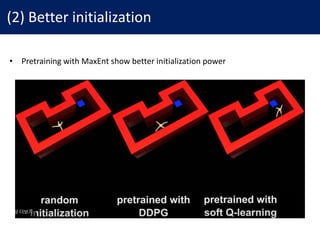
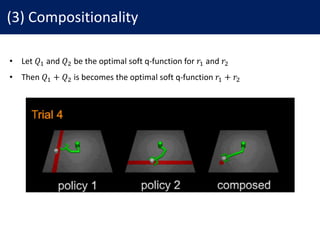
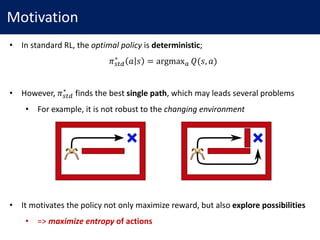
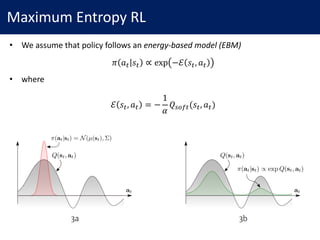
This document discusses reinforcement learning with deep energy-based policies. It motivates using maximum entropy reinforcement learning to find policies that not only maximize reward but also explore possibilities. It presents an approach using energy-based models for the policy and soft Q-learning to find the optimal maximum entropy policy. The method uses neural networks to approximate the soft Q-function and a sampling network to draw samples from the policy. Experiments show maximum entropy policies provide better exploration, initialization, compositionality and robustness compared to deterministic policies.

![Maximum Entropy RL
• maximum entropy policy:
𝜋3.456# = argmax7 8 𝔼 ":,.: ~<=
[𝑟 𝑠#, 𝑎# + 𝛼 ℋ(⋅ |𝑠#)]
#
• In this paper, we consider continuous state/action space
• We assume that policy follows an energy-based model (EBM)
𝜋 𝑎# 𝑠# ∝ exp −ℰ 𝑠#, 𝑎#
• where
ℰ 𝑠#, 𝑎# = −
1
𝛼
𝑄"NO#(𝑠#, 𝑎#)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/171011soft-q-learning-171011080717/85/Reinforcement-Learning-with-Deep-Energy-Based-Policies-3-320.jpg)
![Relation to Soft Q-learning
• As the analogy of standard RL, define
𝑄"NO#
∗
𝑠#, 𝑎# = 𝑟# + 𝔼 ":PQ,…, ∼<=
8 𝛾U
V
UWX
𝑟#YU + 𝛼 ℋ 𝜋3.456#
∗
⋅ 𝑠#YU
𝑉"NO#
∗
𝑠# = 𝛼 log ] exp
1
𝛼
𝑄"NO#
∗
(𝑠#, 𝑎^) 𝑑𝑎^
`
• Theorem 1. The optimal MaxEnt policy is
𝜋3.456#
∗
𝑎# 𝑠# = exp
1
𝛼
𝑄"NO#
∗
𝑠#, 𝑎# − 𝑉"NO#
∗
𝑠#
• Theorem 2. The soft Q-function satisfies the soft Bellman equation
𝑄"NO#
∗
𝑠#, 𝑎# = 𝑟# + 𝛾𝔼":PQ∼ab
[𝑉"NO#
∗
𝑠#YX ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/171011soft-q-learning-171011080717/85/Reinforcement-Learning-with-Deep-Energy-Based-Policies-5-320.jpg)
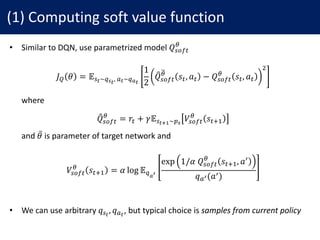
![Soft Q-Iteration
• Thus, we can find MaxEnt policy by soft Q-learning
• As Q-iteration, we can obtain 𝑄"NO#
∗
and 𝑉"NO#
∗
by soft Q-iteration
• Theorem 3. With mild condition1, the iteration converges to 𝑄"NO#
∗
and 𝑉"NO#
∗
𝑄"NO#
𝑠#, 𝑎# ← 𝑟# + 𝛾𝔼":PQ∼ab
𝑉"NO#
𝑠#YX , ∀𝑠#, 𝑎#
𝑉"NO#
𝑠# ← 𝛼 log ] exp
1
𝛼
𝑄"NO#
(𝑠#, 𝑎^) 𝑑𝑎^
`
, ∀𝑠#
• However, there are some challenges for this algorithm
1. Computing soft value function 𝑉"NO#
𝑠# is intractable
2. Sampling from policy function 𝜋3.456#
𝑎# 𝑠# is intractable
1. 𝑄"NO#, 𝑉"NO# are bounded, ∫ exp
X
f
𝑄"NO# ⋅, 𝑎^
𝑑𝑎′`
< ∞, 𝑄"NO#
∗
< ∞ exisits](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/171011soft-q-learning-171011080717/85/Reinforcement-Learning-with-Deep-Energy-Based-Policies-6-320.jpg)
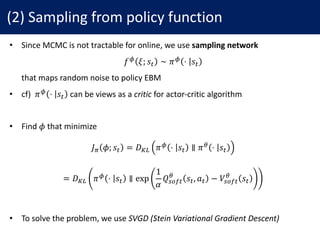
![(2) Sampling from policy function
• ∆𝑓y is the optimal direction in RKHS of 𝜅 (typically Gaussian kernel)
∆𝑓y ⋅ ; 𝑠# = 𝔼.:~7ƒ[𝜅 𝑎#, 𝑓y ⋅ ; 𝑠# 𝛻.u 𝑄"NO#
j
𝑠#, 𝑎# …
.uW.:
+𝛼 𝛻.u 𝜅 𝑎^, 𝑓y ⋅ ; 𝑠# …
.uW.:
]
• We can compute the gradient 𝜕𝐽/𝜕𝜙 with ∆𝑓y
𝜕𝐽7 𝜙; 𝑠#
𝜕𝜙
∝ 𝔼‡ ∆𝑓y 𝜉; 𝑠#
𝜕𝑓y(𝜉; 𝑠#)
𝜕𝜙
• Putting (1) and (2), we can implement soft Q-learning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/171011soft-q-learning-171011080717/85/Reinforcement-Learning-with-Deep-Energy-Based-Policies-9-320.jpg)