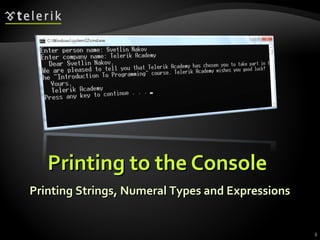
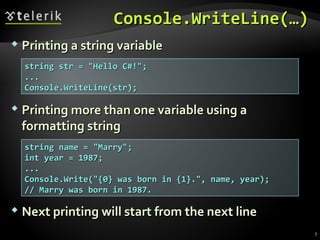
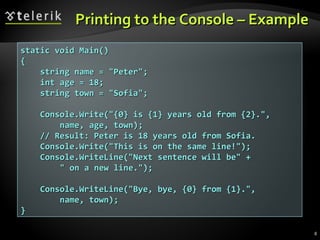
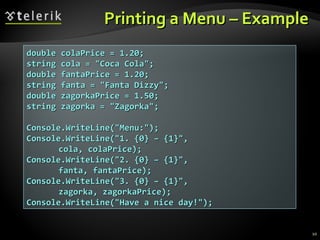
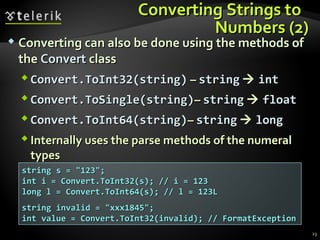
The document discusses console input and output in C#. It describes how to print to the console using Console.Write and Console.WriteLine, and how to read from the console using Console.Read, Console.ReadLine, and parsing strings to numeric types. Examples are provided for printing text with variables, reading names from the user, and converting strings to integers to perform calculations from user input.









![Console.Read()Console.Read()
Gets a single character from the console (afterGets a single character from the console (after
[Enter] is pressed)[Enter] is pressed)
Returns a result of typeReturns a result of type intint
ReturnsReturns -1-1 if there aren’t more symbolsif there aren’t more symbols
To get the actually read character weTo get the actually read character we
need to cast it toneed to cast it to charchar
int i = Console.Read();int i = Console.Read();
char ch = (char) i; // Cast the int to charchar ch = (char) i; // Cast the int to char
// Gets the code of the entered symbol// Gets the code of the entered symbol
Console.WriteLine("The code of '{0}' is {1}.", ch, i);Console.WriteLine("The code of '{0}' is {1}.", ch, i);
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-console-input-output-110627100151-phpapp01-140828070700-phpapp02/85/04-Console-input-output-14-320.jpg)

![Console.ReadKey()Console.ReadKey()
Waits until a combination of keys is pressedWaits until a combination of keys is pressed
Reads a single character from console or aReads a single character from console or a
combination of keyscombination of keys
Returns a result of typeReturns a result of type ConsoleKeyInfoConsoleKeyInfo
KeyCharKeyChar – holds the entered character– holds the entered character
ModifiersModifiers – holds the state of [Ctrl], [Alt], …– holds the state of [Ctrl], [Alt], …
ConsoleKeyInfo key = Console.ReadKey();ConsoleKeyInfo key = Console.ReadKey();
Console.WriteLine();Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Character entered: " + key.KeyChar);Console.WriteLine("Character entered: " + key.KeyChar);
Console.WriteLine("Special keys: " + key.Modifiers);Console.WriteLine("Special keys: " + key.Modifiers);
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-console-input-output-110627100151-phpapp01-140828070700-phpapp02/85/04-Console-input-output-16-320.jpg)


















![Exercises (3)Exercises (3)
7.7. Write a program that gets a numberWrite a program that gets a number nn and after thatand after that
gets moregets more nn numbers and calculates and prints theirnumbers and calculates and prints their
sum.sum.
8.8. Write a program that reads an integer numberWrite a program that reads an integer number nn
from the console and prints all the numbers in thefrom the console and prints all the numbers in the
interval [interval [11....nn], each on a single line.], each on a single line.
9.9. Write a program to print the first 100 members ofWrite a program to print the first 100 members of
the sequence of Fibonaccithe sequence of Fibonacci: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21,: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21,
34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, …34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, …
10.10. Write a program to calculate the sum (with accuracyWrite a program to calculate the sum (with accuracy
of 0.001): 1 + 1/2 - 1/3 + 1/4 - 1/5 + ...of 0.001): 1 + 1/2 - 1/3 + 1/4 - 1/5 + ...
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04-console-input-output-110627100151-phpapp01-140828070700-phpapp02/85/04-Console-input-output-36-320.jpg)