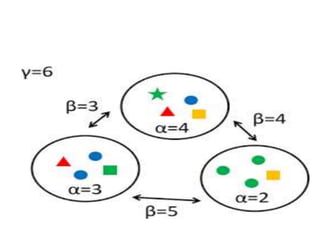
Alpha diversity refers to the mean diversity of species within individual sites or ecosystems at a local scale. It is measured by counting the number of distinct taxa like species, genera, or families within an ecosystem. Alpha diversity, along with beta diversity (diversity between habitats along environmental gradients) and gamma diversity (overall diversity in a region), were concepts introduced by R.H. Whittaker to describe biodiversity at different scales.