This document discusses different types of fuels and their properties. It covers solid, liquid, and gaseous fuels. For each fuel type, it lists relevant properties like heating value, composition, viscosity, etc. It also discusses concepts like stoichiometry, excess air, flue gas composition and volume, heating values and calculations to determine air required and flue gas produced when combusting different fuels.





![BASIS OF ANALYSIS
AS RECEIVED
Ultimate C +H +O +N +S +A +M =100
Proximate VM +FC +M +A = 100
AIR DRY [100C/(100-Ma)]
DRY ASH FREE [100C/(100-M-A)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04fuelscombustioncalculation09-140331080648-phpapp01/85/04-fuels-combustion-calculation09-8-320.jpg)
![II-1 CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Combustion
C + O2 = CO2 + 32,790 kJ/kg of carbon,
Heat of formation at 25C is 393.7 kJ/mol [Perry p-2-188]
mCn Hm + (n +m/4)O2 = nCO2 + m/2 H2O + Q
S + O2 = SO2 + 9260 kJ/kg of sulfur
Calcination
CaCO3 = CaO + CO2 – 1830 kJ/kg of CaCO3gCO3
= MgO + CO2 – 1183 kJ/kg of MgCO3.
Sulfation
CaO + SO2 + 1/2 O2 = CaSO4 + 15141 kJ/kg S.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04fuelscombustioncalculation09-140331080648-phpapp01/85/04-fuels-combustion-calculation09-10-320.jpg)

![Limestone required for S capture
Limestone required for
unit mass of fuel
[R = Calcium to Sulfur molar
ratio]
If appreciable amount
of CaO is present in
coal ash replace R
with R’
R
X
S
Lq
caco332
100
S
X
RR cao
56
32
'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04fuelscombustioncalculation09-140331080648-phpapp01/85/04-fuels-combustion-calculation09-13-320.jpg)
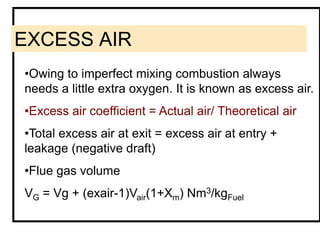
![AIR REQUIRED/mass fuel burnt
Theoretical dry air requirement
Mda= [11.53 C + 34.34 (H – O/8) + 4.34 S+ A.S]
kg/kg coal
where A = 2.38 for S-capture;
= 0 for no S-capture
Actual dry air required
Tda = Excess air Coeff. X Mda kg/kg
Actual wet air required
Mwa = Tda (1 + Xm).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04fuelscombustioncalculation09-140331080648-phpapp01/85/04-fuels-combustion-calculation09-15-320.jpg)

![SOLID WASTE PRODUCED
Solid residues = Ash + Spent sorbents
Spent sorbents = CaSO4+CaO+MgO+inert
Wa = [Lw + ASH + (1 – Ec) – Xcao],
Gas product = CO2+H2O+N2+O2+SO2+Fly ash
inert
mgcosorcaco
sor LqX
LqXSELqX
E
S
Lw
84
40
32100
56
32
136
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/04fuelscombustioncalculation09-140331080648-phpapp01/85/04-fuels-combustion-calculation09-17-320.jpg)