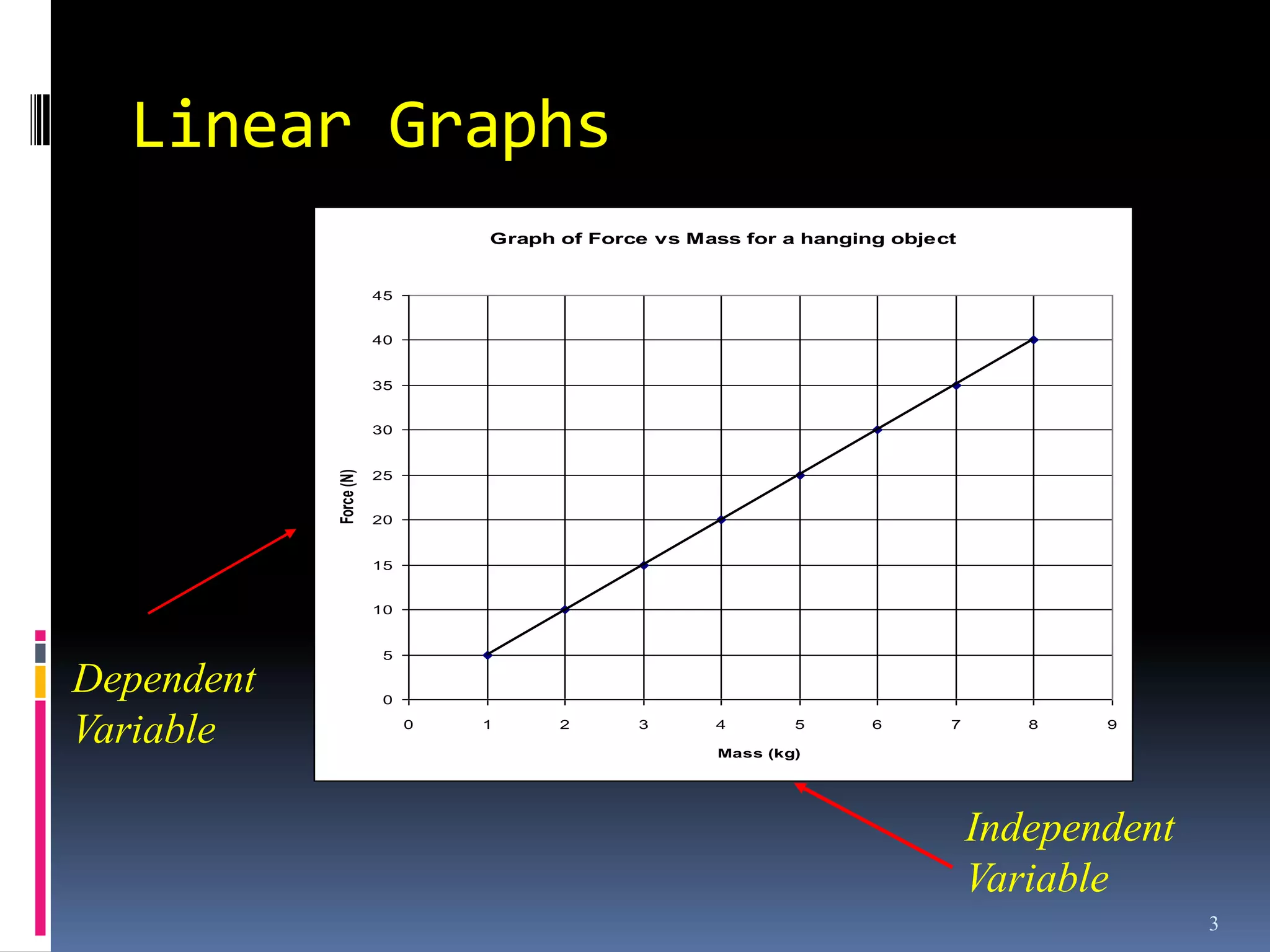
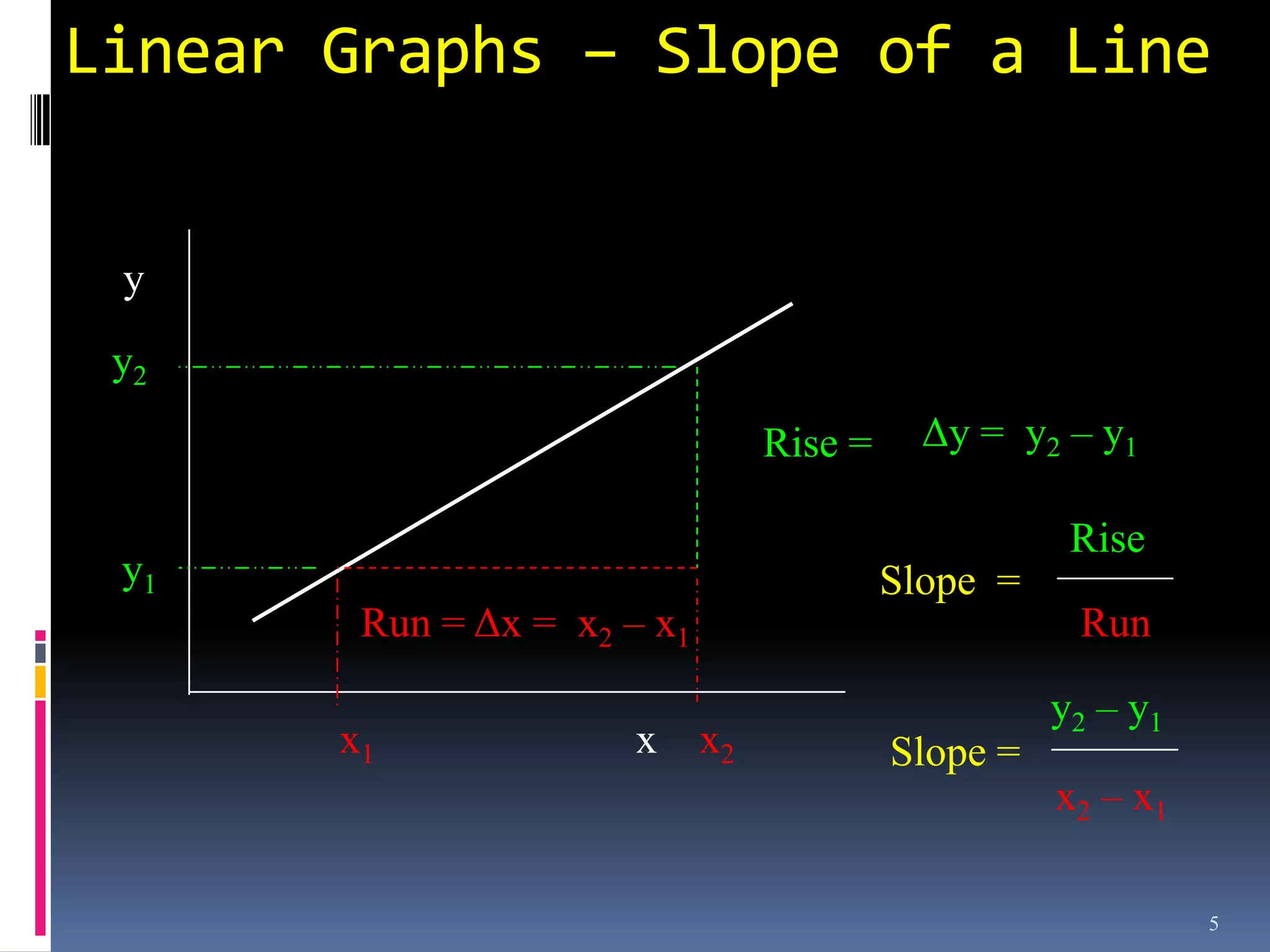
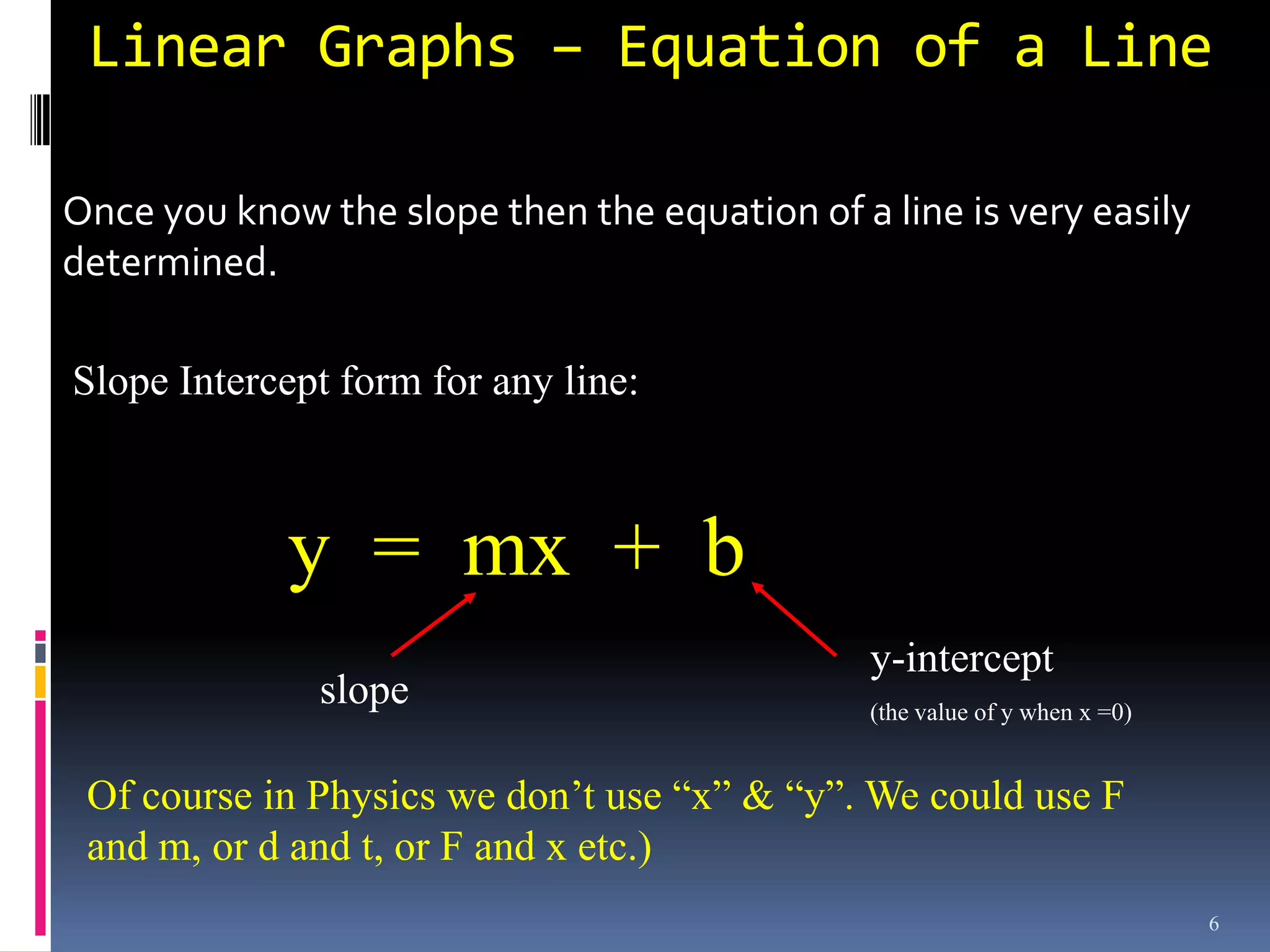
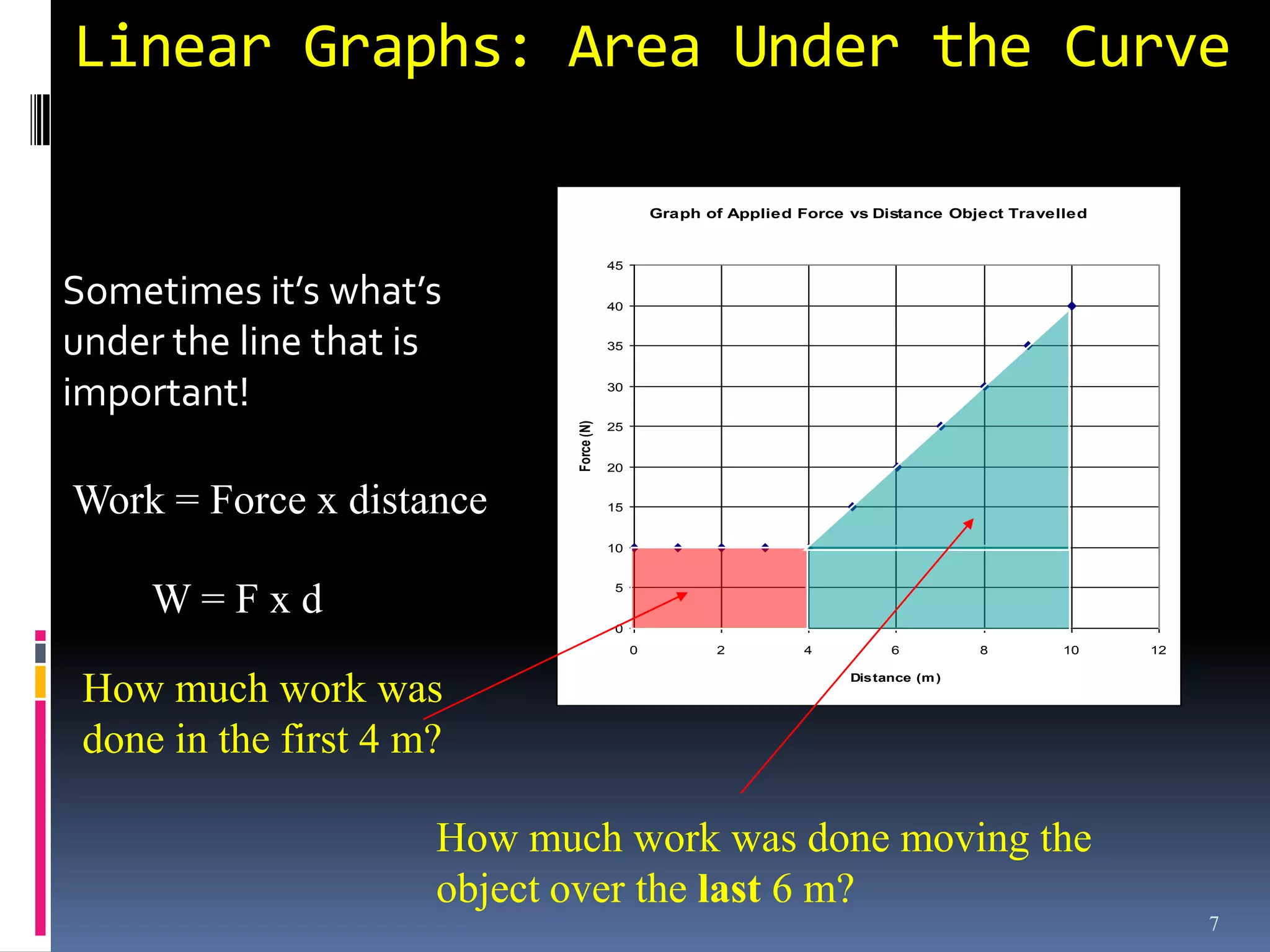
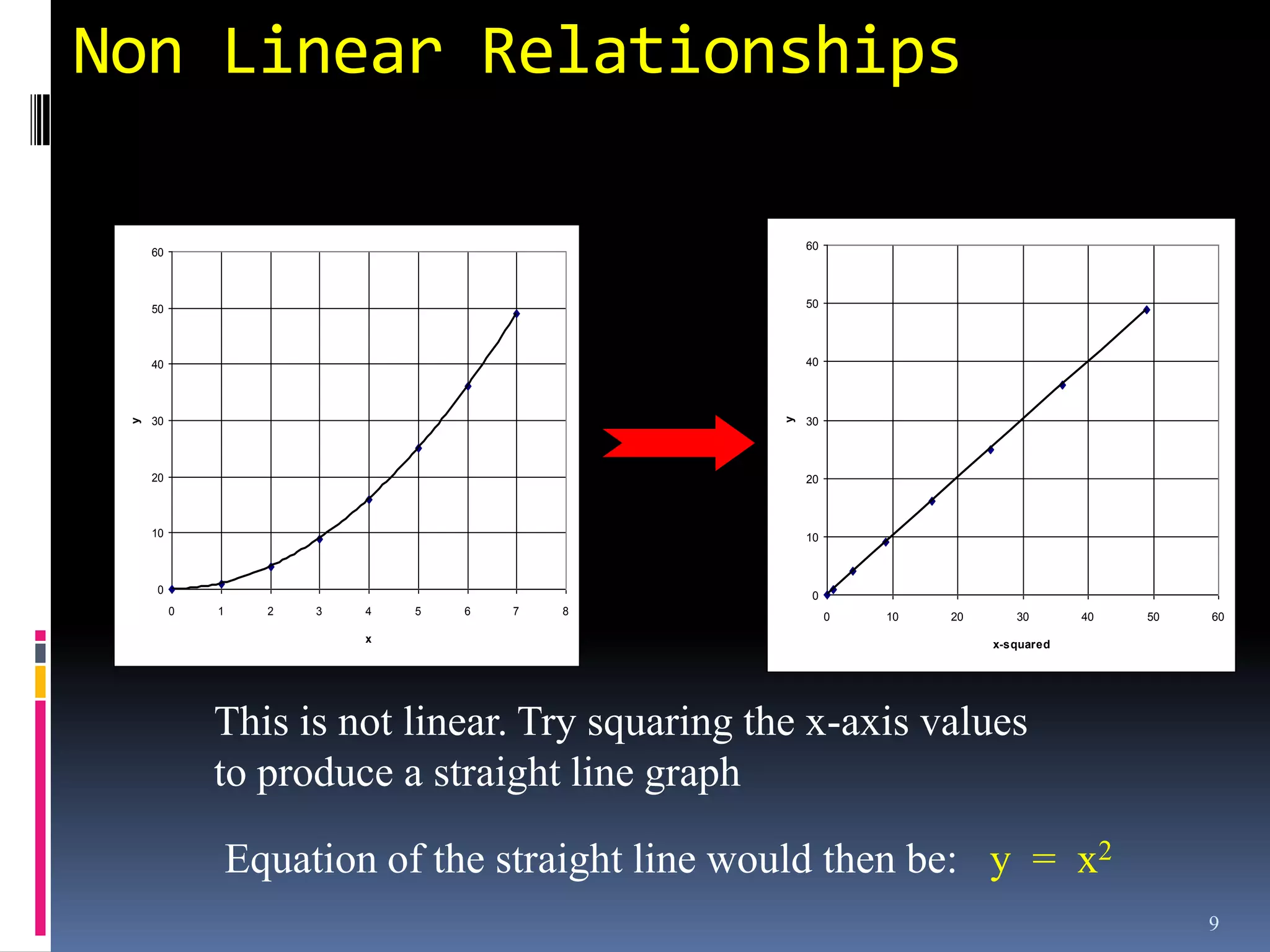
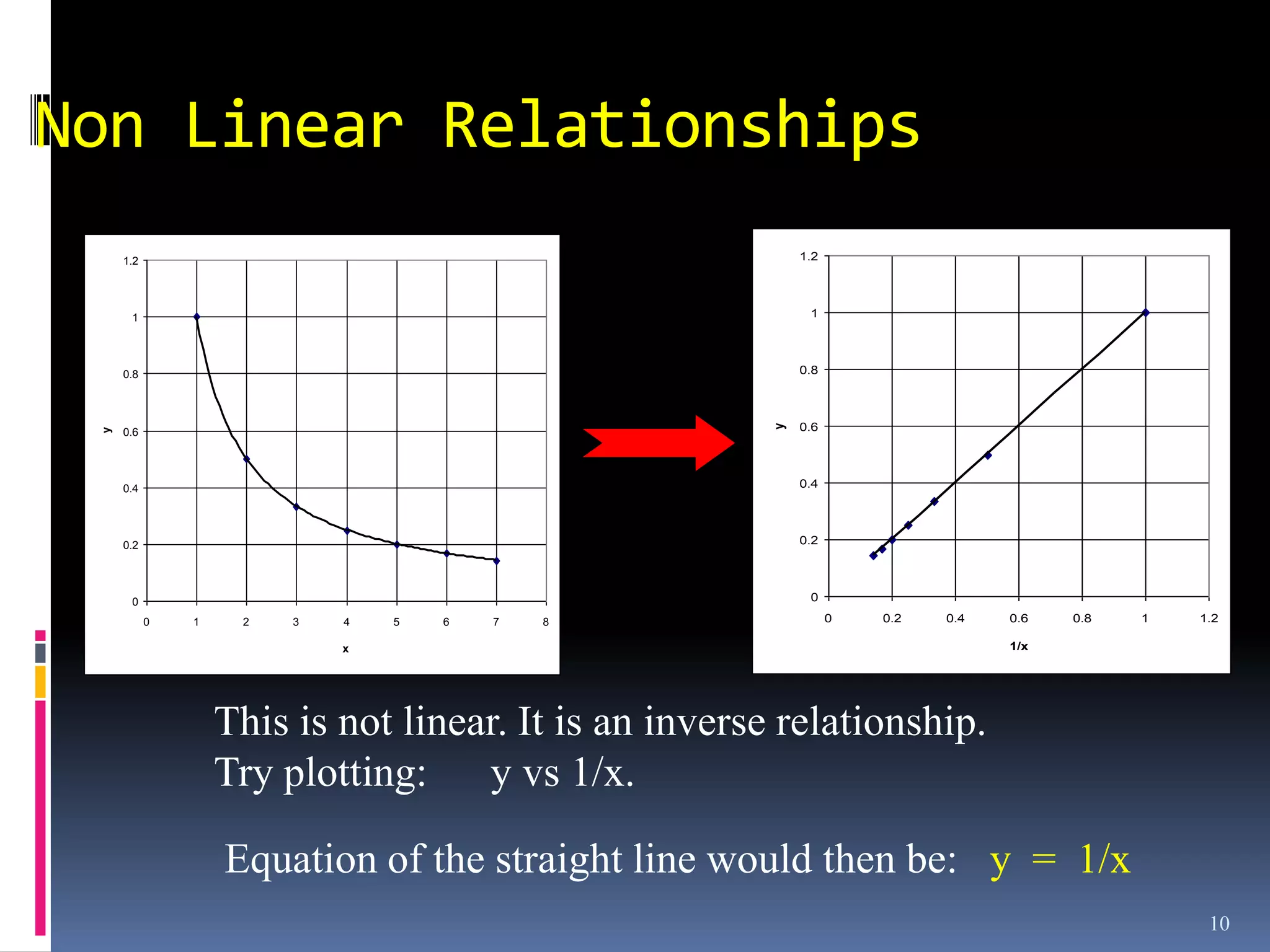
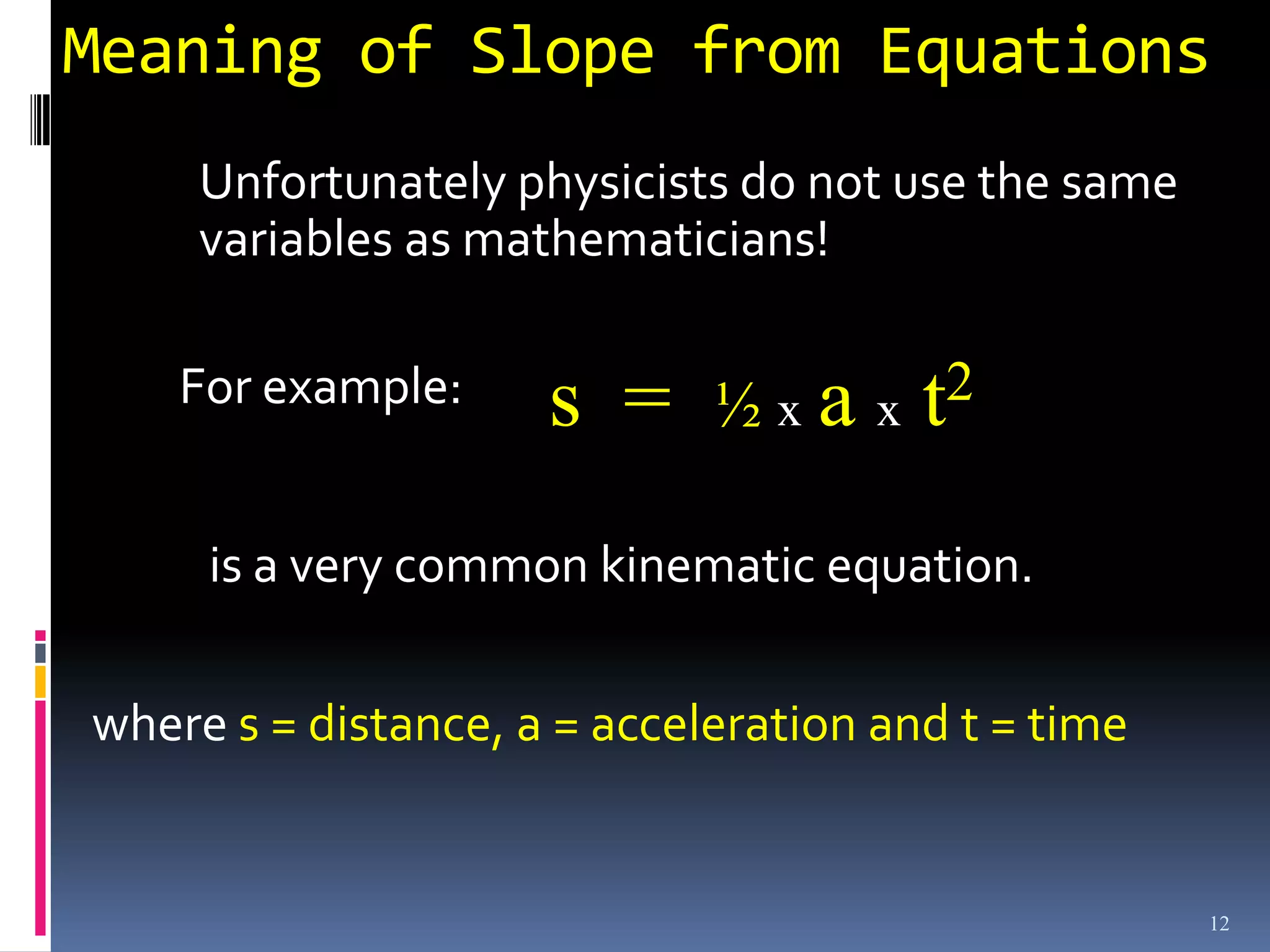
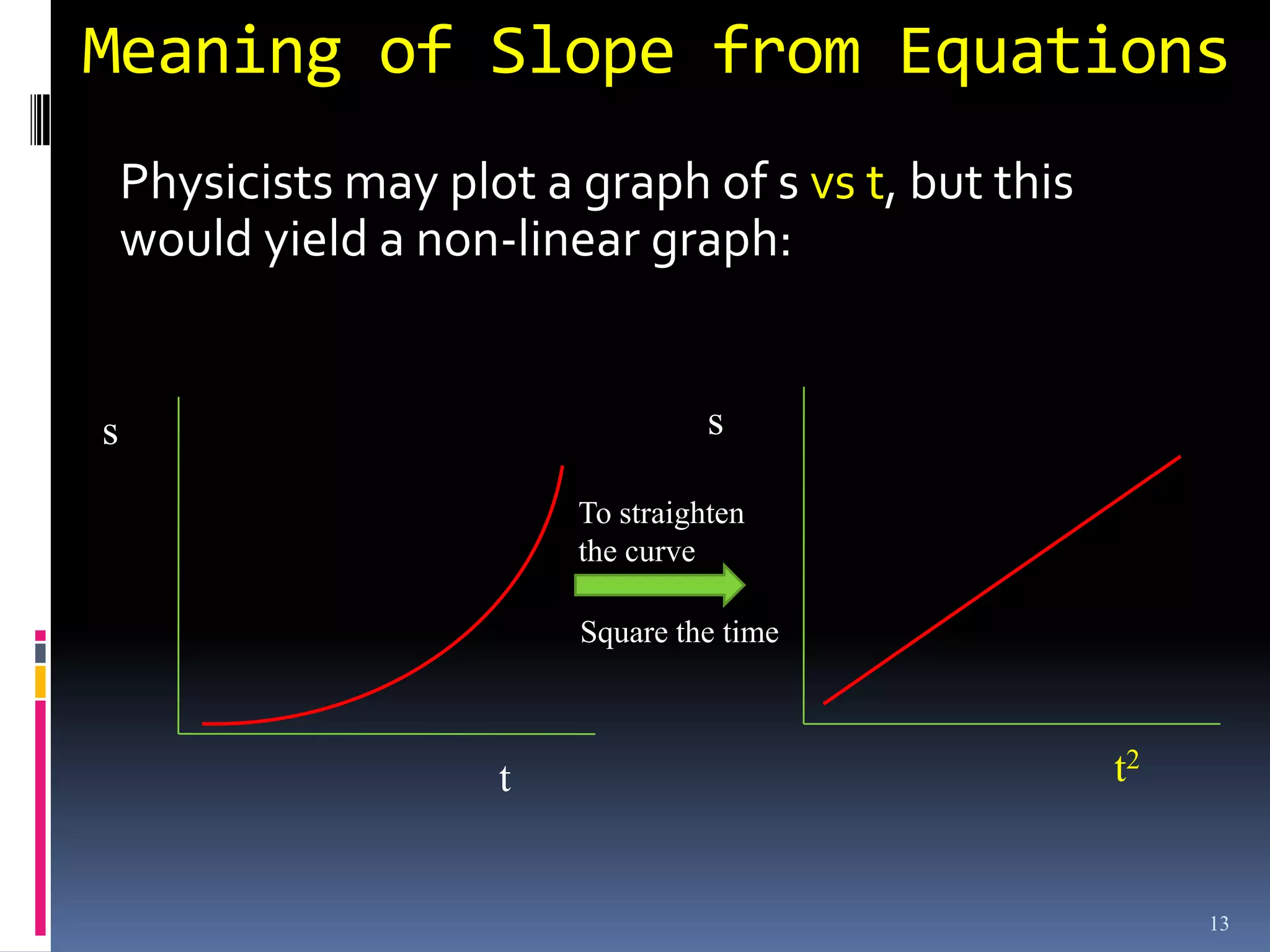
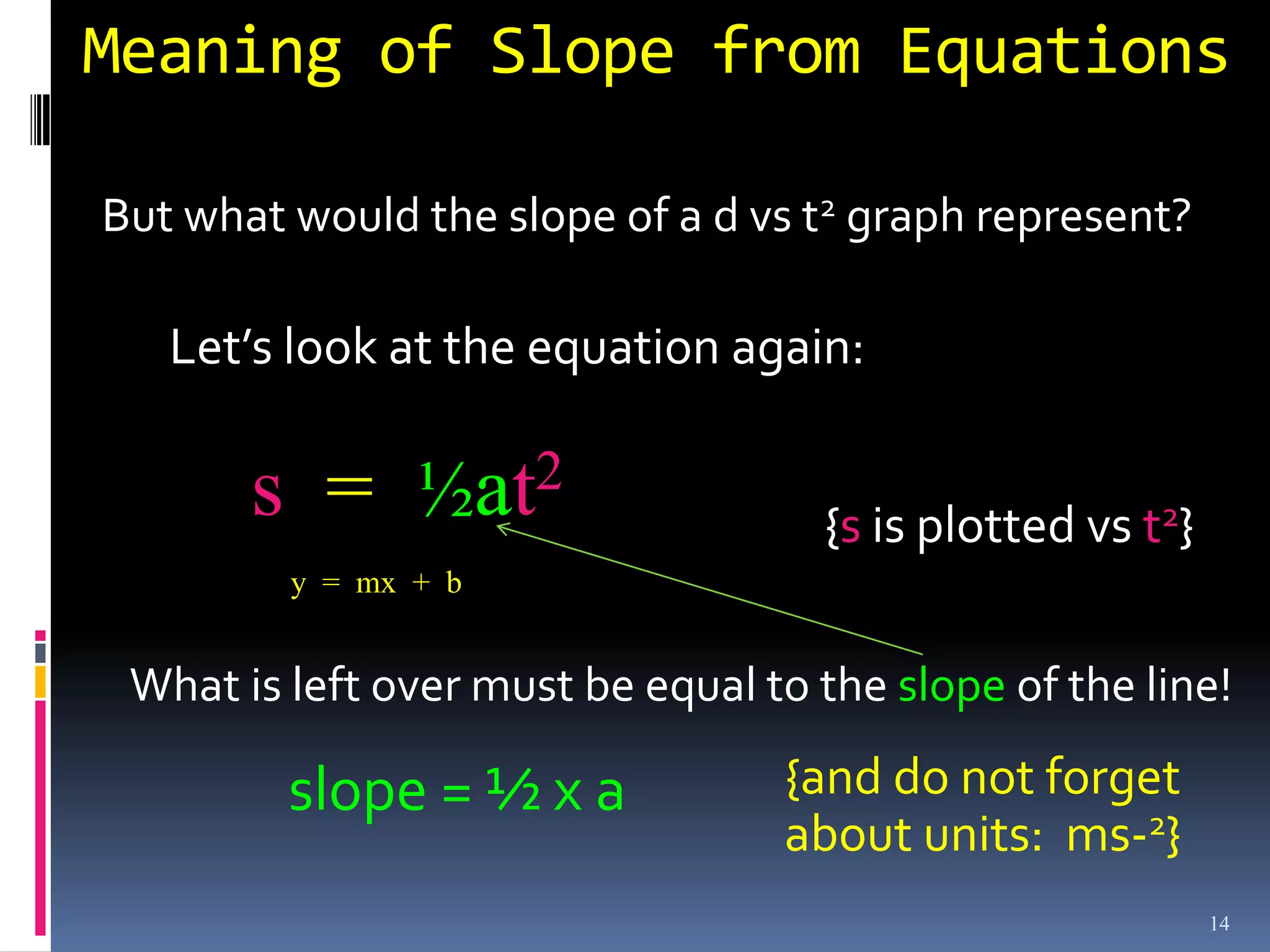
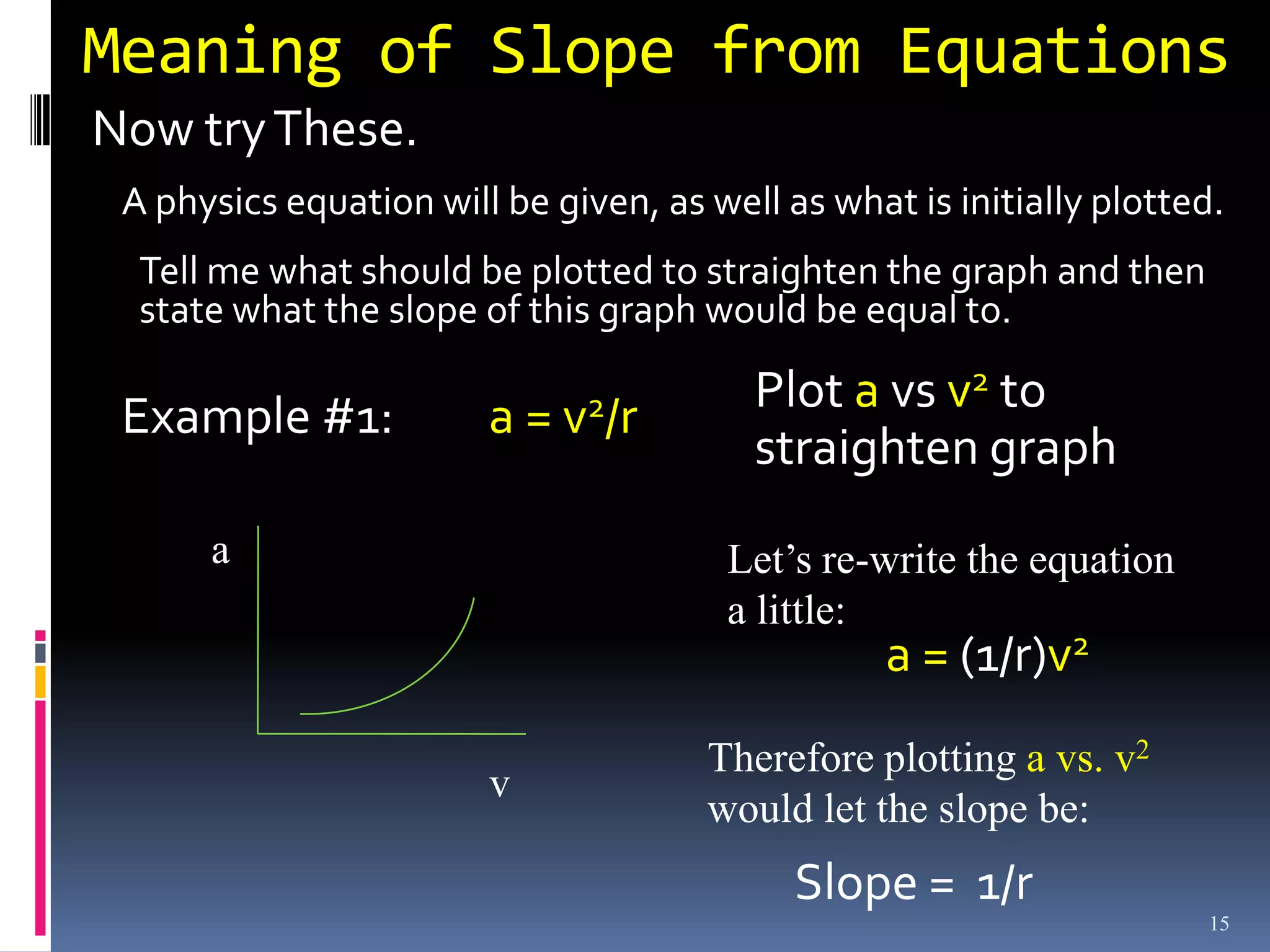
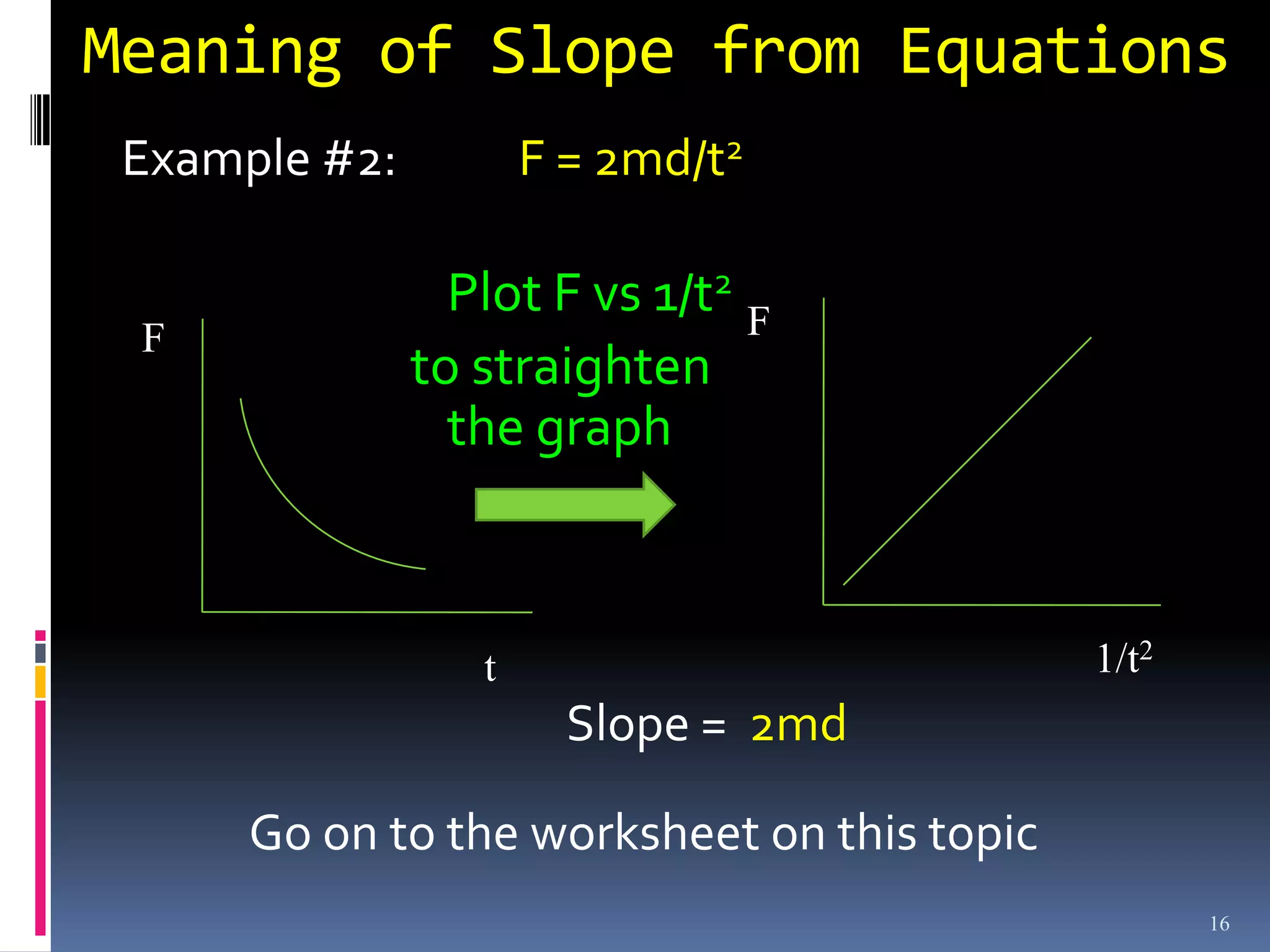
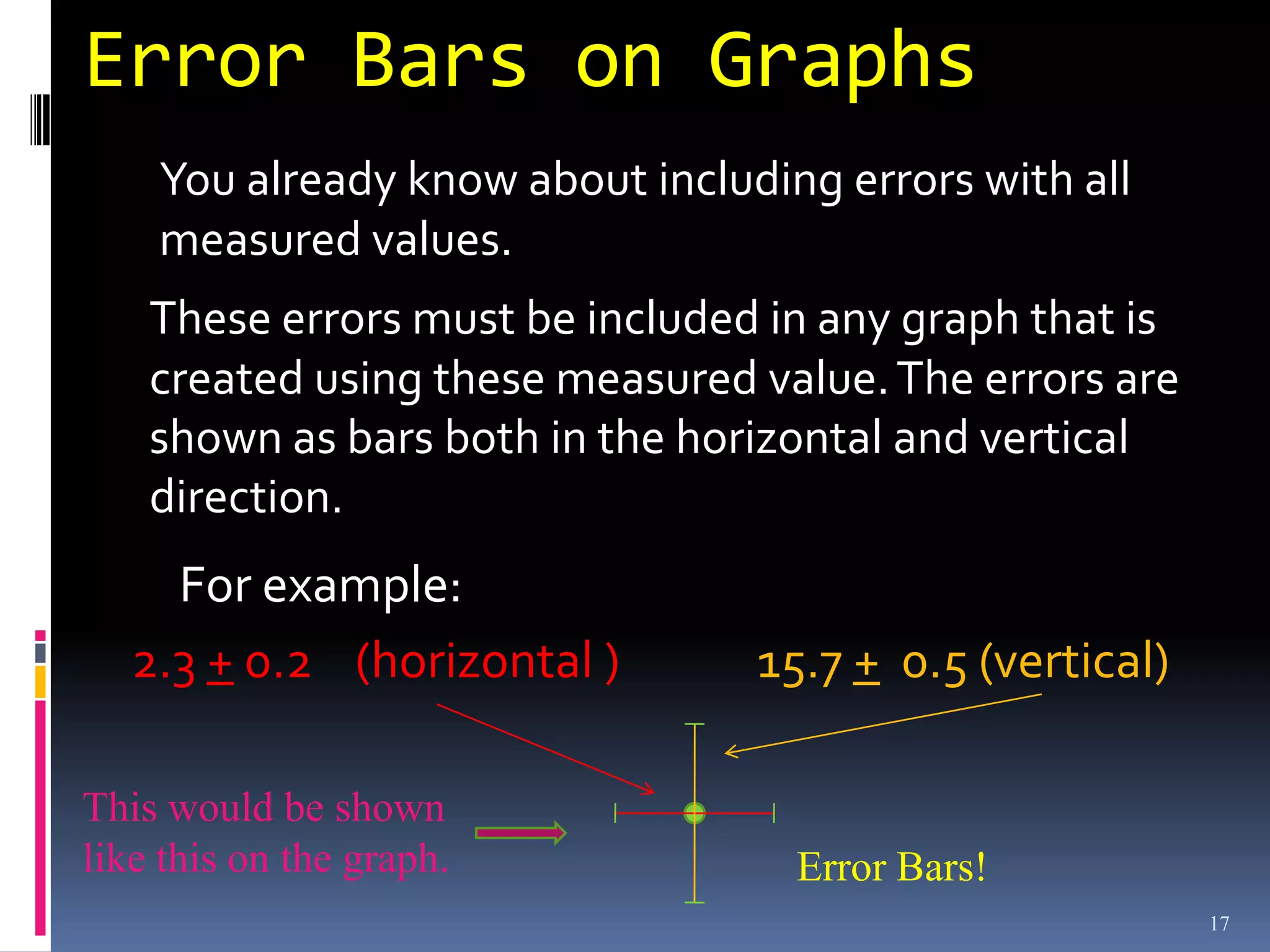
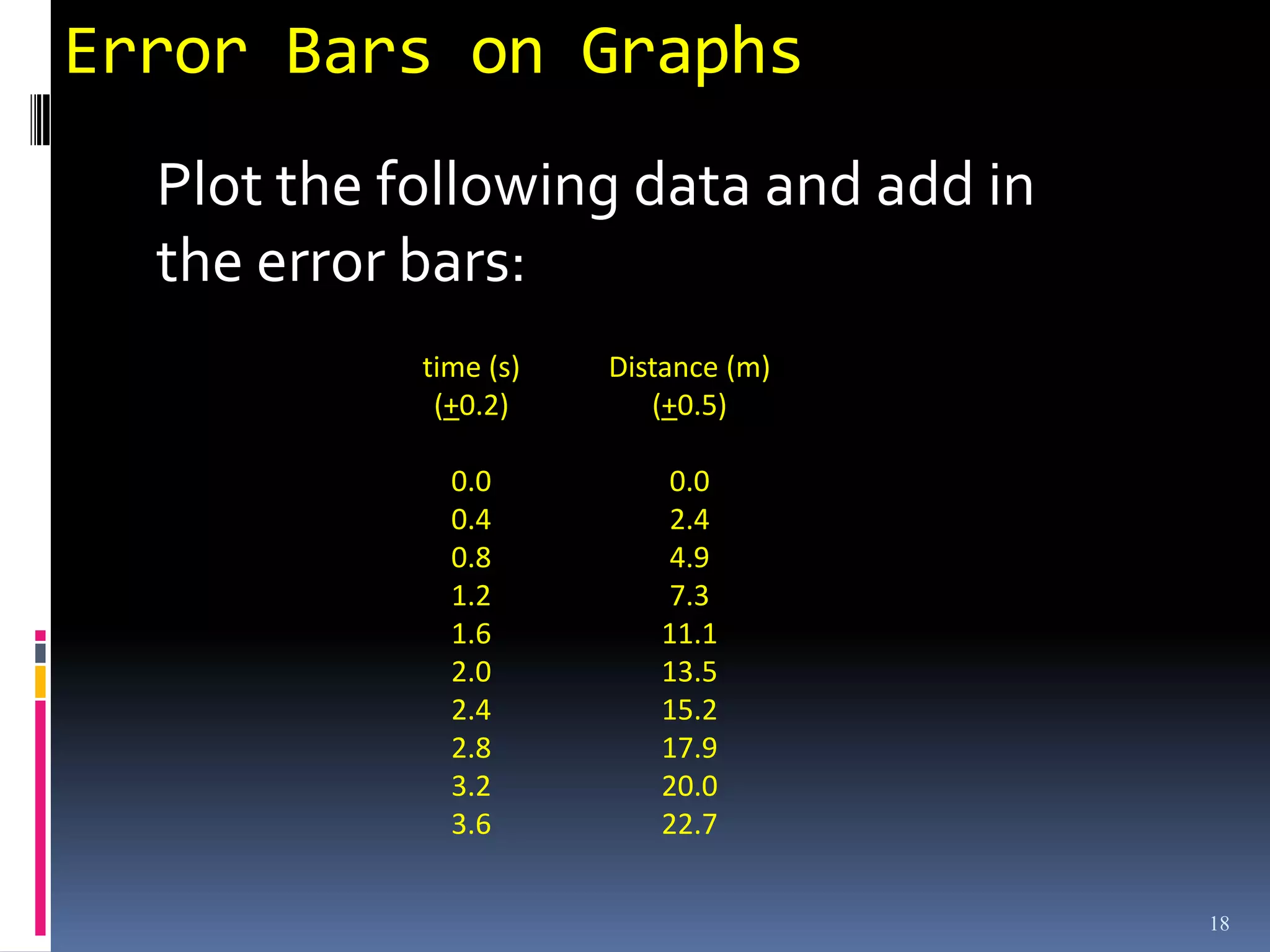
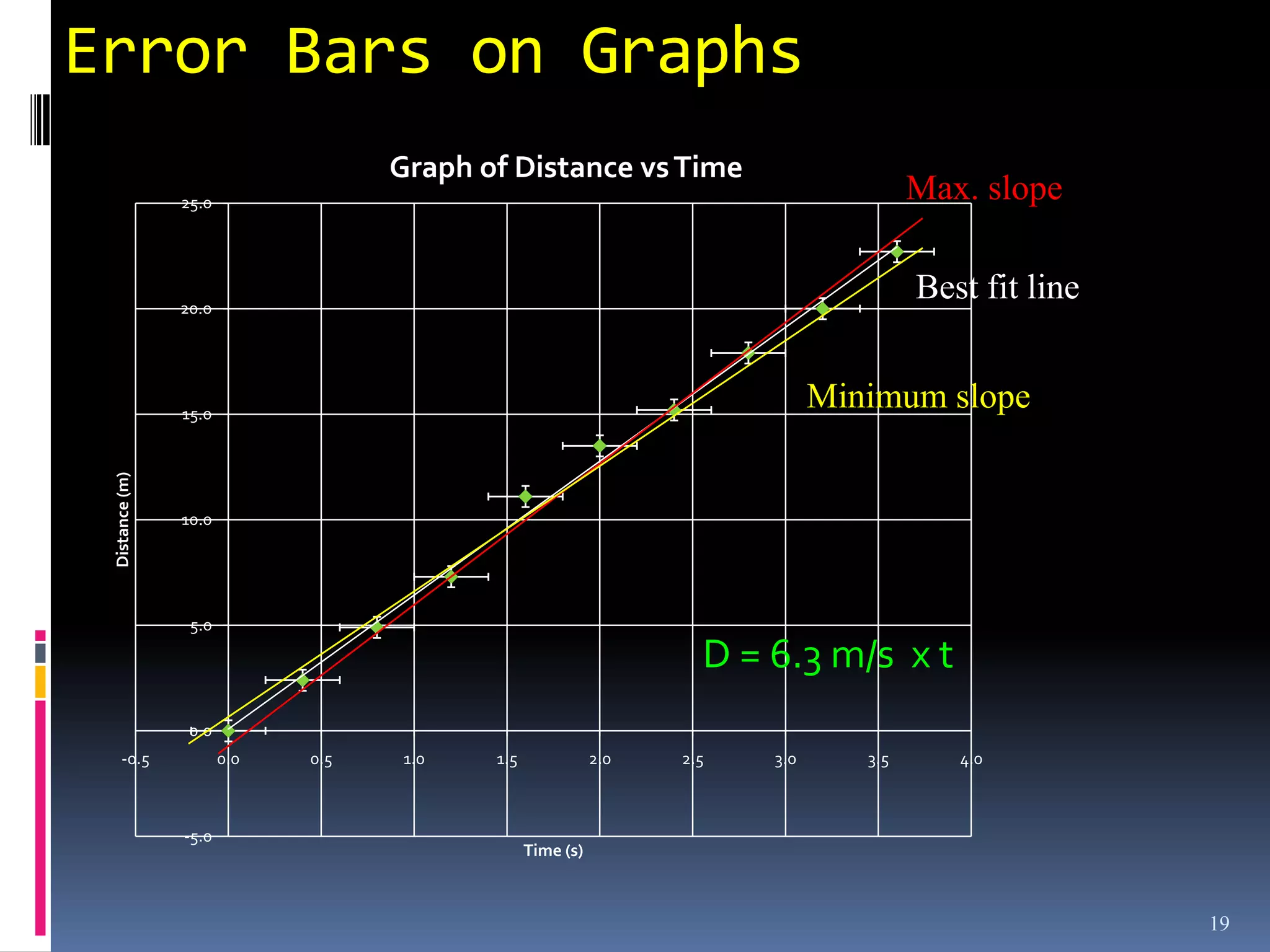
Graphs are used in physics to show relationships between variables. A linear graph indicates a direct proportional relationship between variables. The slope of a linear graph is calculated by taking the rise over the run and represents the ratio of change in the dependent variable to the change in the independent variable. For nonlinear relationships, manipulating the variables, such as squaring or taking reciprocals, can linearize the relationship. The slope of the resulting linear graph then represents a physical quantity defined by the original equation.