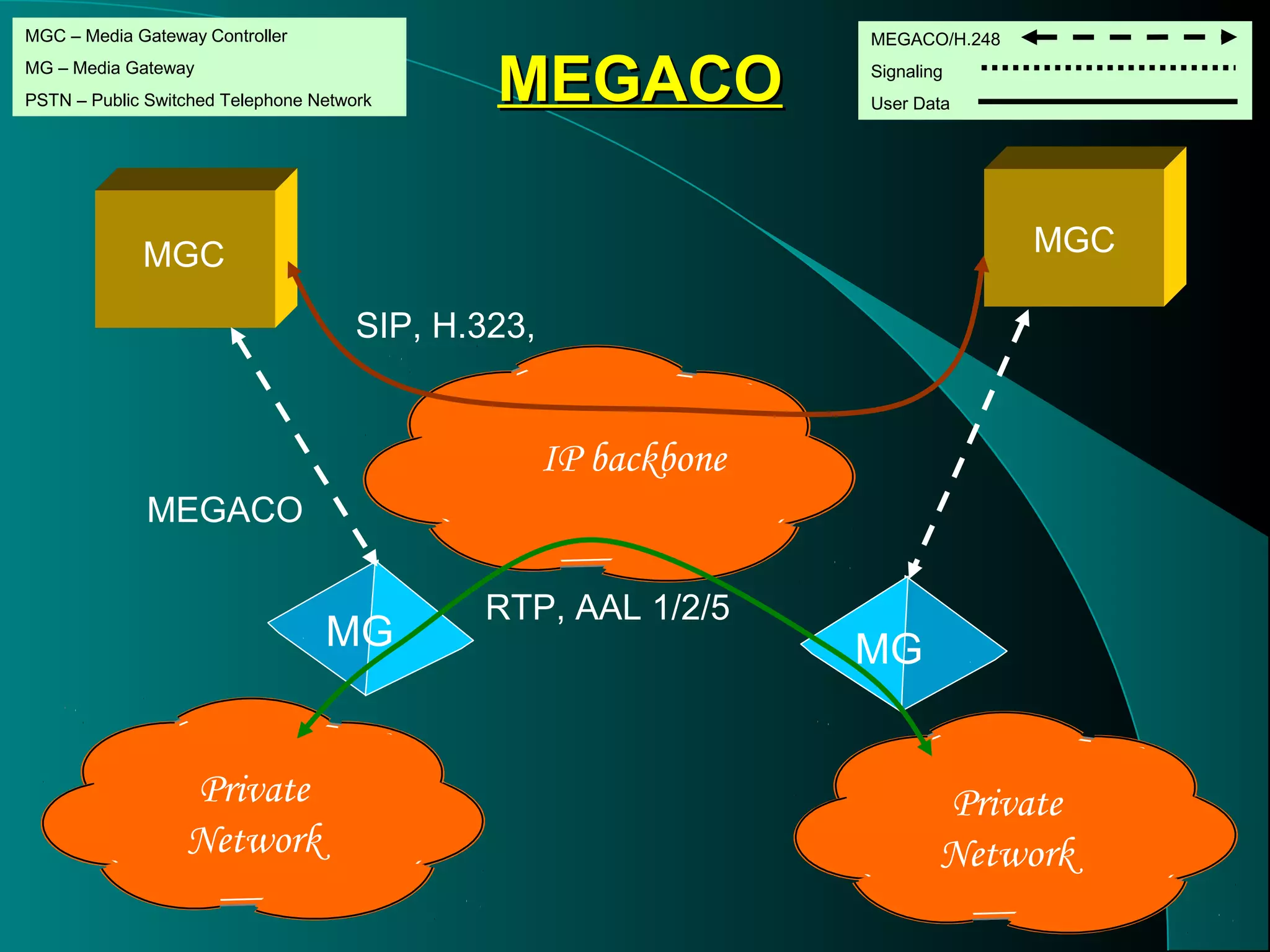
This document provides an overview of internet telephony (also known as voice over internet protocol or VoIP). It discusses how VoIP works by sending audio over the internet in real-time between computer users. The document also outlines the key factors and protocols that enable VoIP, including improvements in compression techniques, full-duplex sound cards, more powerful PCs, and protocols like SIP, RTP, and H.323. Both advantages and disadvantages of VoIP are presented, such as lower long distance costs but also potential issues with internet integration and latency.