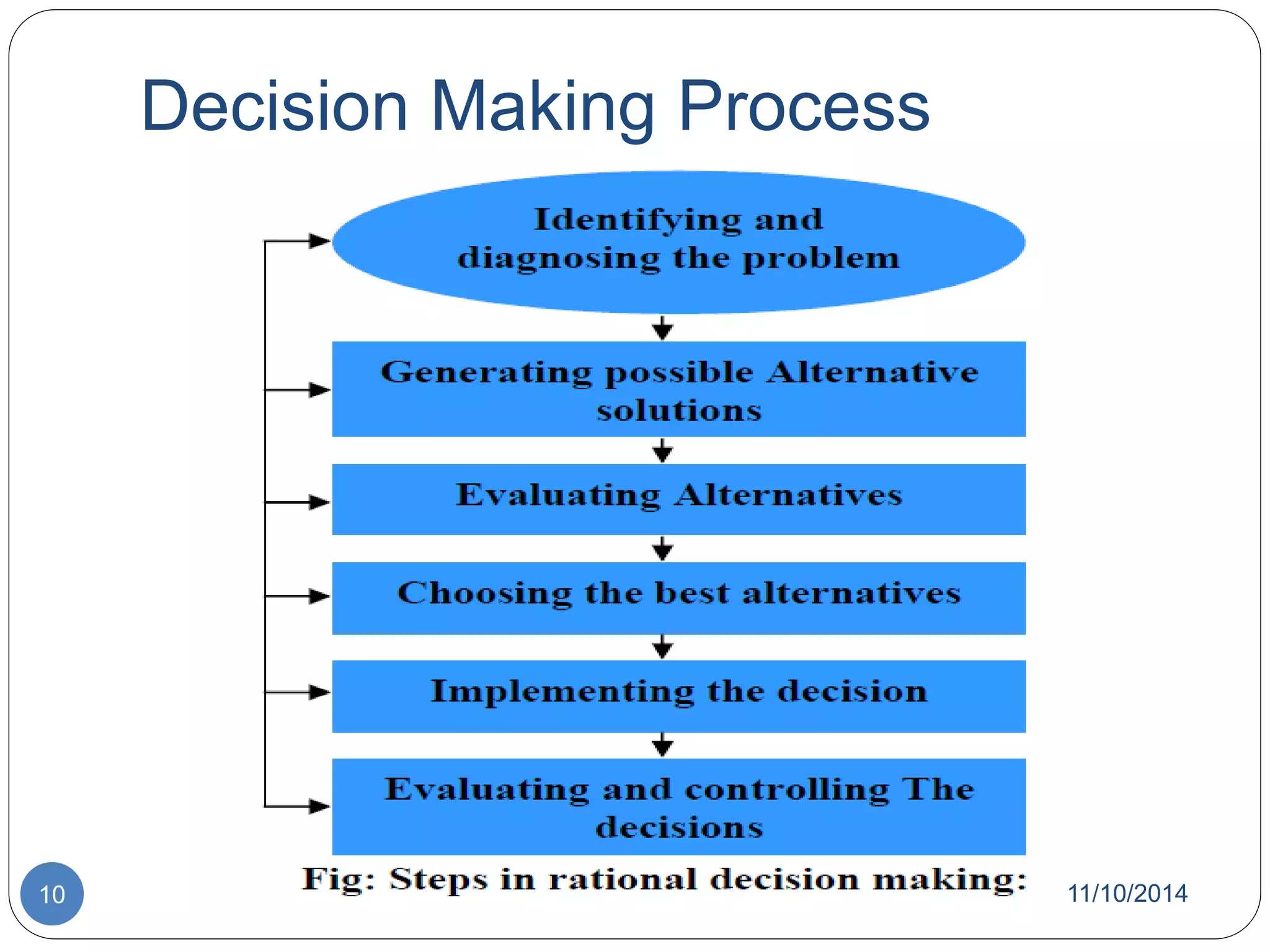
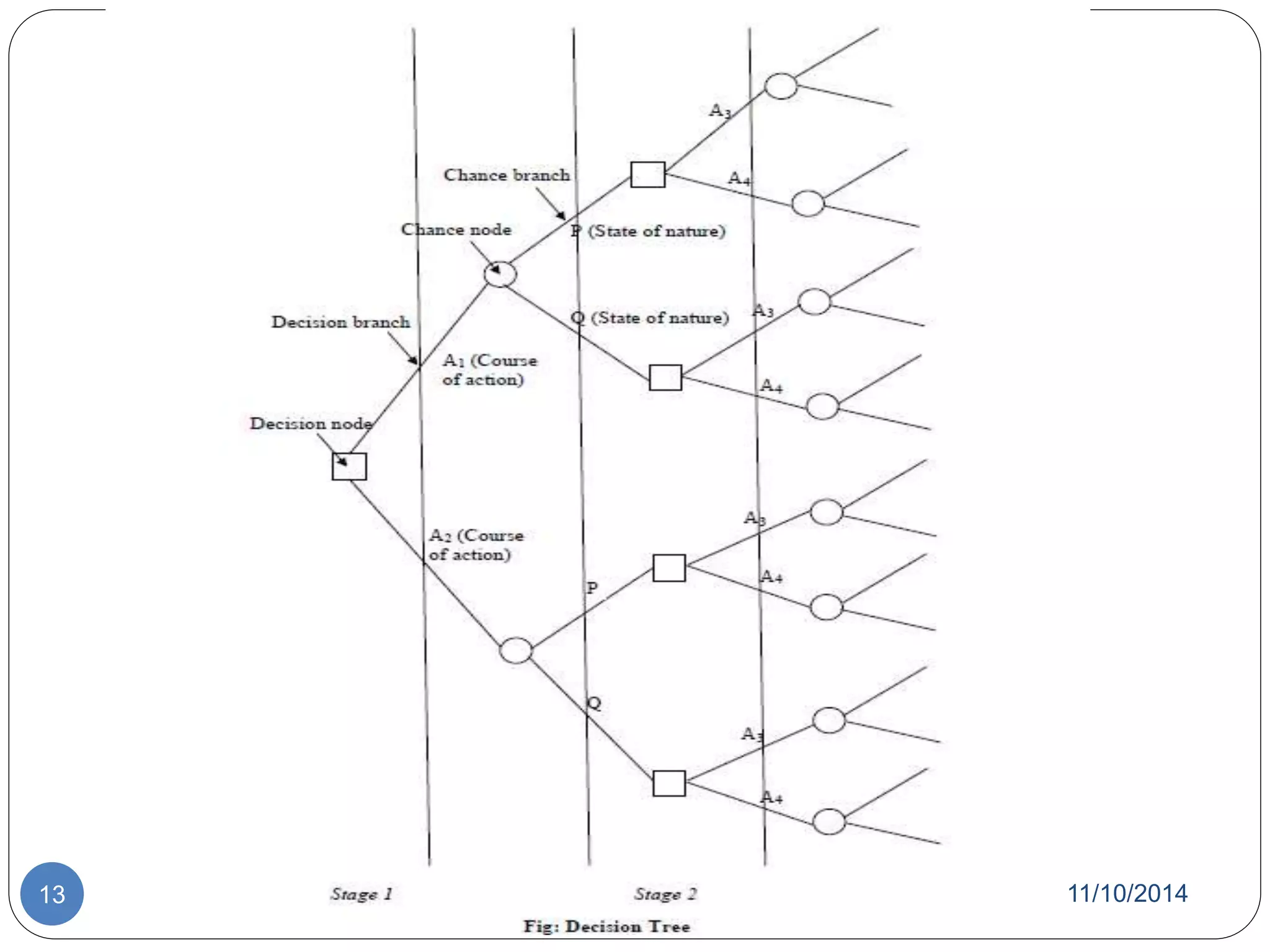
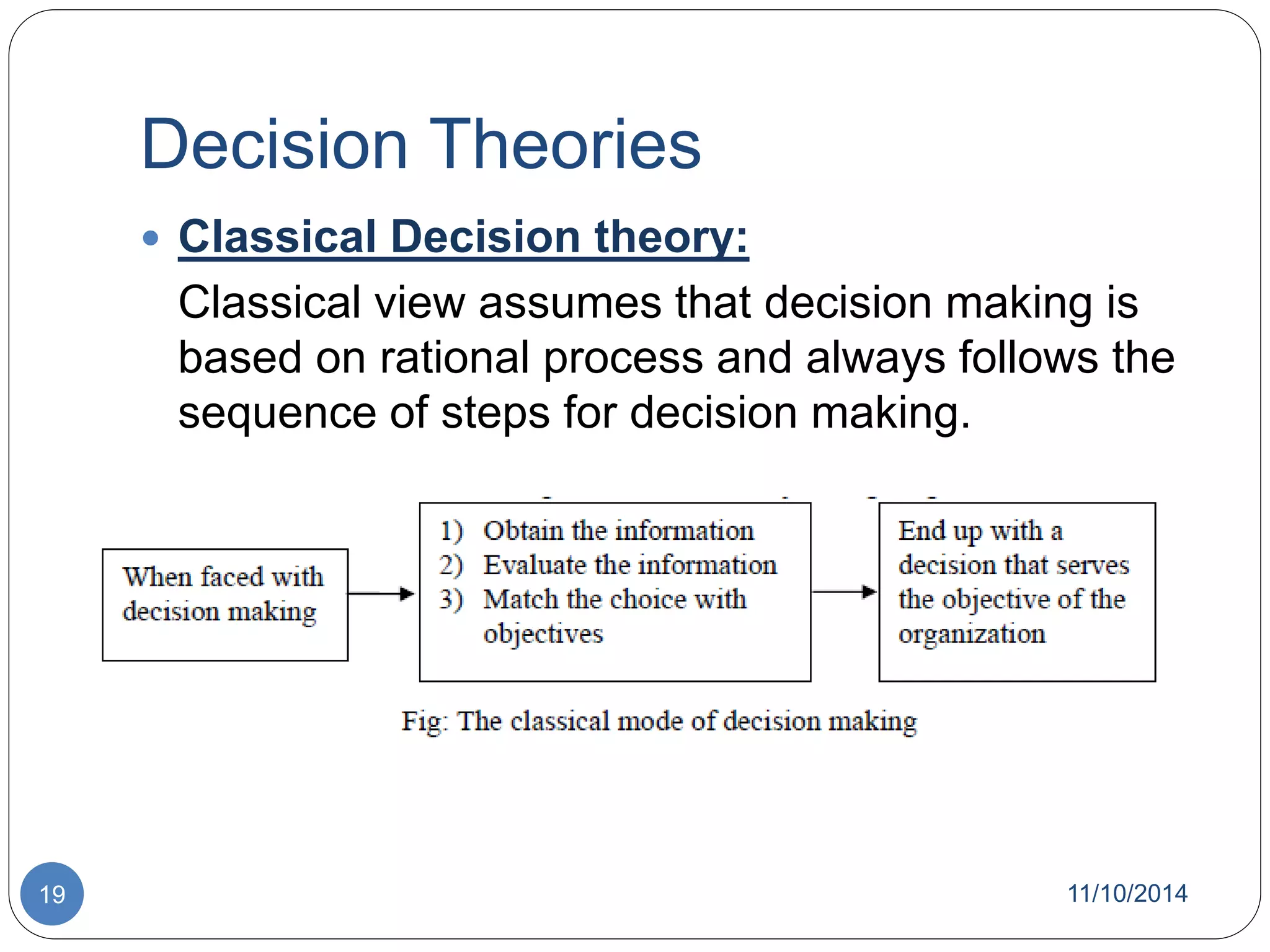
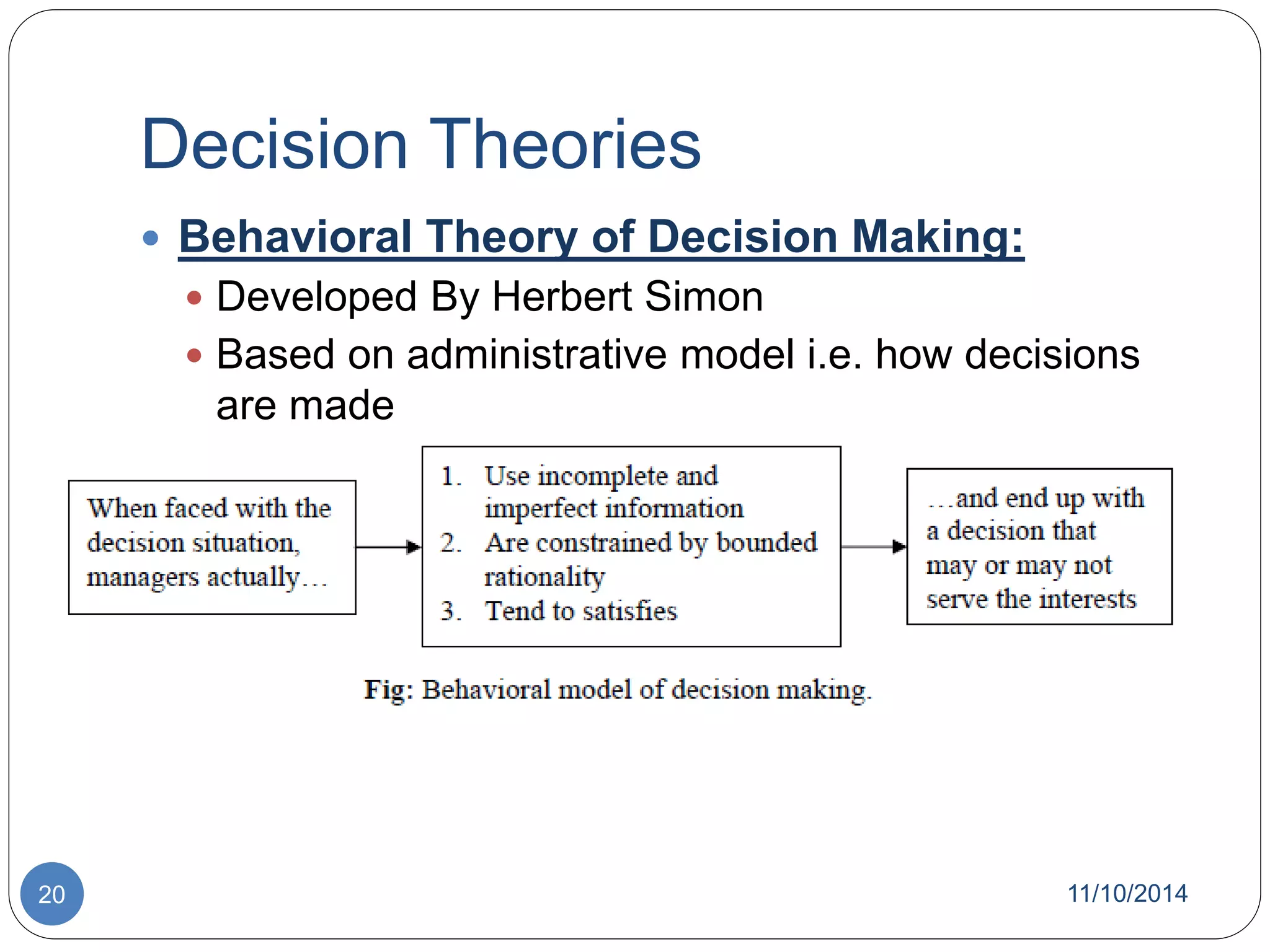
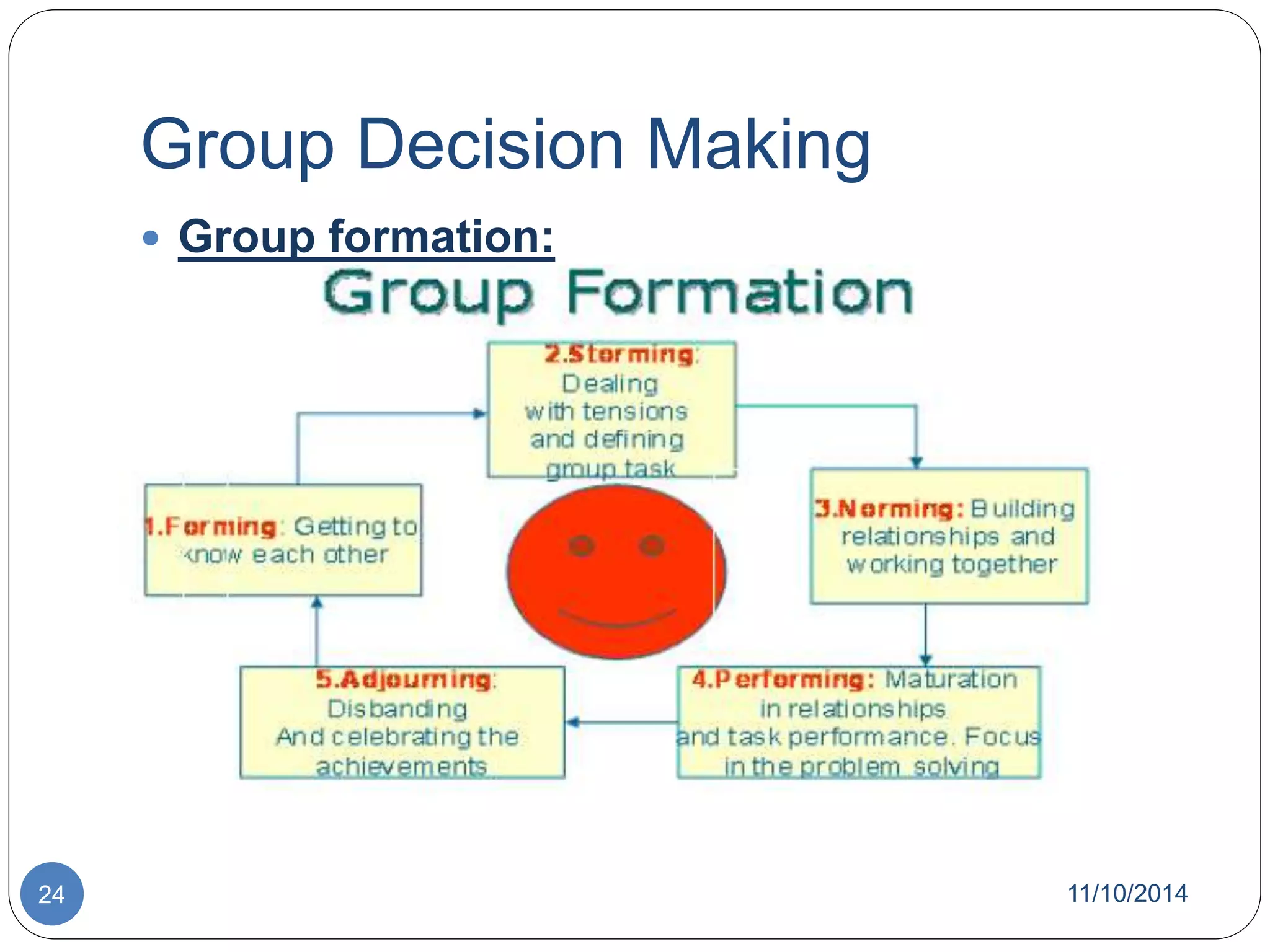
The document discusses decision theory and decision making. It defines decision making as identifying and evaluating choices to select the best alternative. It describes different types of decisions, conditions for decision making, processes, tools like decision trees, and styles. It also discusses group decision making, techniques to improve it like brainstorming, and theories like classical and behavioral decision theory.