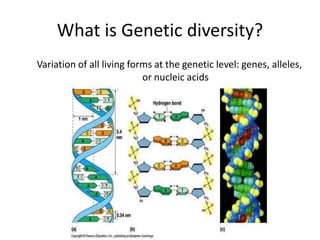
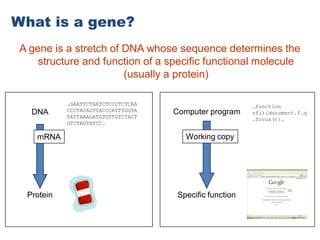
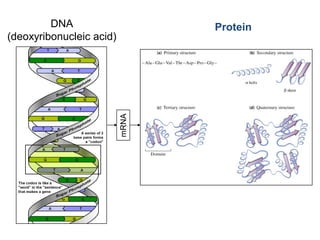
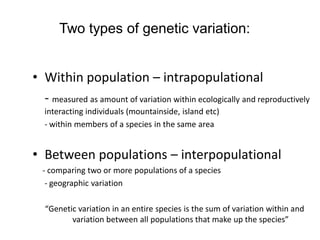
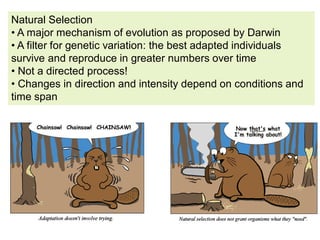
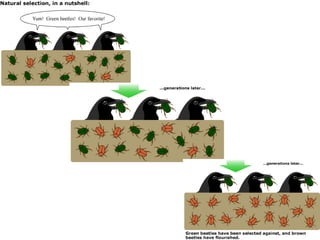
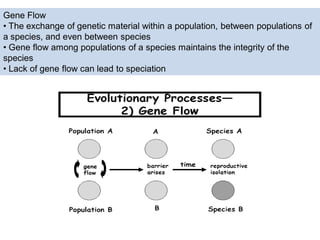
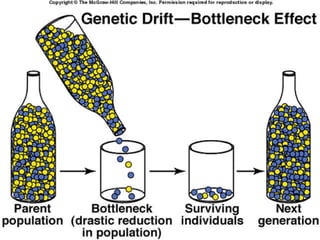
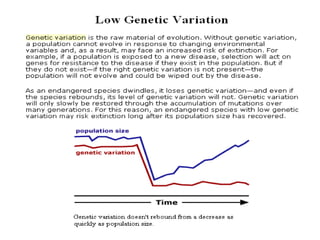
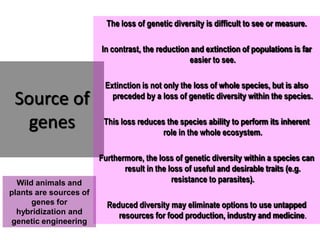
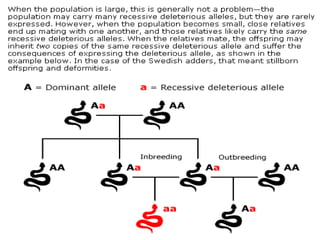
Genetic diversity is the variation of genes within and between populations of a species. It is important for species survival and adaptability. Loss of genetic diversity reduces a species' ability to adapt to environmental changes and increases risks of inbreeding, which can lead to extinction. Key causes of loss of diversity include habitat loss and degradation, pollution, monocultures in agriculture that replace diverse landraces and varieties, and overexploitation of wild species. Conservation aims to preserve natural patterns of genetic diversity to maintain options for future evolution. Loss of genetic diversity is potentially the most serious environmental problem because it cannot be reversed within just a few generations.