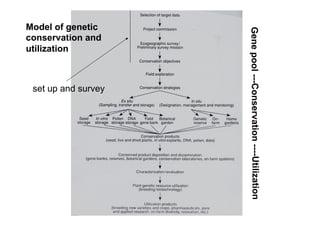
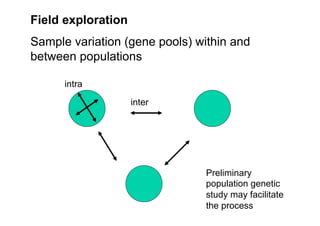
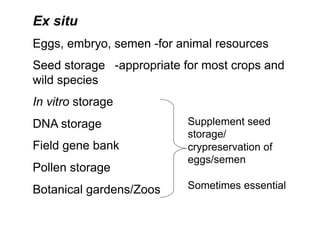
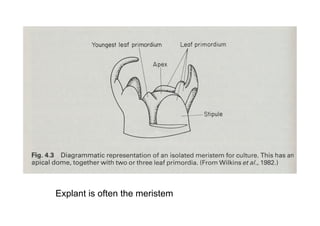
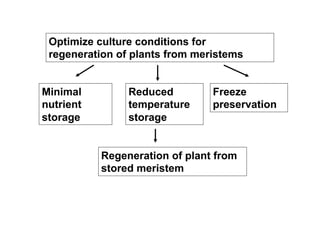
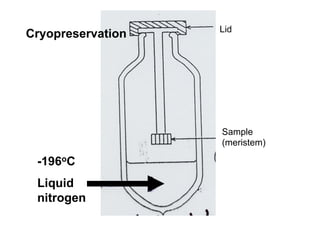
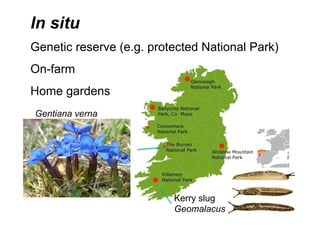
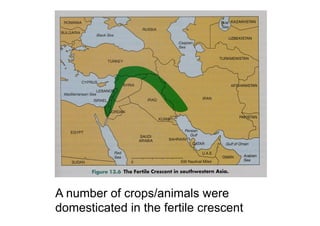
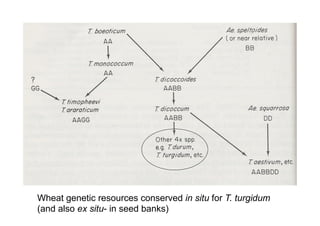
This document discusses genetic resource conservation. It describes ex situ conservation methods like seed banks, in vitro storage, cryopreservation, and botanical gardens. Seed banks are the most widely used method, storing seeds at low moisture and sub-zero temperatures to preserve them for decades. In vitro storage maintains plant explants in sterile culture but risks somaclonal variation. Cryopreservation freezes plant materials in liquid nitrogen and may allow indefinite storage. Field gene banks and botanical gardens conserve small numbers of species. In situ conservation maintains genetic variation on site through protected areas, on-farms, and home gardens. The document emphasizes an integrated approach using complementary ex situ and in situ methods.