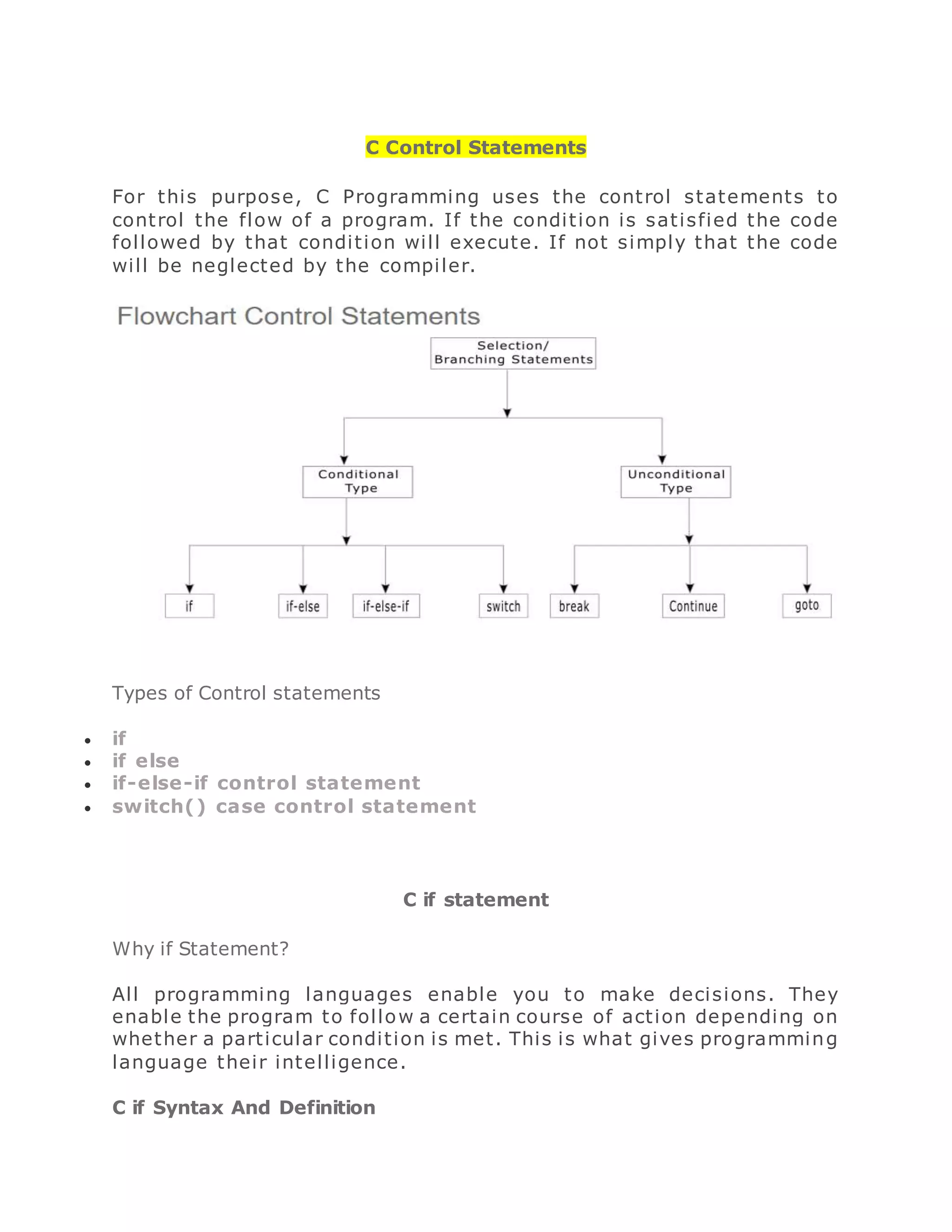
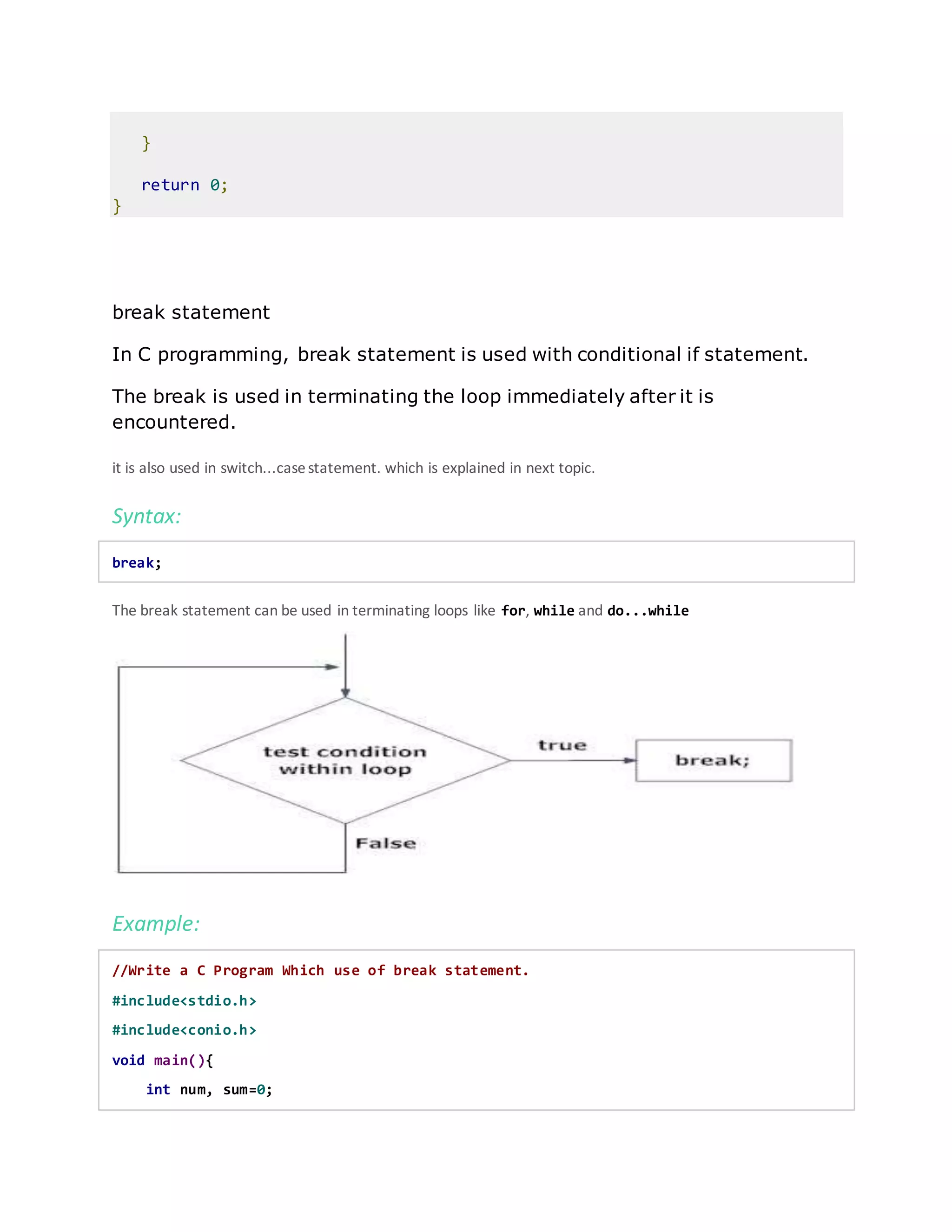
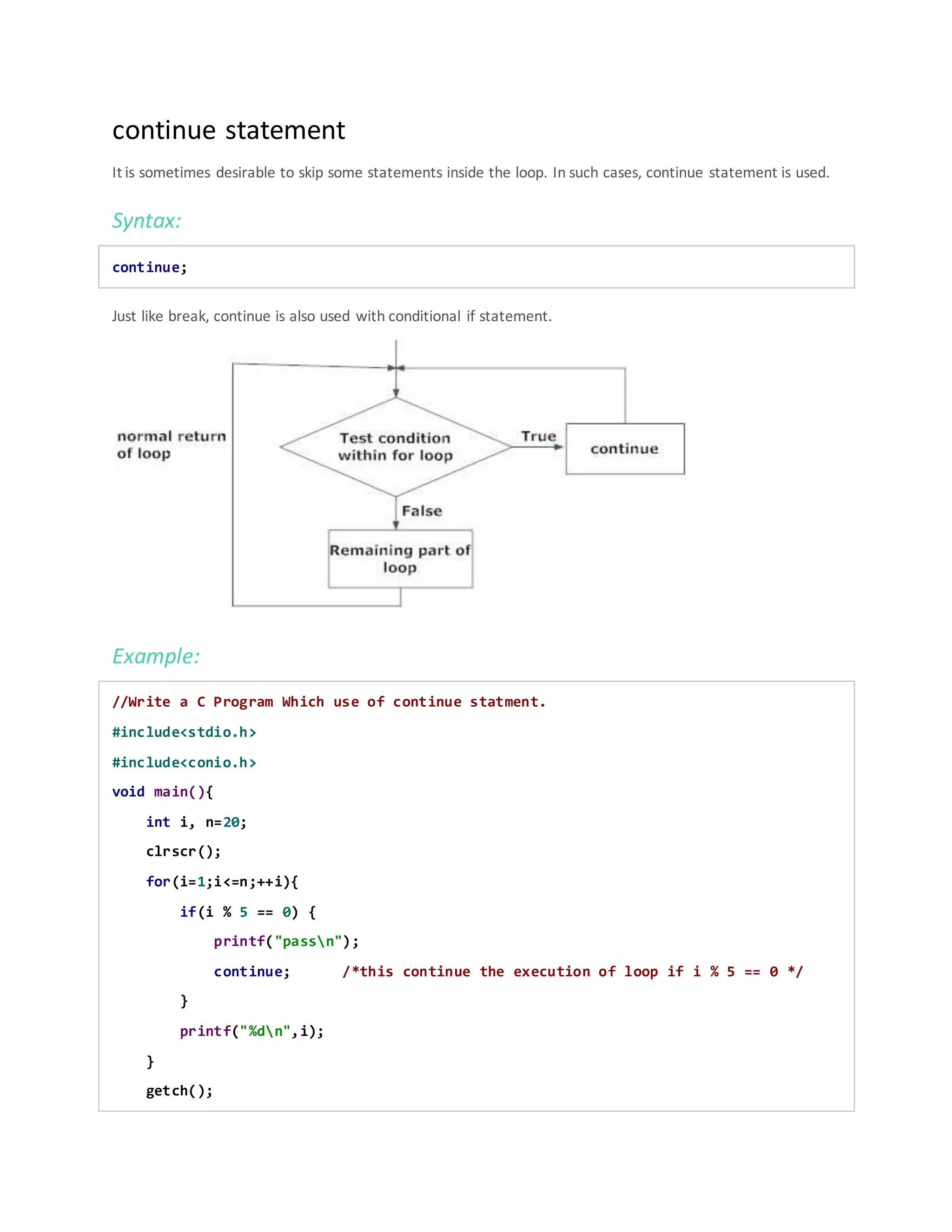
The document discusses various control statements in C programming such as if, if-else, nested if, switch case, break, continue, and goto statements. It provides the syntax and examples of using each statement. Key control statements covered include:
- if statement which executes code if a condition is true
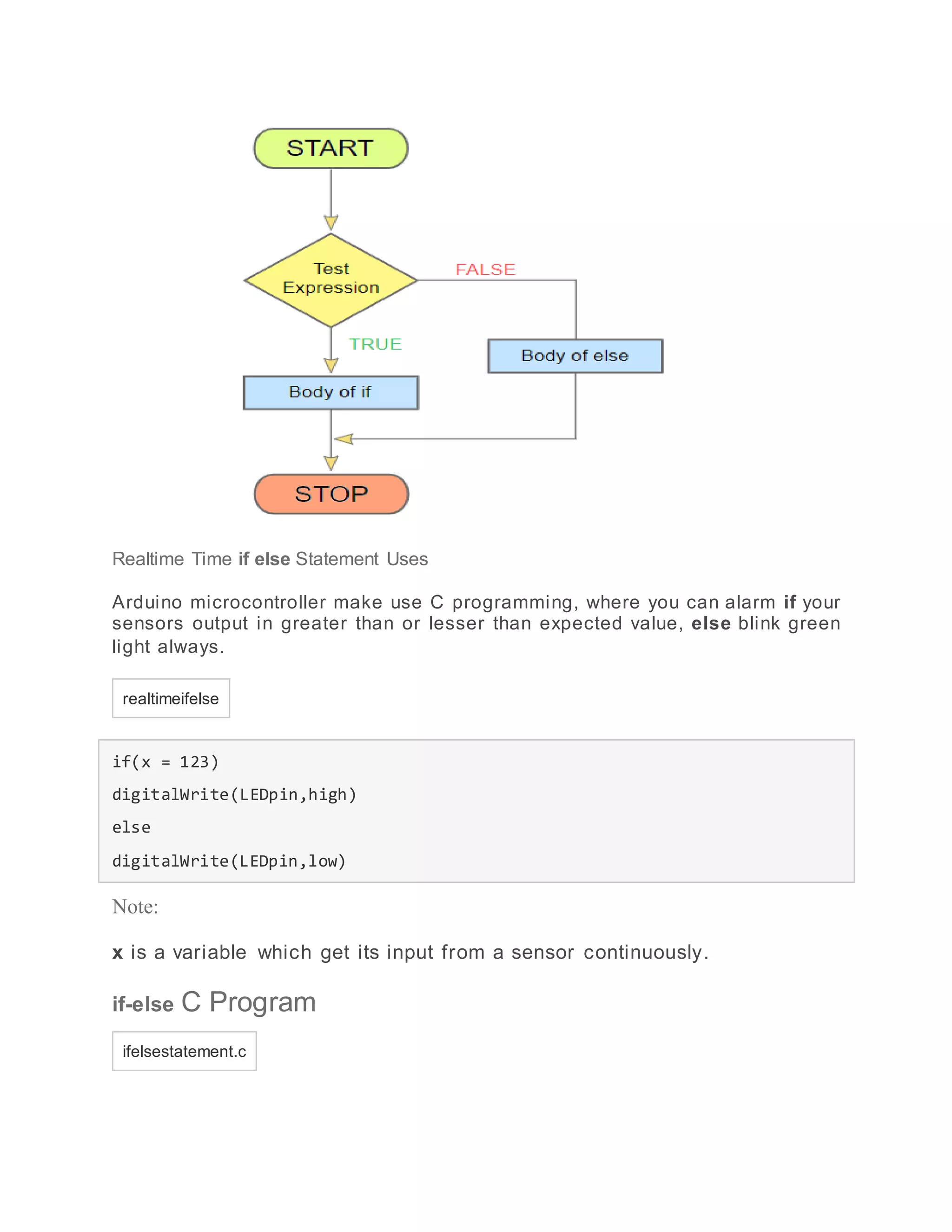
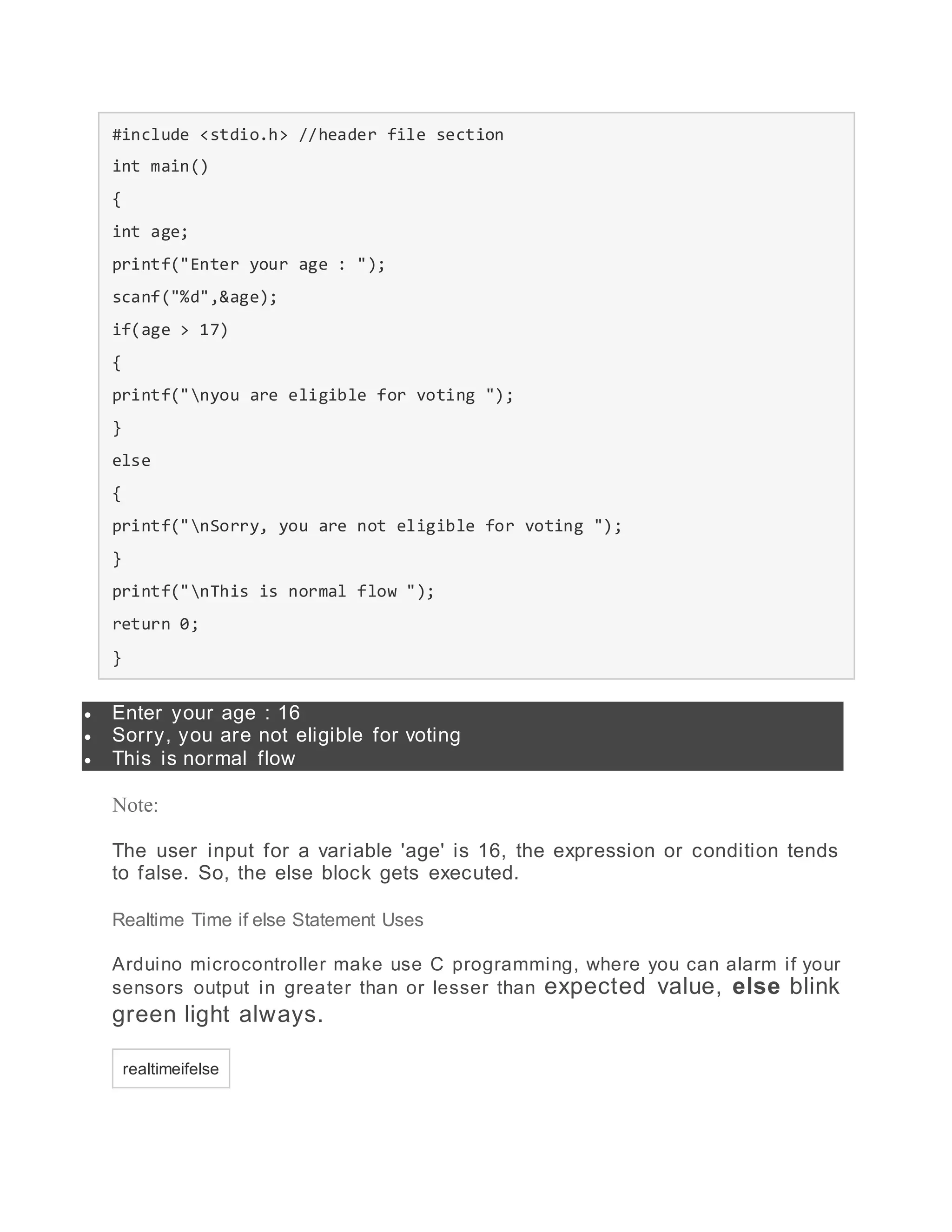
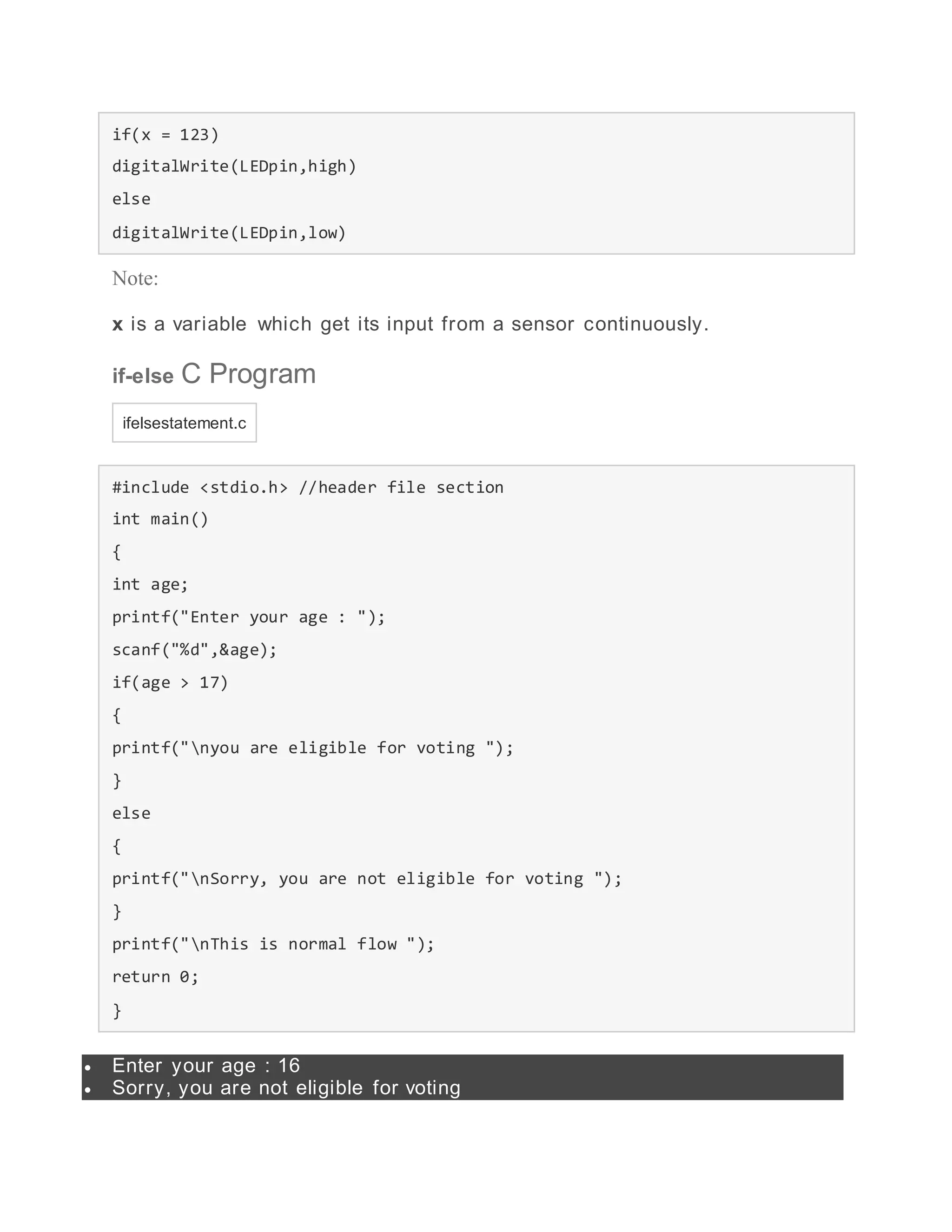
- if-else statement which allows executing one code block if a condition is true and another if it is false
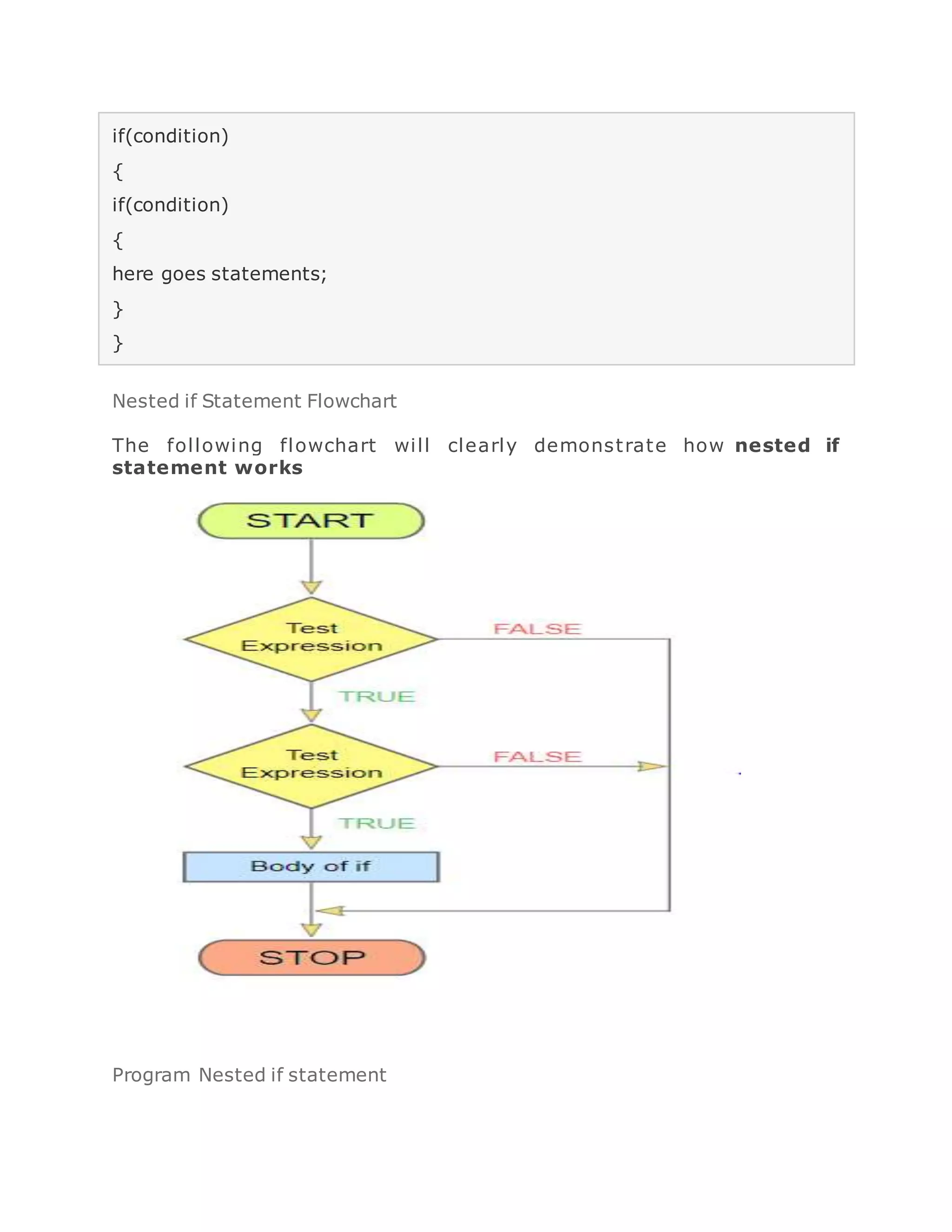
- nested if statements which allow logical conditions to be checked within other if blocks
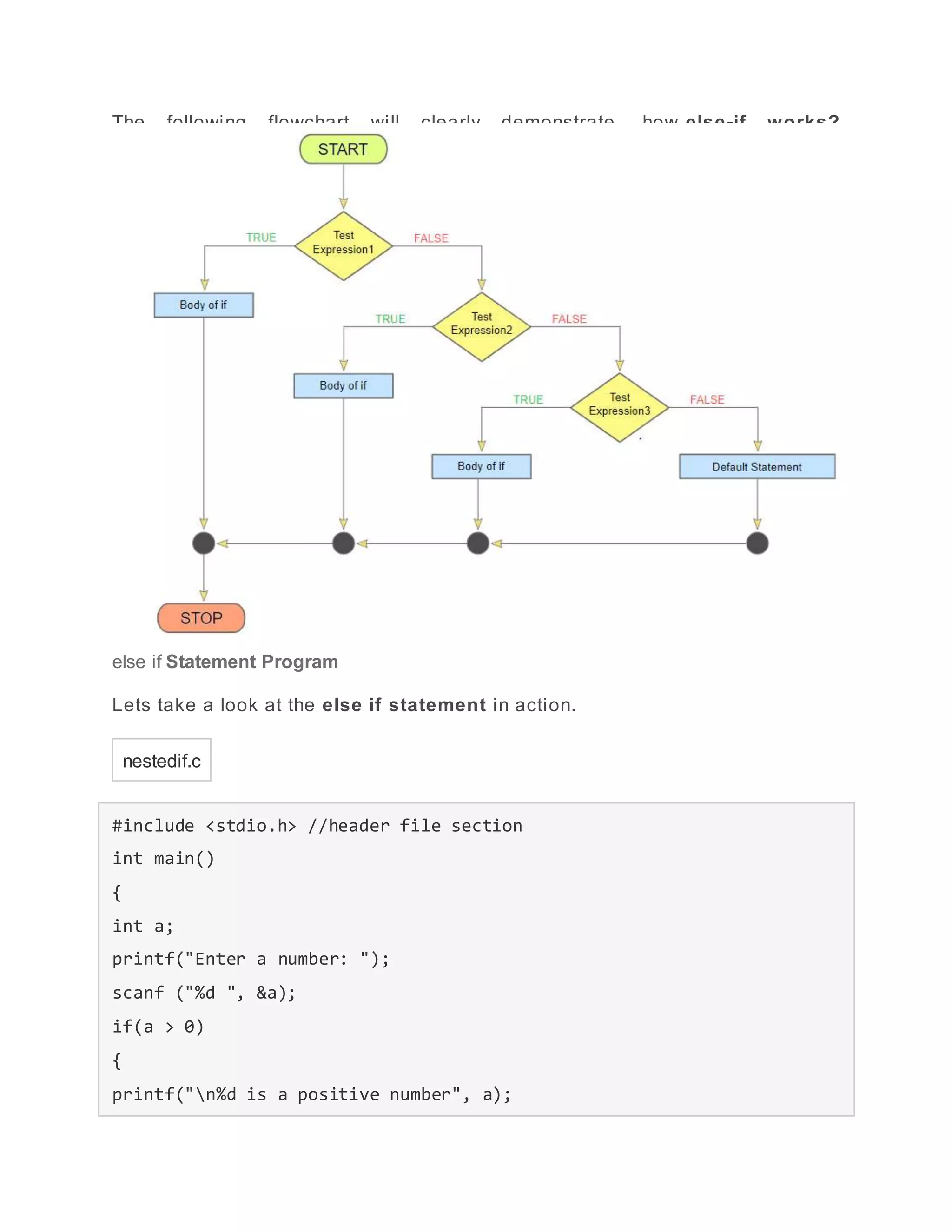
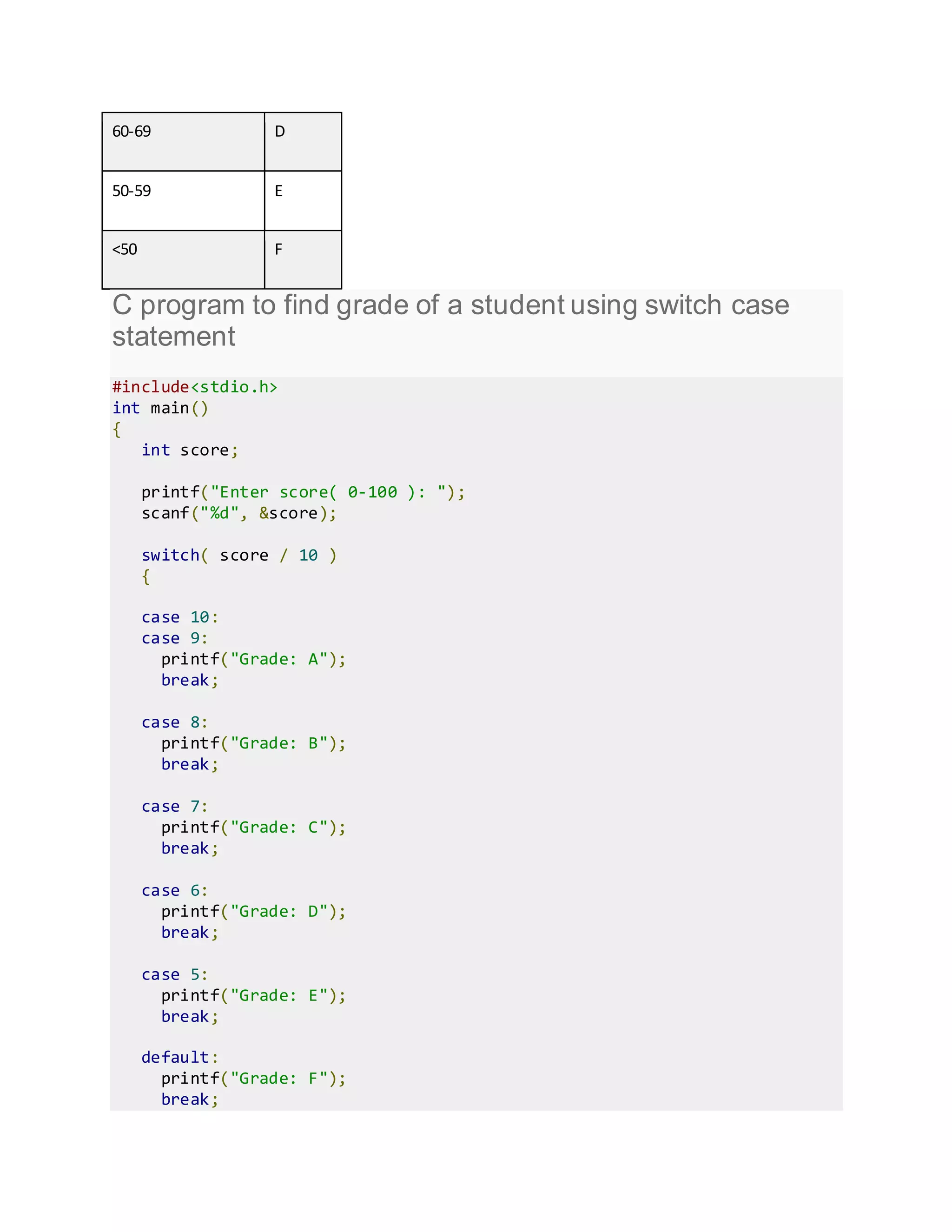
- switch case statement which allows a variable to be tested against multiple values and execute the corresponding code block