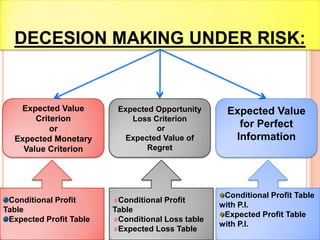
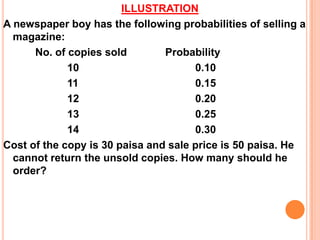
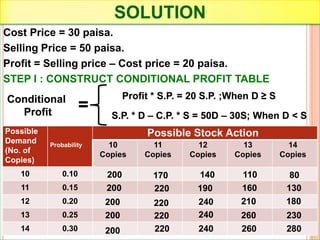
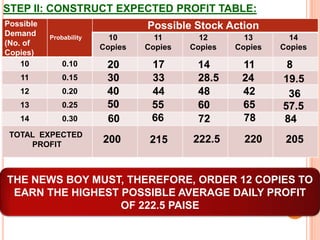
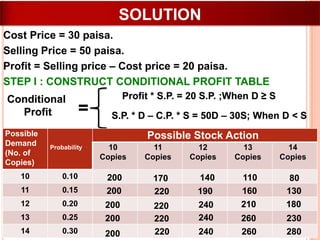
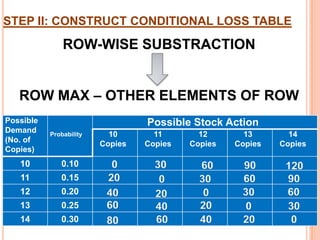
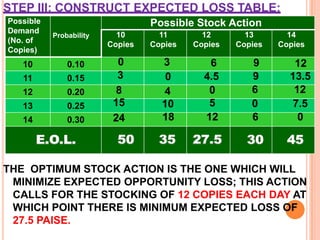
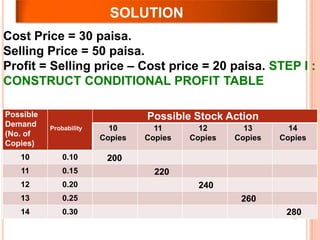
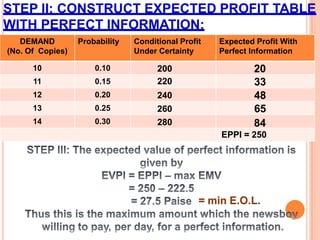
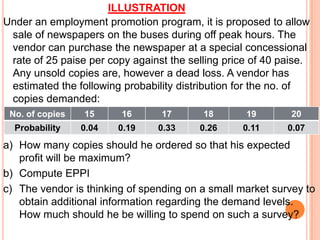
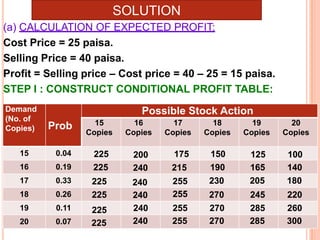
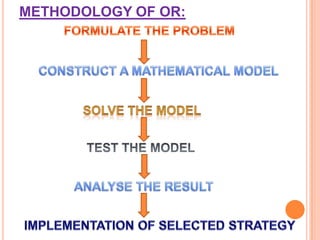
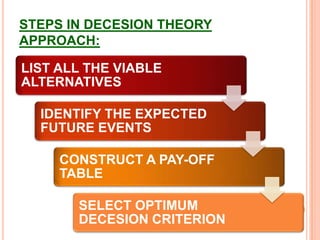
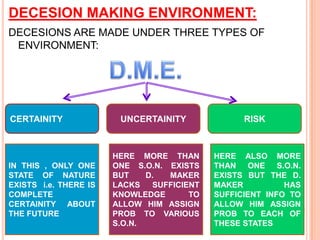
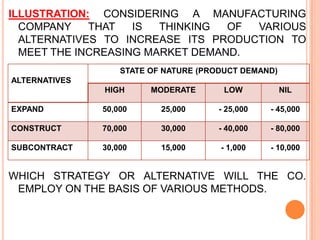
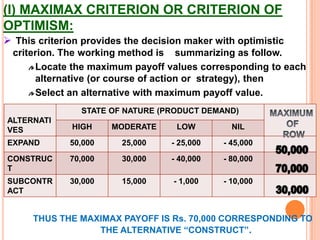
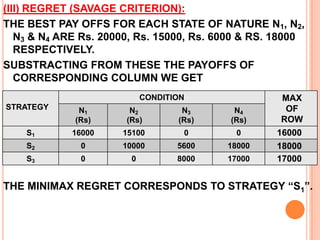
The document discusses various concepts and approaches related to operation research and decision making under uncertainty and risk. It defines operation research and provides characteristics and scope of OR, including areas such as allocation, production, procurement, marketing, finance, and personnel. The methodology of OR includes problem formulation, model construction, solution, testing, and implementation. Decision making environments like certainty, uncertainty, and risk are explained. Approaches for decision making under uncertainty like maximax, maximin, minimax regret, Hurwicz, and Laplace criteria are illustrated with examples. Decision making under risk assumes state probabilities are known and expected value criterion is used.












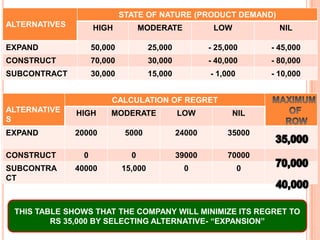

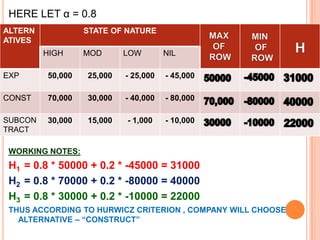

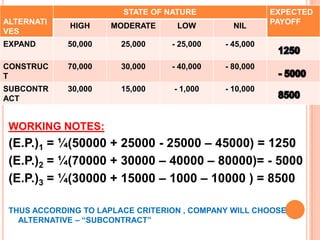

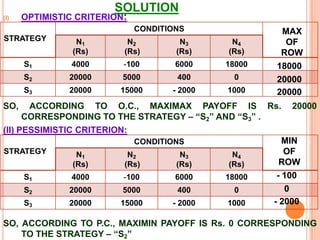

![(V) Laplace Criterion or Criterion of Rationality: Also known as equal probabilities criterion or criterion of rationality. Since the probability of states of nature are not known, it is assumed that all states of nature will occur with equal probability, i.e. assign an equal probability. The working method is summarizing as follow:Determine expected value for each alternative; if n denotes the number of events and P’s denote the payoffs, then expected value is given by 1\n[P1+P2+….+Pn]Choose the alternative that yields the maximum value of P.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orunitippt-101221004721-phpapp01/85/decision-making-criterion-27-320.jpg)