1. The document discusses scalar products (dot products) of vectors, work, power, and kinetic energy. It provides examples of calculating scalar products, work done by forces, and kinetic energy.
2. Key points made include that scalar product is also called dot product, work is force times distance, the unit of work and energy is the Joule, and kinetic energy is one-half mass times velocity squared.
3. Practice problems are provided to calculate scalar products, work, power, and kinetic energy given different vectors and scenarios.



















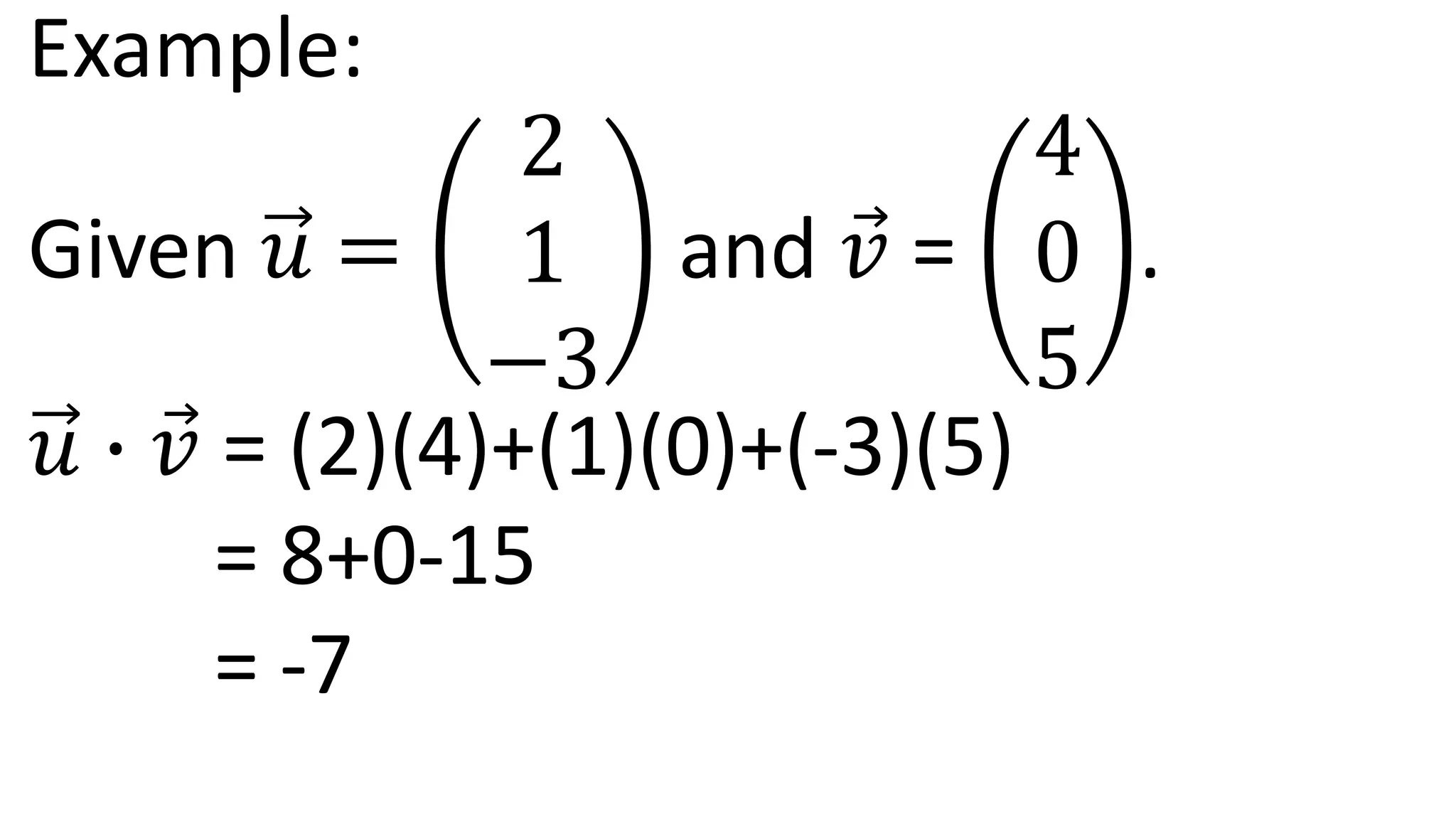
















![P = 𝑾/𝑻
Example
A garage hoist lifts a truck up 2
meters above the ground in 15
seconds. Find the power delivered
to the truck. [Given: 1000 kg as the
mass of the truck]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade12dotorscalarproduct-231126053152-ec9b2ef6/75/grade-12-DOT-or-SCALAR-PRODUCT-pptx-37-2048.jpg)
![Example
A garage hoist lifts a truck up 2
meters above the ground in 15
seconds. Find the power delivered
to the truck. [Given: 1000 kg as
the mass of the truck]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade12dotorscalarproduct-231126053152-ec9b2ef6/75/grade-12-DOT-or-SCALAR-PRODUCT-pptx-38-2048.jpg)











![9. Find the vector u × v when
u = [3,−1,1] and v = [2,5,1].
a. 1 b. 0
c. 3 d. 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade12dotorscalarproduct-231126053152-ec9b2ef6/75/grade-12-DOT-or-SCALAR-PRODUCT-pptx-50-2048.jpg)
![10. Find the vector u × v when
u = [3,4,6] and v = [0,1,1]
a. 8 b. 9
c. 10 d. 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade12dotorscalarproduct-231126053152-ec9b2ef6/75/grade-12-DOT-or-SCALAR-PRODUCT-pptx-51-2048.jpg)