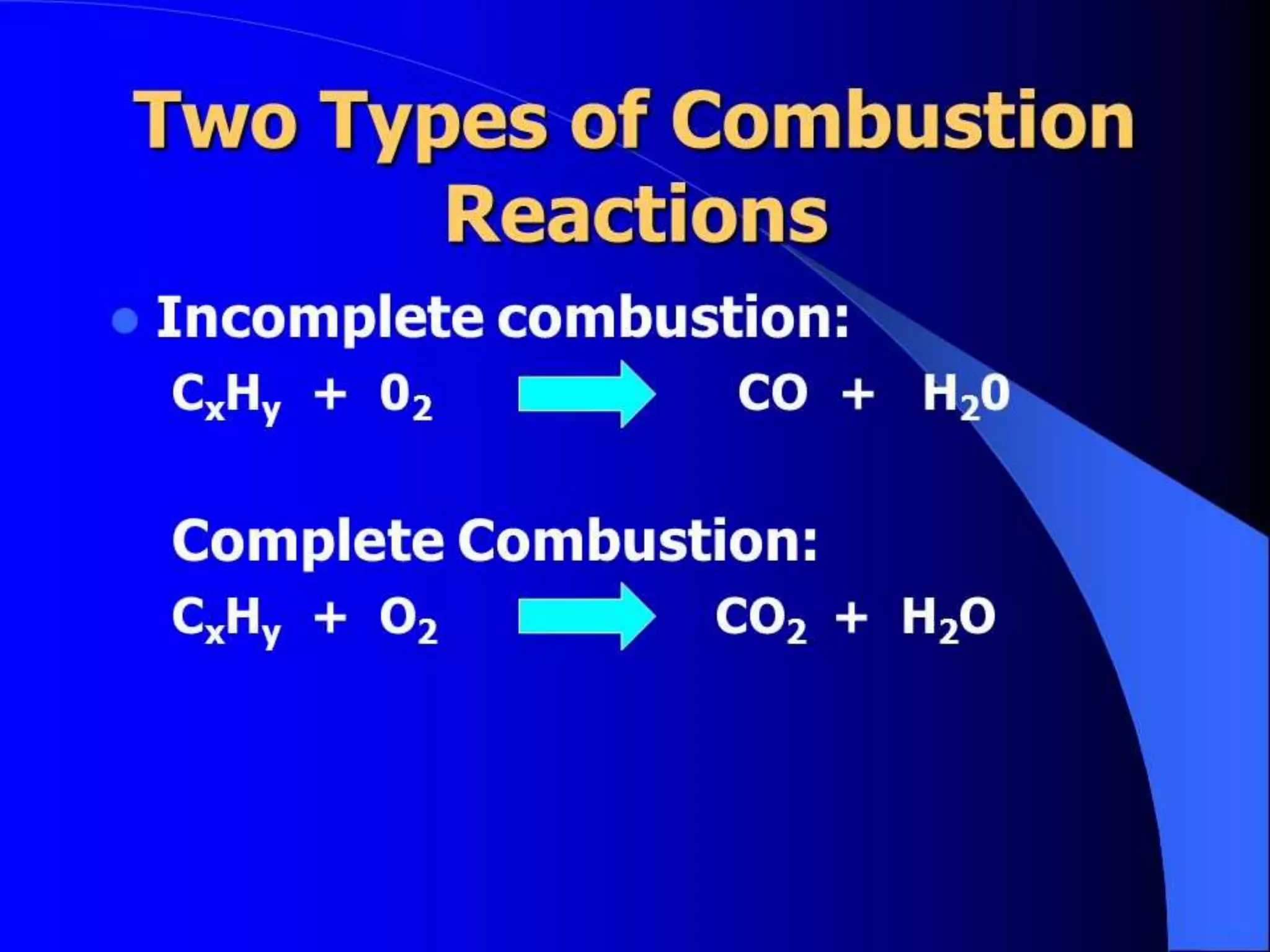
The document defines combustion as a chemical process where a substance reacts with oxygen in air to produce heat and light. There are several types of combustion described, including spontaneous, rapid, complete, and incomplete combustion as well as explosions. Rapid combustion occurs when a substance burns quickly, producing heat and flame, often with the introduction of external heat. Incomplete combustion results in only partial burning of a fuel due to a lack of oxygen or low temperature, producing carbon monoxide. For combustion to occur, there must be a combustible substance, a supply of oxygen (air), and enough heat to raise the substance to its ignition temperature.