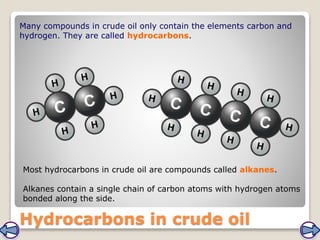
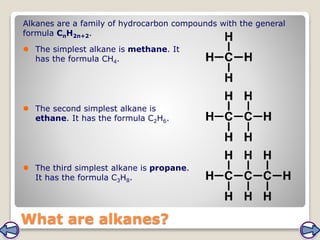
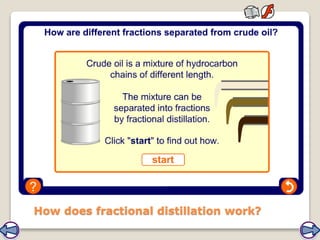
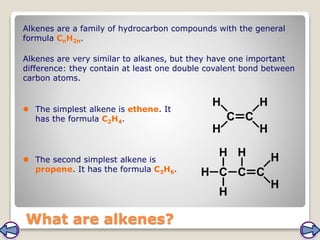
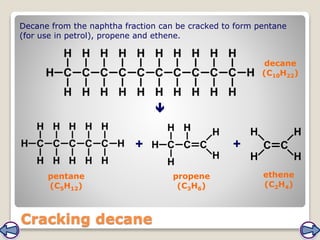
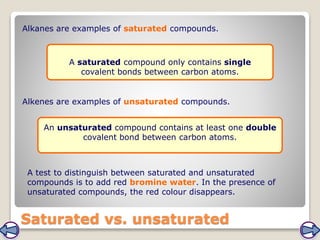
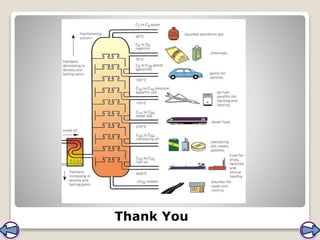
Crude oil, a vital fossil fuel, is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons used in fuel production, heating, and manufacturing plastics. Its formation involved ancient marine organisms subjected to heat and pressure, while refining processes like fractional distillation and catalytic cracking make its compounds useful. Despite its benefits, crude oil poses environmental risks, including pollution and wildlife damage, and its future availability is uncertain.