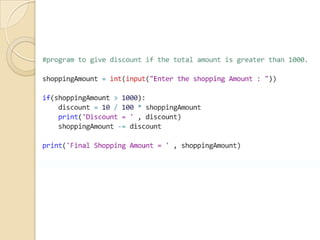
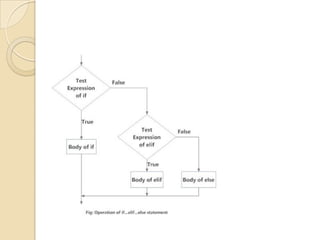
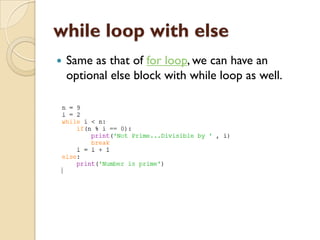
The document discusses various Python flow control statements including if/else, for loops, while loops, break and continue. It provides examples of using if/else statements for decision making and checking conditions. It also demonstrates how to use for and while loops for iteration, including using the range function. It explains how break and continue can be used to terminate or skip iterations. Finally, it briefly mentions pass, for, while loops with else blocks, and nested loops.