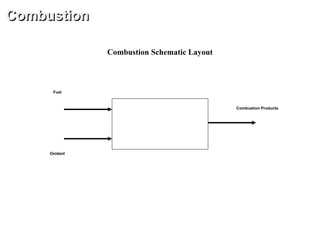
The document outlines a combustion analysis webinar aimed at engineering students and professionals, focusing on ideal combustion processes involving six different fuels (carbon, hydrogen, sulfur, coal, oil, and gas) and their reactions with air and oxygen under various conditions. Key objectives include understanding basic combustion principles, performance trends, and relevant engineering equations. The analysis includes thermodynamic properties, stoichiometric calculations, and detailed graphs illustrating combustion processes.




![Basic Conservation Equations
Continuity Equation
m = ρvA [kg/s]
Momentum Equation
F = (vm + pA) out - in [N]
Energy Equation
Q - W = ((h + v2/2 + gh)m)out - in [kW]
Basic Engineering Equations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-5-320.jpg)
![Ideal Gas State Equation
pv = RT [kJ/kg]
Perfect Gas
cp = constant [kJ/kg*K]
Kappa
χ = cp/cv [/]
For air: χ = 1.4 [/], R = 0.2867 [kJ/kg*K] and
cp = 1.004 [kJ/kg*K]
Basic Engineering Equations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-6-320.jpg)
![Combustion Engineering Equations
Combustion is ideal, complete with no heat loss and
fuel reacts with air and oxygen enriched air as the
oxidant at different stoichiometry values (stoichiometry
=> 1) and oxidant inlet temperature values.
Also,
Flame Temperature [K]
hreactants = hproducts [kJ/kg]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-7-320.jpg)
![Specific Enthalpy vs Temperature
-20,000
-10,000
0
10,000
20,000
30,000
40,000
50,000
60,000
70,000
80,000
90,000
500 800 1,100 1,400 1,700 2,000 2,300 2,600 2,900 3,200 3,500 3,800 4,100 4,400 4,700 5,000
C(S) H2 S(S) N2 O2 H2O(L) CH4 CO2 H2O SO2
Combustion
SpecificEnthalpy[kJ/kg]
Temperature [K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-9-320.jpg)
![Combustion h - T Diagram
SpecificEnthalpy--h[kJ/kg]
Temperature -- T [K]
Reactants
Products
TflameTreference
Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-10-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Oxidant Composition
Fuel Composition
C
[kg/kg]
1.000
0.000
0.000
0.780
0.860
-
H
[kg/kg]
0.000
1.000
0.000
0.050
0.140
-
S
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
1.000
0.030
0.000
-
N
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.040
0.000
-
O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.080
0.000
-
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.020
0.000
-
CH4
[kg/kg]
-
-
-
-
-
1.000
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas
N
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
O
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
N
[kg/kg]
0.767
O
[kg/kg]
0.233
Oxidant
Air](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-11-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.295
0.000
0.000
0.249
0.202
0.151
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.255
0.000
0.041
0.080
0.124
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.378
0.005
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.705
0.745
0.622
0.705
0.718
0.725
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
0.000
0.000
0.170
0.132
0.095
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.210
0.002
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
0.653
0.790
0.759
0.739
0.715
Combustion Products Flame Temperature, Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio and HHV
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,460
2,525
1,972
2,484
2,484
2,327
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
11.444
34.333
4.292
10.487
14.649
17.167
HHV
[Btu/lbm]
14,094
60,997
3,982
14,162
20,660
21,563
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.347
0.000
0.068
0.129
0.190
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-12-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-13-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-14-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products Flame Temperature
1,900
2,000
2,100
2,200
2,300
2,400
2,500
2,600
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Flame Temperature [K]
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
FlameTemperature[K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-15-320.jpg)
![Combustion Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio [/]
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
StoichiometricOxidanttoFuelRatio[/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-16-320.jpg)
![Higher Heating Value (HHV)
0
10,000
20,000
30,000
40,000
50,000
60,000
70,000
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
HHV [Btu/lbm]
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
HHV[Btu/lbm]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-17-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Oxidant Composition
Fuel Composition
C
[kg/kg]
1.000
0.000
0.000
0.780
0.860
-
H
[kg/kg]
0.000
1.000
0.000
0.050
0.140
-
S
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
1.000
0.030
0.000
-
N
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.040
0.000
-
O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.080
0.000
-
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.020
0.000
-
CH4
[kg/kg]
-
-
-
-
-
1.000
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas
N
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
O
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
N
[kg/kg]
0.767
O
[kg/kg]
0.233
Oxidant
Air](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-18-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Stoichiometric Combustion
Flame Temperature
Hydrogen
[K]
2,525
2,583
2,640
2,689
2,757
2,818
2,879
2,942
Sulfur
[K]
1,972
2,045
2,118
2,191
2,267
2,343
2,421
2,501
Coal
[K]
2,484
2,551
2,618
2,686
2,756
2,827
2,899
2,972
Oil
[K]
2,484
2,551
2,616
2,683
2,751
2,820
2,891
2,963
Preheat Temperature
[K]
298
400
500
600
700
800
900
1,000
Combustion Products Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio and HHV
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
11.444
34.333
4.292
10.487
14.649
17.167
HHV
[Btu/lbm]
14,094
60,997
3,982
14,162
20,660
21,563
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas
Gas
[K]
2,327
2,391
2,455
2,520
2,586
2,653
2,721
2,791
Carbon
[K]
2,460
2,531
2,602
2,674
2,747
2,822
2,898
2,976](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-19-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products Flame Temperature
0
1,000
2,000
3,000
298 400 500 600 700 800 900 1,000
FlameTemperature[K]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Oxidant Preheat Temperature for Stoichiometric Combustion Conditions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-20-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Oxidant Composition
Fuel Composition
C
[kg/kg]
1.000
0.000
0.000
0.780
0.860
-
H
[kg/kg]
0.000
1.000
0.000
0.050
0.140
-
S
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
1.000
0.030
0.000
-
N
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.040
0.000
-
O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.080
0.000
-
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.020
0.000
-
CH4
[kg/kg]
-
-
-
-
-
1.000
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas
N
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
O
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
N
[kg/kg]
0.767
O
[kg/kg]
0.233
Oxidant
Air](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-21-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,460
1,506
1,145
952
831
748
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
11.444
22.889
34.333
45.778
57.222
68.667
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fuel: Carbon
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.295
0.153
0.104
0.083
0.063
0.053
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.705
0.735
0.745
0.751
0.754
0.756
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.112
0.151
0.171
0.183
0.191
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
0.105
0.070
0.053
0.042
0.035
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
0.790
0.790
0.790
0.790
0.790
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.105
0.140
0.157
0.168
0.175](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-22-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,525
1,645
1,269
1,059
924
830
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
34.333
68.667
103.000
137.333
171.667
206.000
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fuel: Hydrogen
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.255
0.129
0.087
0.065
0.052
0.043
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.745
0.756
0.760
0.761
0.763
0.763
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.115
0.154
0.173
0.185
0.193
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.653
0.715
0.738
0.751
0.758
0.763
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.347
0.190
0.131
0.100
0.081
0.068
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.095
0.131
0.150
0.161
0.169
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Oxidant to Fuel Ratio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-23-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Flame Temperature
[K]
1,972
1,229
949
799
705
641
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
4.292
8.583
12.875
17.167
21.458
25.750
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fuel: Sulfur
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.378
0.209
0.144
0.110
0.089
0.075
N2
[kg/kg]
0.622
0.687
0.712
0.725
0.733
0.738
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.104
0.144
0.165
0.178
0.187
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
0.105
0.070
0.053
0.042
0.035
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
0.790
0.790
0.790
0.790
0.790
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.105
0.140
0.158
0.168
0.175
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Oxidant to Fuel Ratio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-24-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Fuel: Coal
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.249
0.130
0.088
0.067
0.053
0.045
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.041
0.021
0.014
0.011
0.009
0.007
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.005
0.003
0.002
0.001
0.001
0.001
N2
[kg/kg]
0.705
0.735
0.745
0.750
0.754
0.756
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.111
0.151
0.171
0.183
0.191
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.170
0.087
0.059
0.044
0.035
0.030
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.002
0.001
0.001
0.001
0.001
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.760
0.774
0.779
0.782
0.783
0.785
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.068
0.035
0.024
0.018
0.014
0.012
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.103
0.138
0.156
0.166
0.174
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,484
1,544
1,178
981
856
769
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
10.487
20.992
31.497
42.002
52.507
63.013
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Oxidant to Fuel Ratio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-25-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,484
1,555
1,187
989
863
776
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
14.694
29.298
43.947
58.596
73.244
87.893
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fuel: Oil
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.202
0.104
0.070
0.053
0.042
0.035
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.080
0.042
0.028
0.021
0.017
0.014
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.718
0.742
0.750
0.754
0.757
0.758
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.113
0.152
0.172
0.184
0.192
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.132
0.068
0.046
0.035
0.028
0.023
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.739
0.764
0.772
0.777
0.779
0.781
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.129
0.067
0.045
0.034
0.027
0.023
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.102
0.137
0.155
0.166
0.173
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Oxidant to Fuel Ratio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-26-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,327
1,480
1,137
951
832
750
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
17.167
34.333
51.500
68.667
85.833
103.000
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
Fuel: Gas
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.151
0.078
0.052
0.039
0.032
0.026
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.124
0.064
0.043
0.032
0.026
0.022
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.725
0.745
0.752
0.756
0.758
0.760
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.113
0.152
0.172
0.184
0.192
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.095
0.050
0.034
0.026
0.021
0.017
Stoichiometry
[/]
1
2
3
4
5
6
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.715
0.751
0.763
0.770
0.774
0.776
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.190
0.100
0.068
0.051
0.041
0.034
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.100
0.135
0.153
0.165
0.172
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Oxidant to Fuel Ratio](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-27-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Stoichiometry [/]
Fuel: Carbon
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-28-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Stoichiometry [/]
Fuel: Carbon
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-29-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Hydrogen
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-30-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Hydrogen
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-31-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Sulfur
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-32-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Sulfur
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-33-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Coal
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-34-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Coal
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-35-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Oil
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-36-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Oil
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-37-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Gas
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-38-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
1 2 3 4 5 6
Combustion
Fuel: Gas
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-39-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products Flame Temperature
600
1,100
1,600
2,100
2,600
1 2 3 4 5 6
FlameTemperature[K]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-40-320.jpg)
![Combustion Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
0
40
80
120
160
200
240
1 2 3 4 5 6
OxidanttoFuelRatio[/]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometry [/]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-41-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Oxidant Composition
N
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
0.580
0.370
O
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
0.420
0.630
N
[kg/kg]
0.767
0.550
0.340
O
[kg/kg]
0.233
0.450
0.660
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
Fuel Composition
C
[kg/kg]
1.000
0.000
0.000
0.780
0.860
-
H
[kg/kg]
0.000
1.000
0.000
0.050
0.140
-
S
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
1.000
0.030
0.000
-
N
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.040
0.000
-
O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.080
0.000
-
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
0.020
0.000
-
CH4
[kg/kg]
-
-
-
-
-
1.000
Fuel
Carbon
Hydrogen
Sulfur
Coal
Oil
Gas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-42-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
11.444
5.889
4.037
Fuel: Carbon
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.295
0.532
0.728
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.705
0.468
0.272
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
0.420
0.630
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
0.580
0.370
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,460
3,985
> 5,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-43-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Fuel: Hydrogen
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.255
0.482
0.686
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.745
0.518
0.314
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.653
0.408
0.227
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.347
0.592
0.773
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
34.333
17.667
12.111
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,525
3,625
4,294](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-44-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Fuel: Sulfur
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.378
0.623
0.796
N2
[kg/kg]
0.622
0.377
0.204
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.210
0.420
0.630
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.790
0.580
0.370
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
4.292
2.208
1.514
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
Flame Temperature
[K]
1,972
3,167
4,125](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-45-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Fuel: Coal
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.249
0.448
0.610
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.041
0.074
0.100
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.005
0.009
0.013
N2
[kg/kg]
0.705
0.469
0.277
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.170
0.326
0.470
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.002
0.005
0.007
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.759
0.538
0.335
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.068
0.131
0.189
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,484
3,889
4,913
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
10.487
5.388
3.688
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-46-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Fuel: Oil
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.202
0.369
0.511
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.081
0.148
0.204
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.718
0.483
0.284
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.132
0.248
0.351
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.739
0.510
0.307
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.129
0.242
0.343
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
14.649
7.538
5.167
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,484
3,836
4,789](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-47-320.jpg)
![Combustion
Fuel: Gas
CO2
[kg/kg]
0.151
0.280
0.390
H2O
[kg/kg]
0.124
0.229
0.319
SO2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kg/kg]
0.725
0.492
0.291
O2
[kg/kg]
0.000
0.000
0.000
CO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.095
0.174
0.240
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63
SO2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
N2
[kmol/kmol]
0.715
0.479
0.281
H2O
[kmol/kmol]
0.190
0.347
0.479
O2
[kmol/kmol]
0.000
0.000
0.000
Stoichiometric Combustion
Combustion Products Composition on Weight and Mole Basis
Flame Temperature
[K]
2,327
3,505
4,300
Stoichiometric
Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
[/]
17.167
8.833
6.056
Combustion Products Flame Temperature and Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
Oxidant
[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21
O2 - 0.42
O2 - 0.63](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-48-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Carbon
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-49-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Carbon
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-50-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Hydrogen
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-51-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Hydrogen
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-52-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Sulfur
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-53-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Sulfur
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-54-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Coal
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-55-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Coal
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-56-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Oil
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-57-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Oil
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-58-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Weight Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kg/kg]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Gas
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-59-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products -- Mole Basis
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
CO2 H2O SO2 N2 O2
CombustionProducts[kmol/kmol]
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
Combustion
Fuel: Gas
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-60-320.jpg)
![Combustion Products Flame Temperature
0
1,000
2,000
3,000
4,000
5,000
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
FlameTemperature[K]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-61-320.jpg)
![Combustion Stoichiometric Oxidant to Fuel Ratio
0
10
20
30
40
O2 - 0.21 O2 - 0.42 O2 - 0.63
StoichiometricOxidanttoFuelRatio[/]
Carbon Hydrogen Sulfur Coal Oil Gas
Combustion
Fuel and Oxidant Inlet Temperature: 298 [K]
Stoichiometric Combustion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engwarew4-180214044848/85/Power-Cycle-Components-Processes-and-Compressible-Flow-Analysis-Webinar-62-320.jpg)
