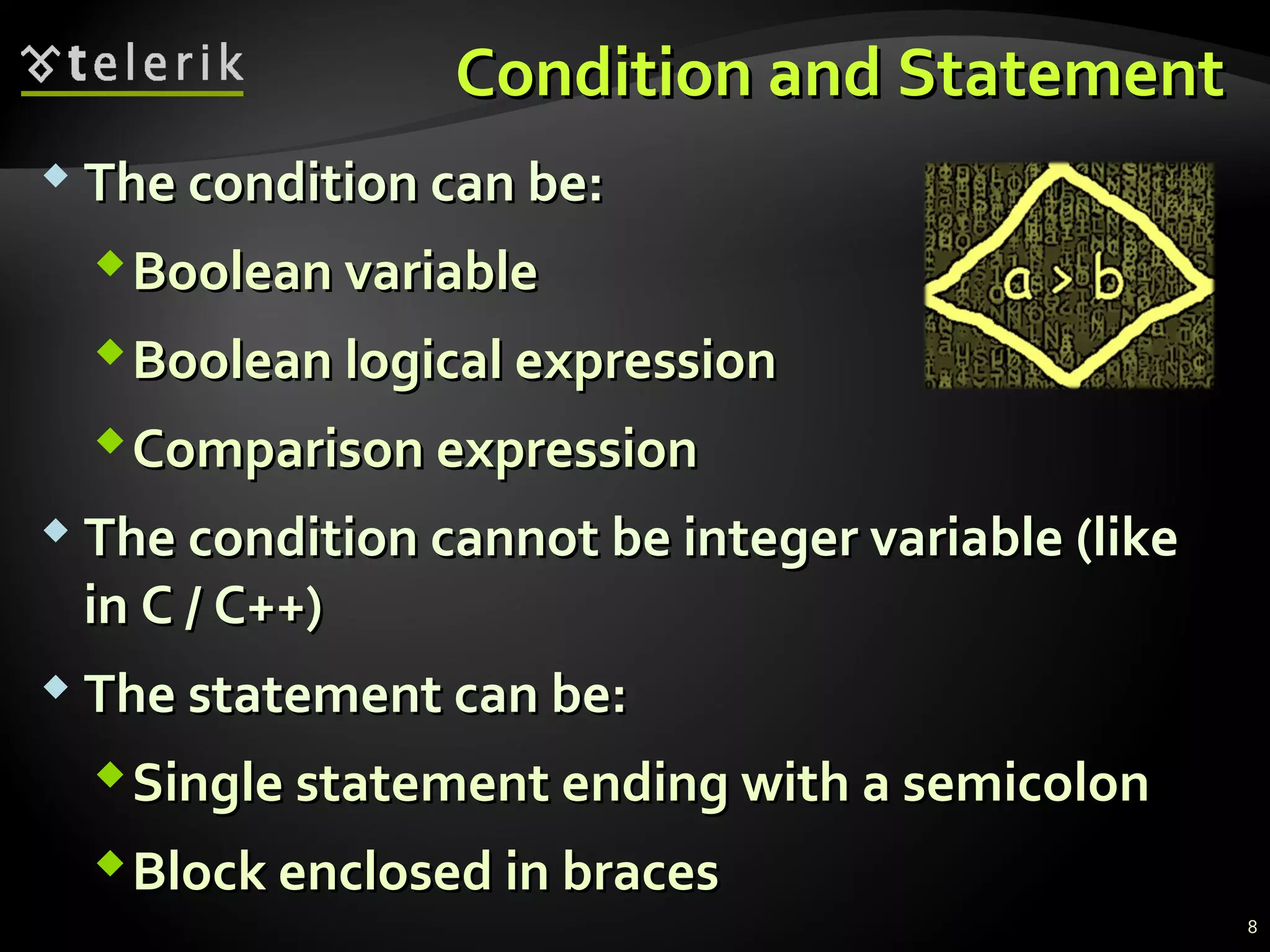
The document discusses conditional statements in C# including if, if-else, nested if statements, and switch-case statements. It covers:
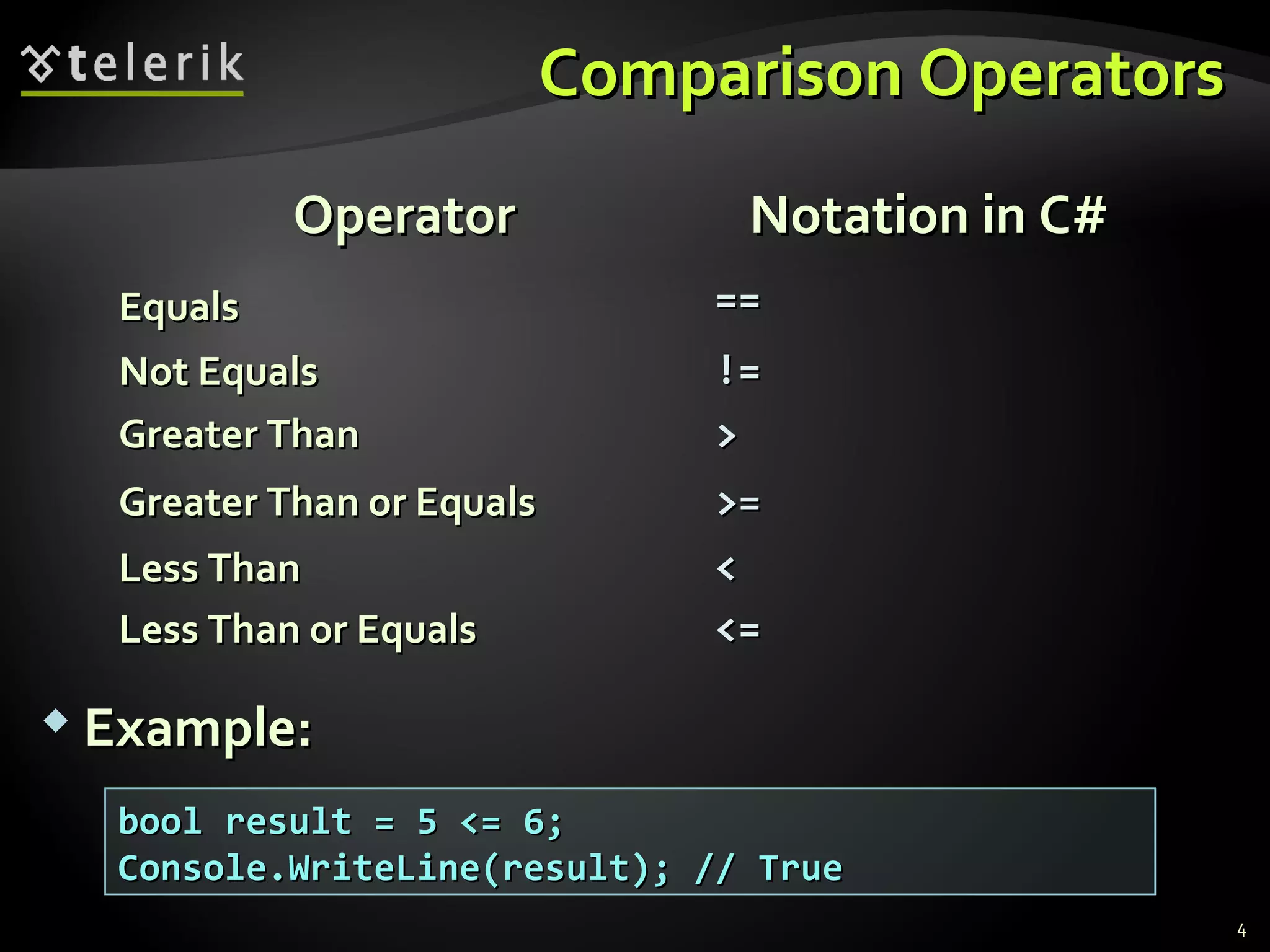
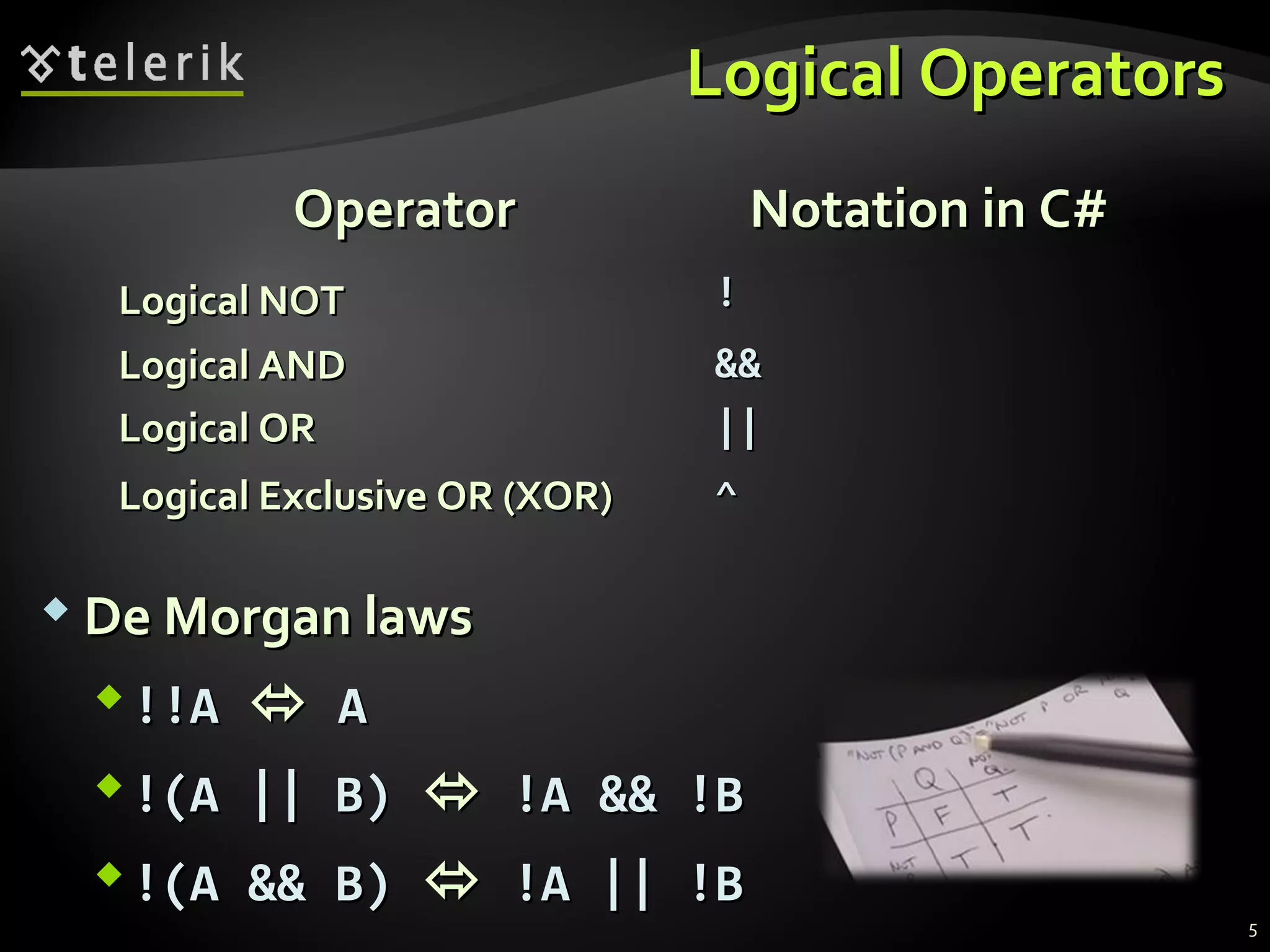
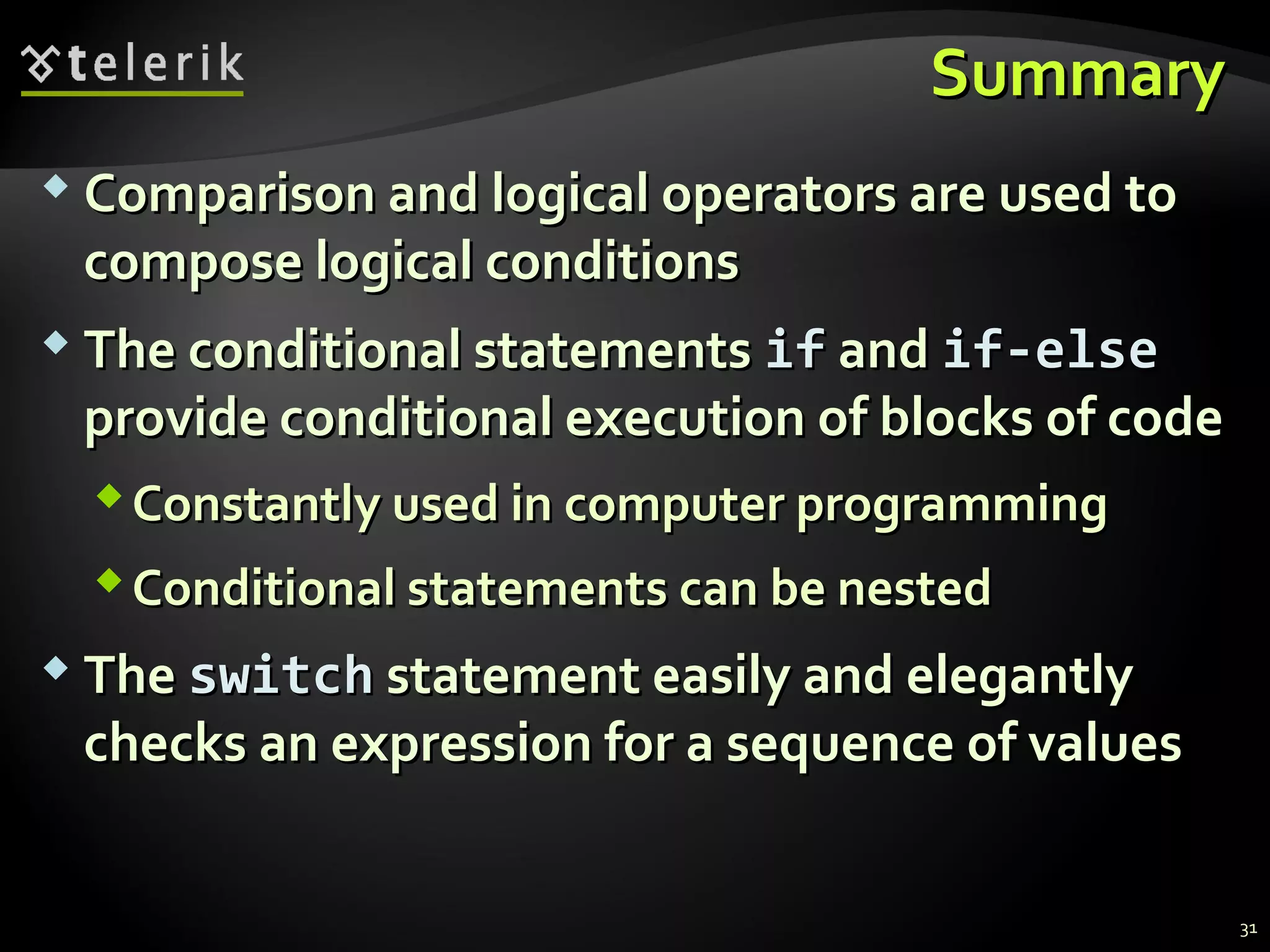
- Comparison and logical operators that are used to compose logical conditions for conditional statements
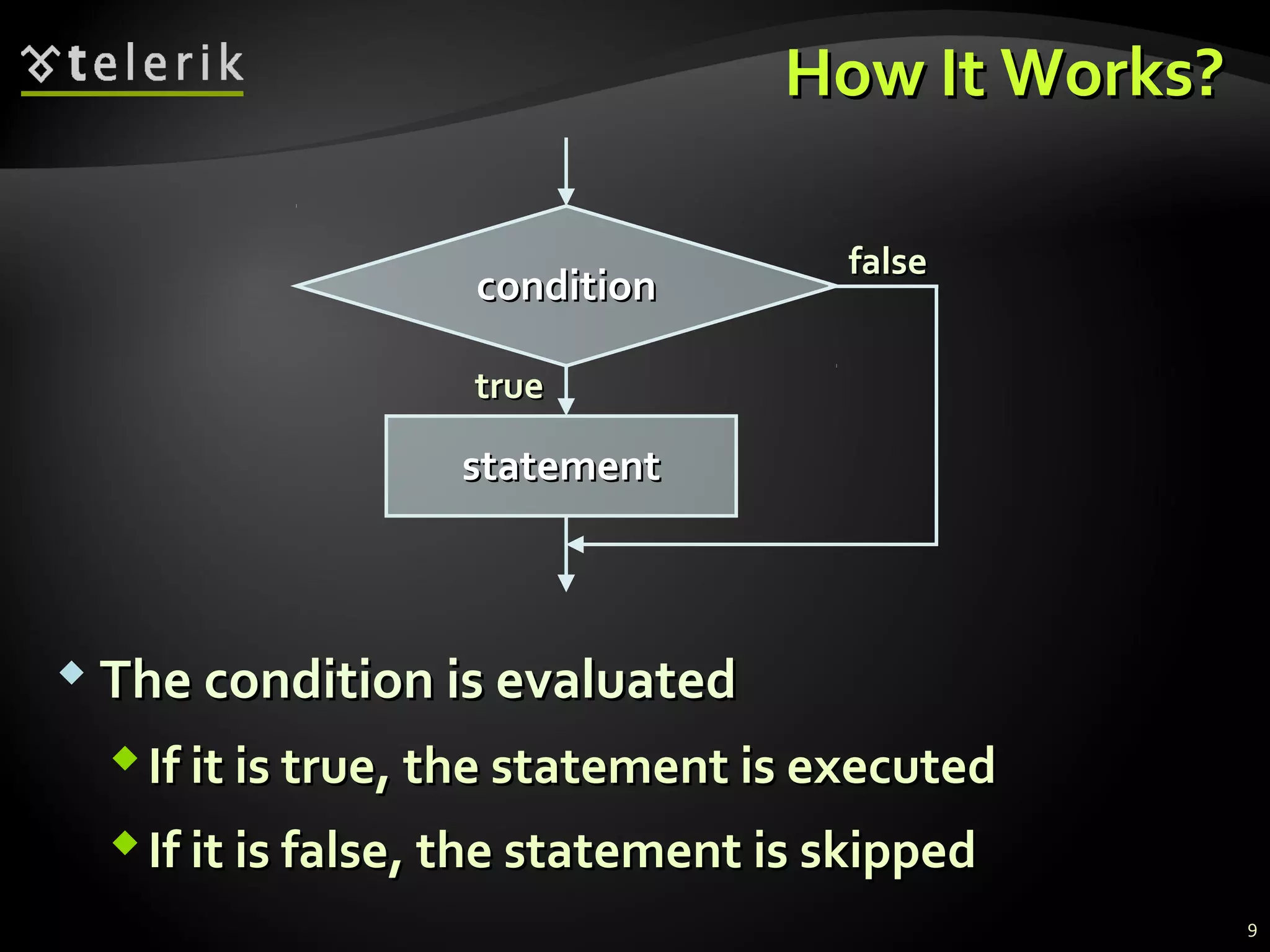
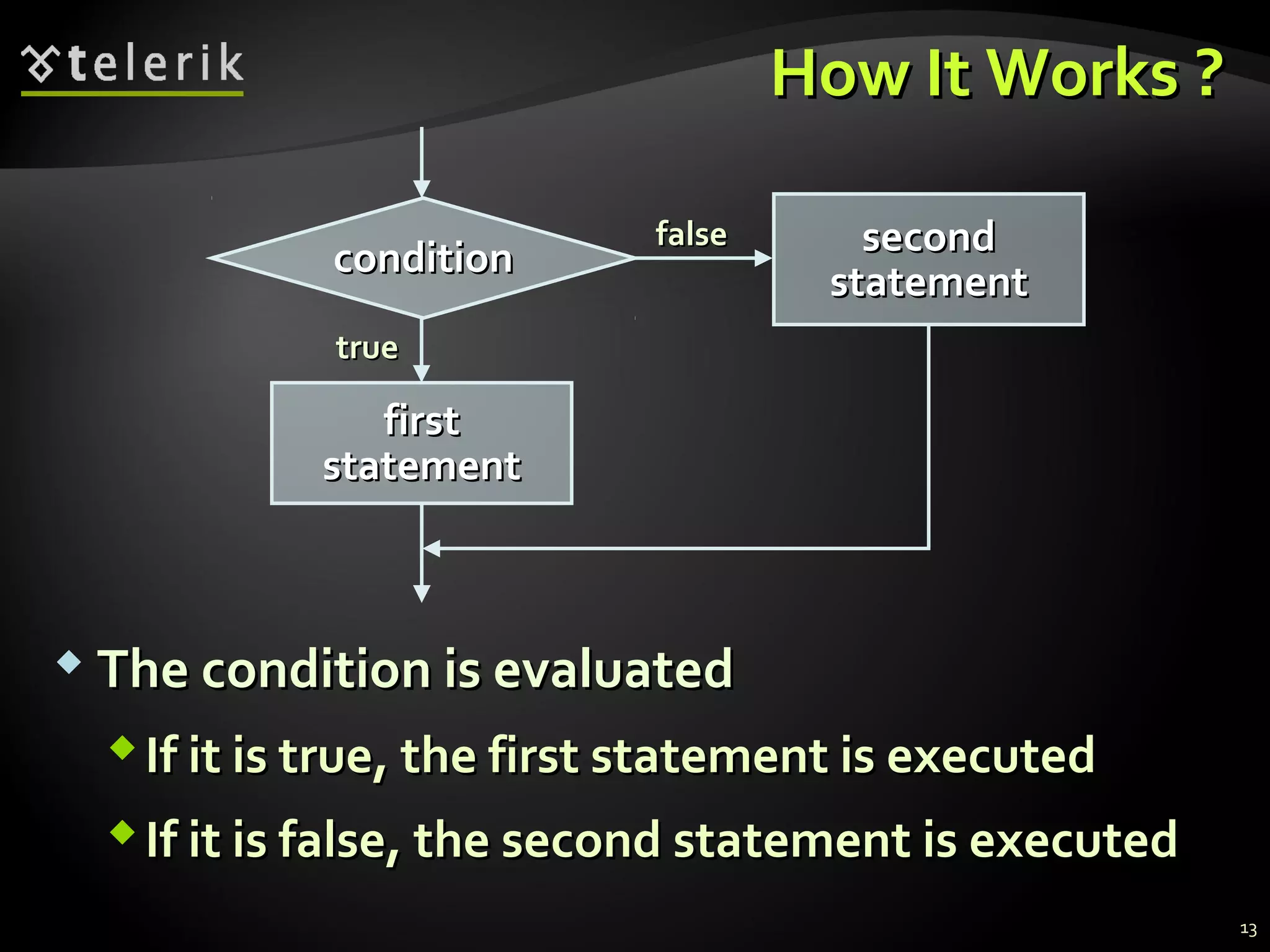
- How the if and if-else statements provide conditional execution of code blocks based on evaluating conditions
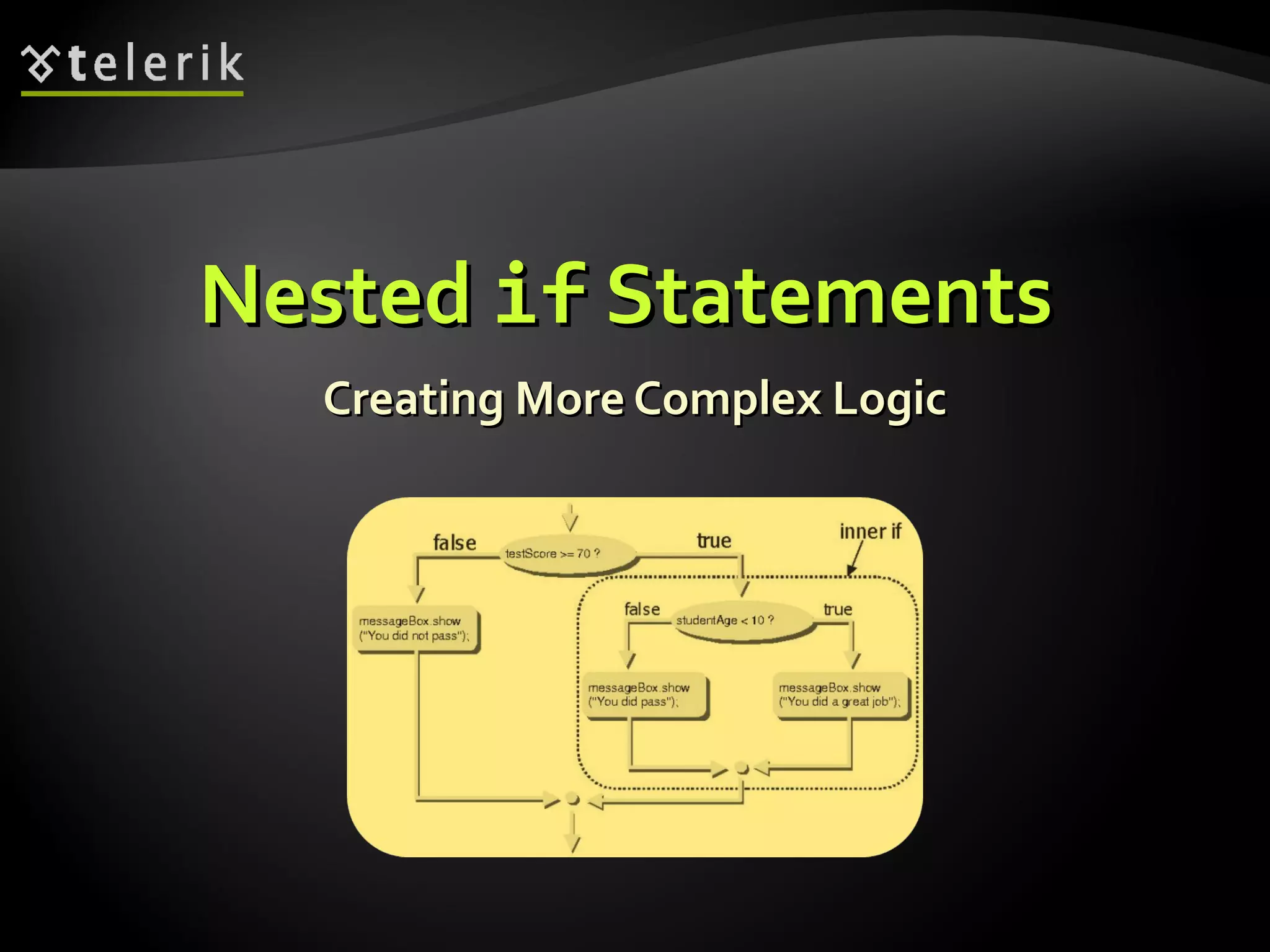
- Nested if statements allow creating more complex logic by placing if statements inside other if or else blocks
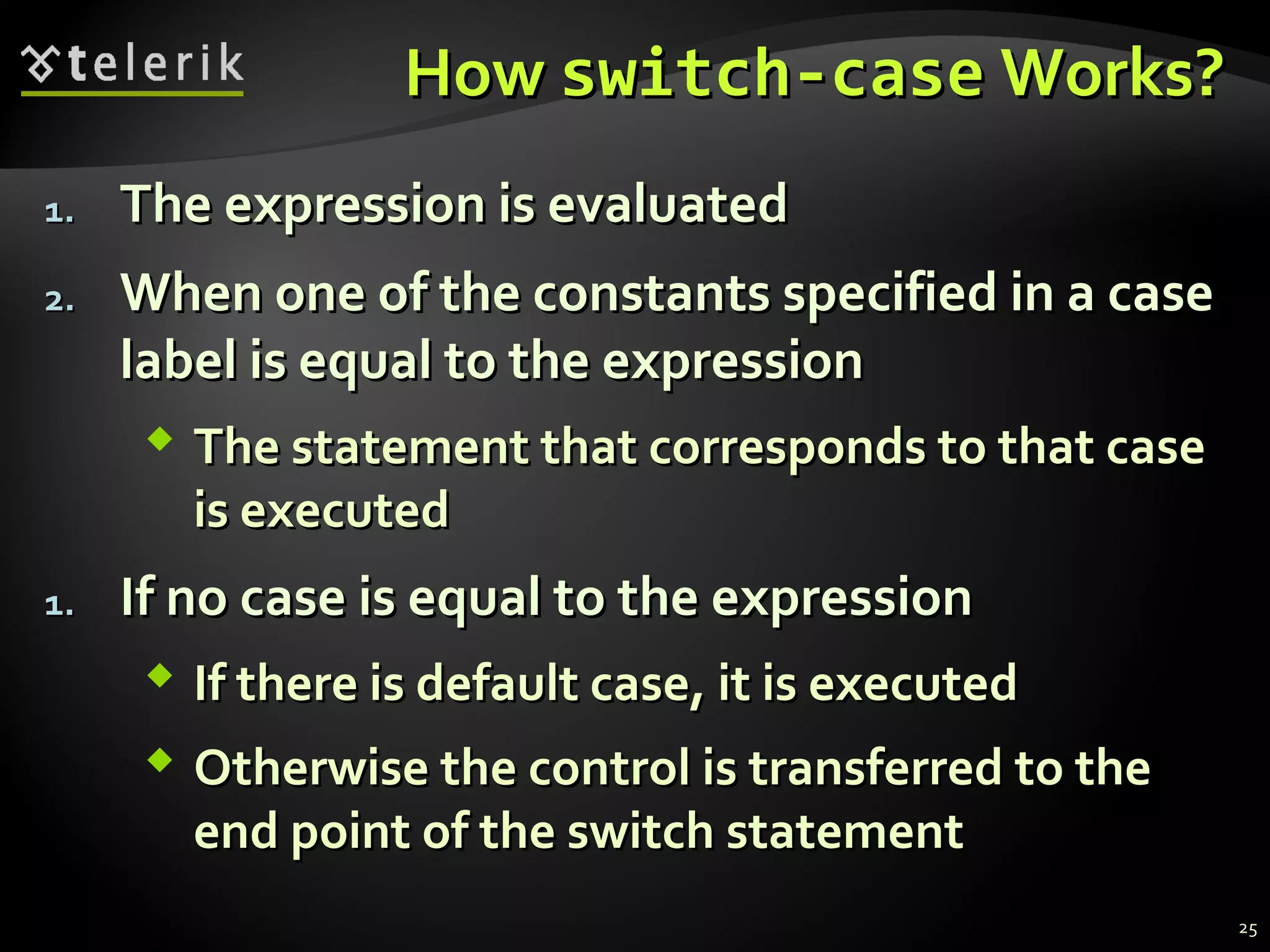
- The switch-case statement selects code for execution depending on the value of an expression, making it useful for multiple comparisons












![Multiple if-else-if-else-…Multiple if-else-if-else-…
Sometimes we need to use anotherSometimes we need to use another ifif--
construction in theconstruction in the elseelse blockblock
ThusThus else ifelse if can be used:can be used:
21
int ch = 'X';int ch = 'X';
if (ch == 'A' || ch == 'a')if (ch == 'A' || ch == 'a')
{{
Console.WriteLine("Vowel [ei]");Console.WriteLine("Vowel [ei]");
}}
else if (ch == 'E' || ch == 'e')else if (ch == 'E' || ch == 'e')
{{
Console.WriteLine("Vowel [i:]");Console.WriteLine("Vowel [i:]");
}}
else if …else if …
else …else …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-conditional-statements-110627100131-phpapp02-140828070845-phpapp01/75/05-Conditional-statements-21-2048.jpg)











![Exercises (4)Exercises (4)
10.10. Write a program that applies bonus scores to givenWrite a program that applies bonus scores to given
scores in the range [1..9]. The program reads a digitscores in the range [1..9]. The program reads a digit
as an input. If the digit is between 1 and 3, theas an input. If the digit is between 1 and 3, the
program multiplies it by 10; if it is between 4 and 6,program multiplies it by 10; if it is between 4 and 6,
multiplies it by 100; if it is between 7 and 9,multiplies it by 100; if it is between 7 and 9,
multiplies it by 1000. If it is zero or if the value is notmultiplies it by 1000. If it is zero or if the value is not
a digit, the program must report an error.a digit, the program must report an error.
Use aUse a switchswitch statement and at the end print thestatement and at the end print the
calculated new value in the console.calculated new value in the console.
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-conditional-statements-110627100131-phpapp02-140828070845-phpapp01/75/05-Conditional-statements-36-2048.jpg)
![Exercises (5)Exercises (5)
11.11. * Write a program that converts a number in the* Write a program that converts a number in the
range [0...999] to a text corresponding to itsrange [0...999] to a text corresponding to its
English pronunciation. Examples:English pronunciation. Examples:
00 ""ZeroZero""
273273 "Two hundred seventy three""Two hundred seventy three"
400400 "Four hundred""Four hundred"
501501 ""Five hundred and oneFive hundred and one""
711711 "Severn hundred and eleven""Severn hundred and eleven"
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-conditional-statements-110627100131-phpapp02-140828070845-phpapp01/75/05-Conditional-statements-37-2048.jpg)