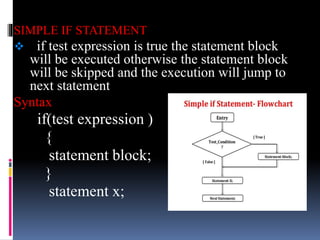
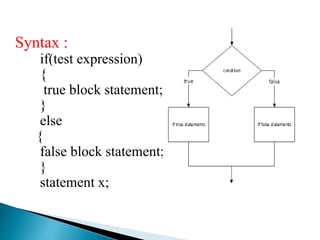
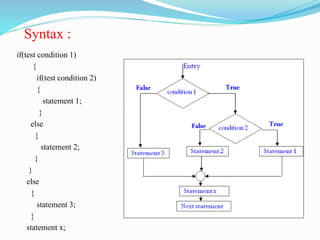
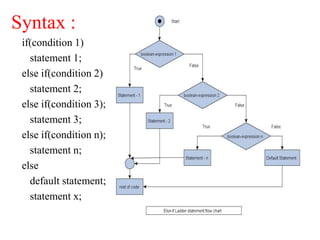
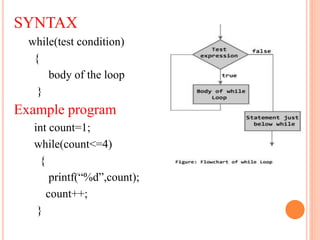
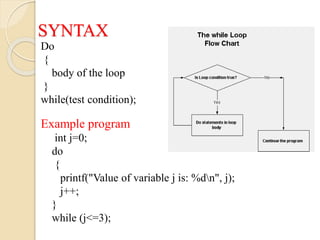
The document discusses different types of decision making and looping statements in C programming. It describes simple if, if-else, nested if-else, and else-if ladder statements for decision making. It also covers while, do-while, and for loops for iterative execution. Examples are provided for each statement type to illustrate their syntax and usage.