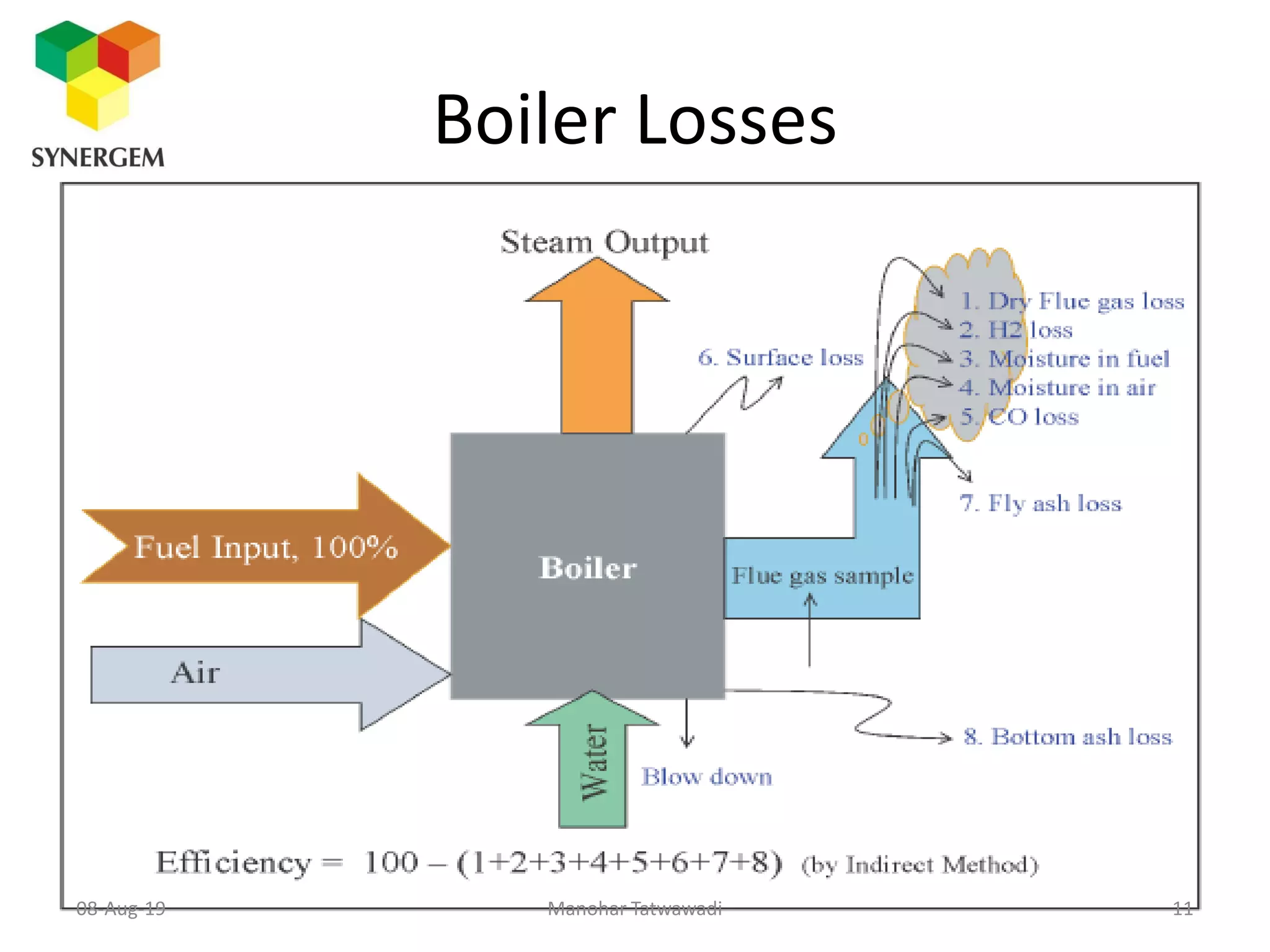
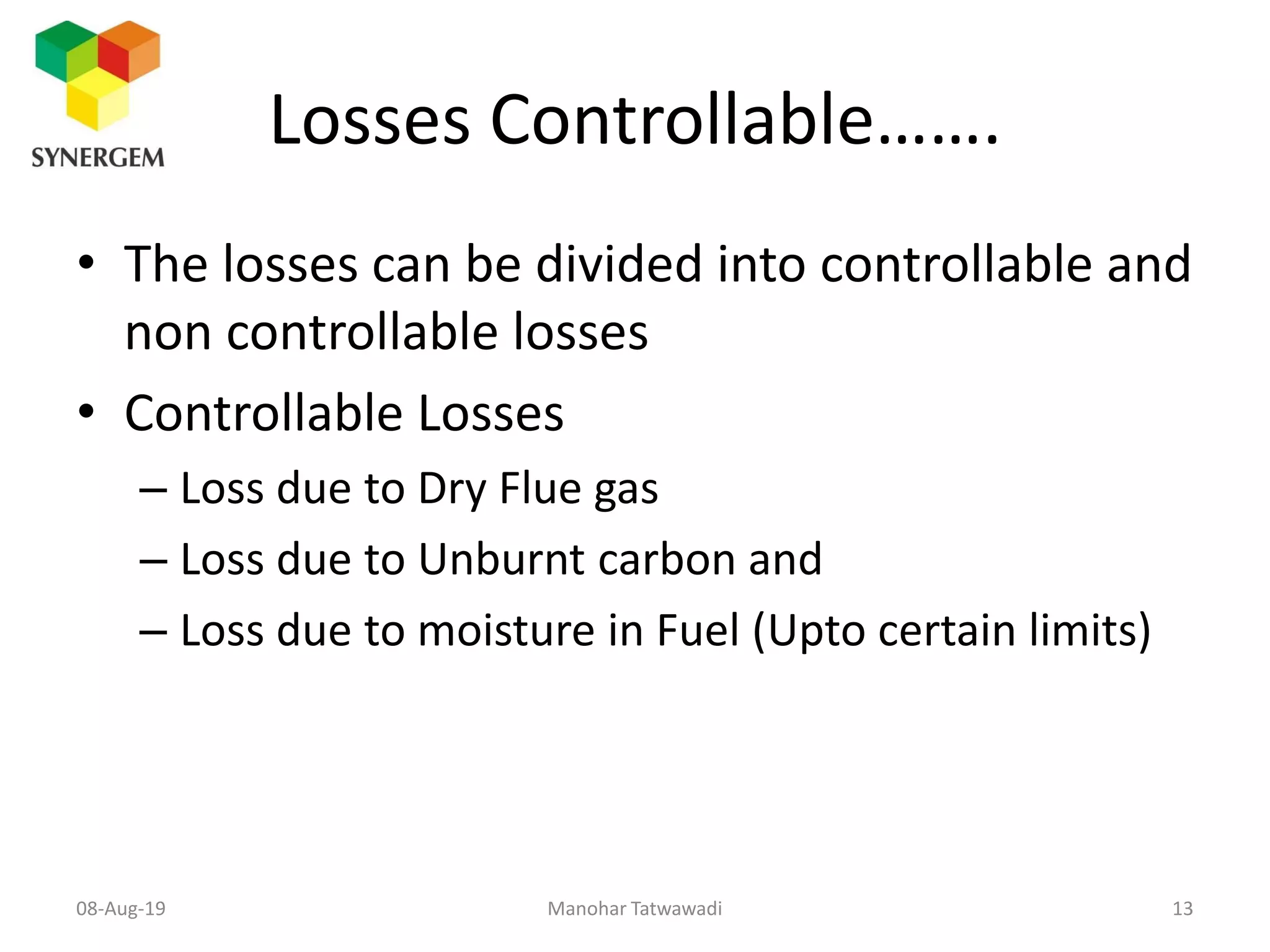
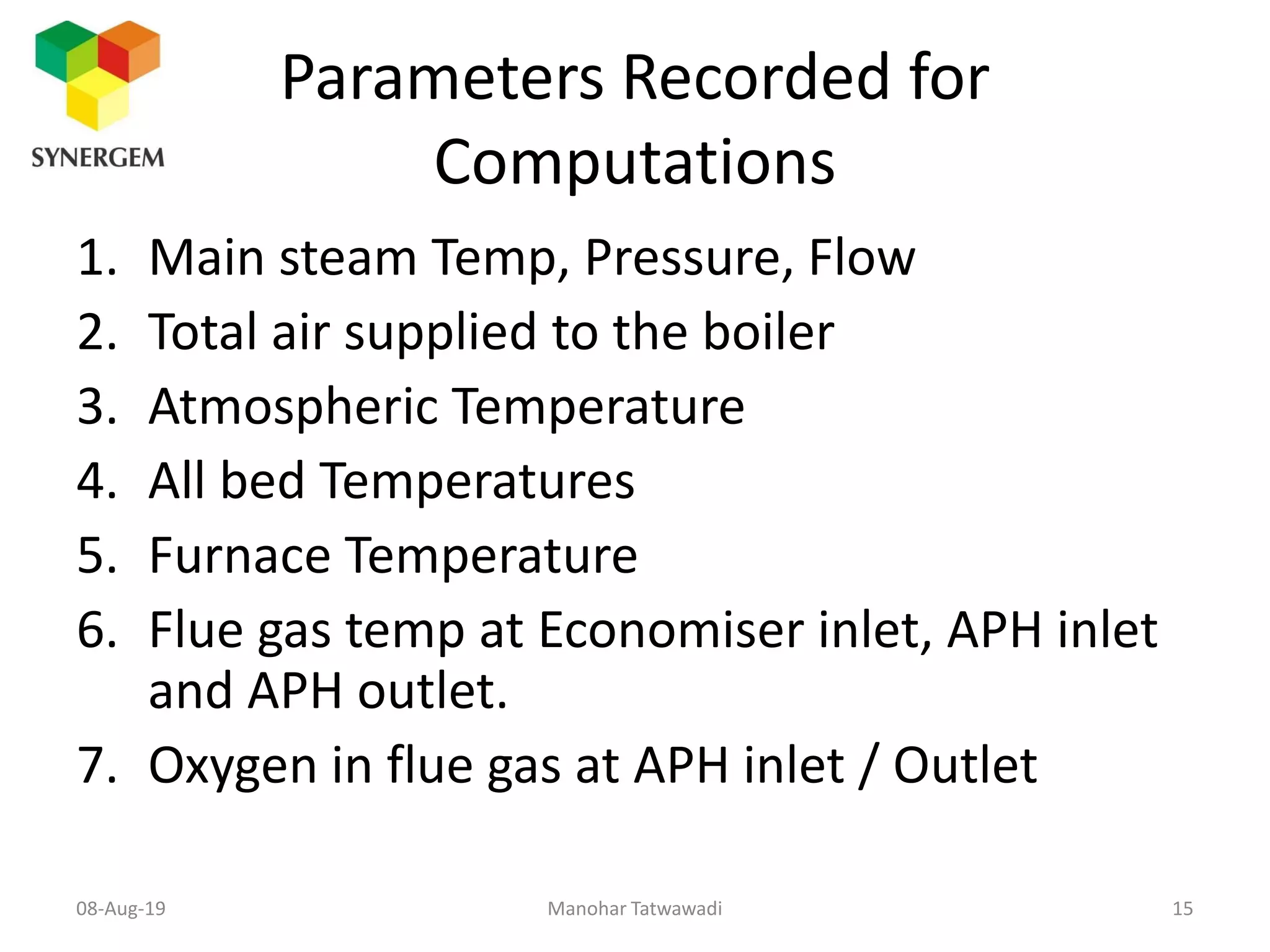
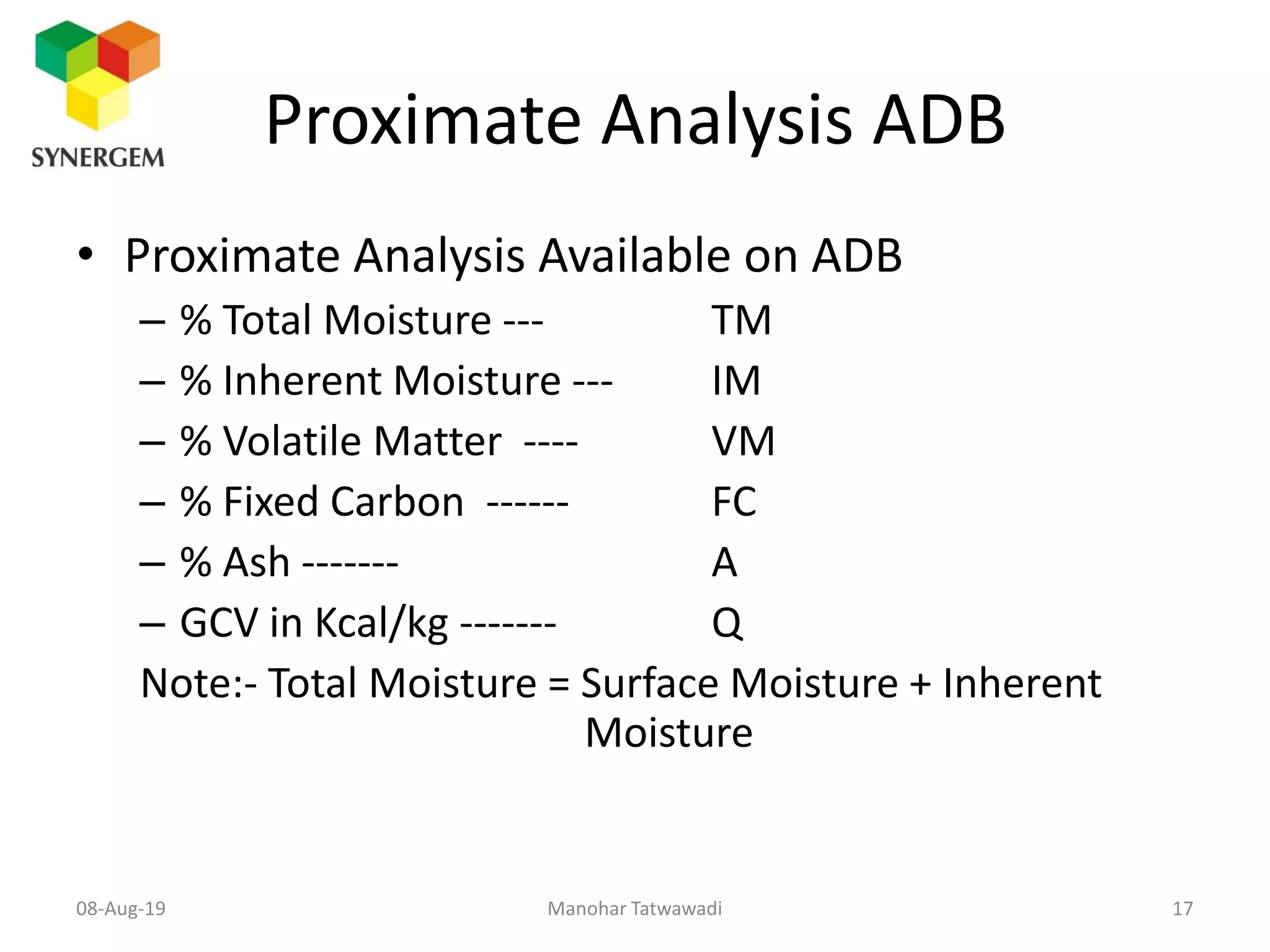
The document provides an overview of boiler efficiency calculations as per various standards, including direct and indirect methods for measuring efficiency. It details the parameters required for these calculations, such as fuel heat value, flow rates, and steam properties, and outlines procedures for testing and recording necessary data. Additionally, it discusses losses in boiler performance and methods for calculating these losses to improve overall efficiency.











![Ultimate Analysis
• Hydrogen Content:- By Parr’s Method -------- H
• H2 Content = (1- 0.01*Z )*Hp +(0.01*A) – (0.015 * S)
where, Hp= Hydrogen content on “ASH free basis”
= (0.0001707*Qp) + (0.0653*Vp) – 2.92
• Nitrogen Content :- By Gebhardt Formula ---- N
• N2 Content = [2.1 -(0.012*VM)]
• Sulphur Content :- By lab testing ---- S
• Oxygen Content = (100 – (C+H+N+S+A+TM)) ----- O
Manohar Tatwawadi08-Aug-19 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hiraboilerefficiencycal-190808083554/75/Boiler-Efficiency-Calculations-20-2048.jpg)