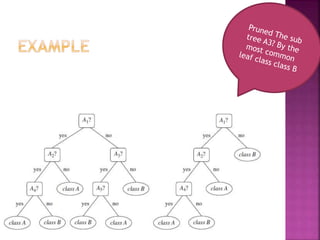
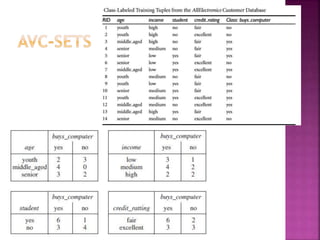
Tree pruning removes parts of a decision tree that overfit the training data due to noise or outliers, making the tree smaller and less complex. There are two pruning strategies: postpruning removes subtrees after full tree growth, while prepruning stops growing branches when information becomes unreliable. Decision tree algorithms are efficient for small datasets but have performance issues for very large real-world datasets that may not fit in memory.