Embed presentation
Downloaded 180 times






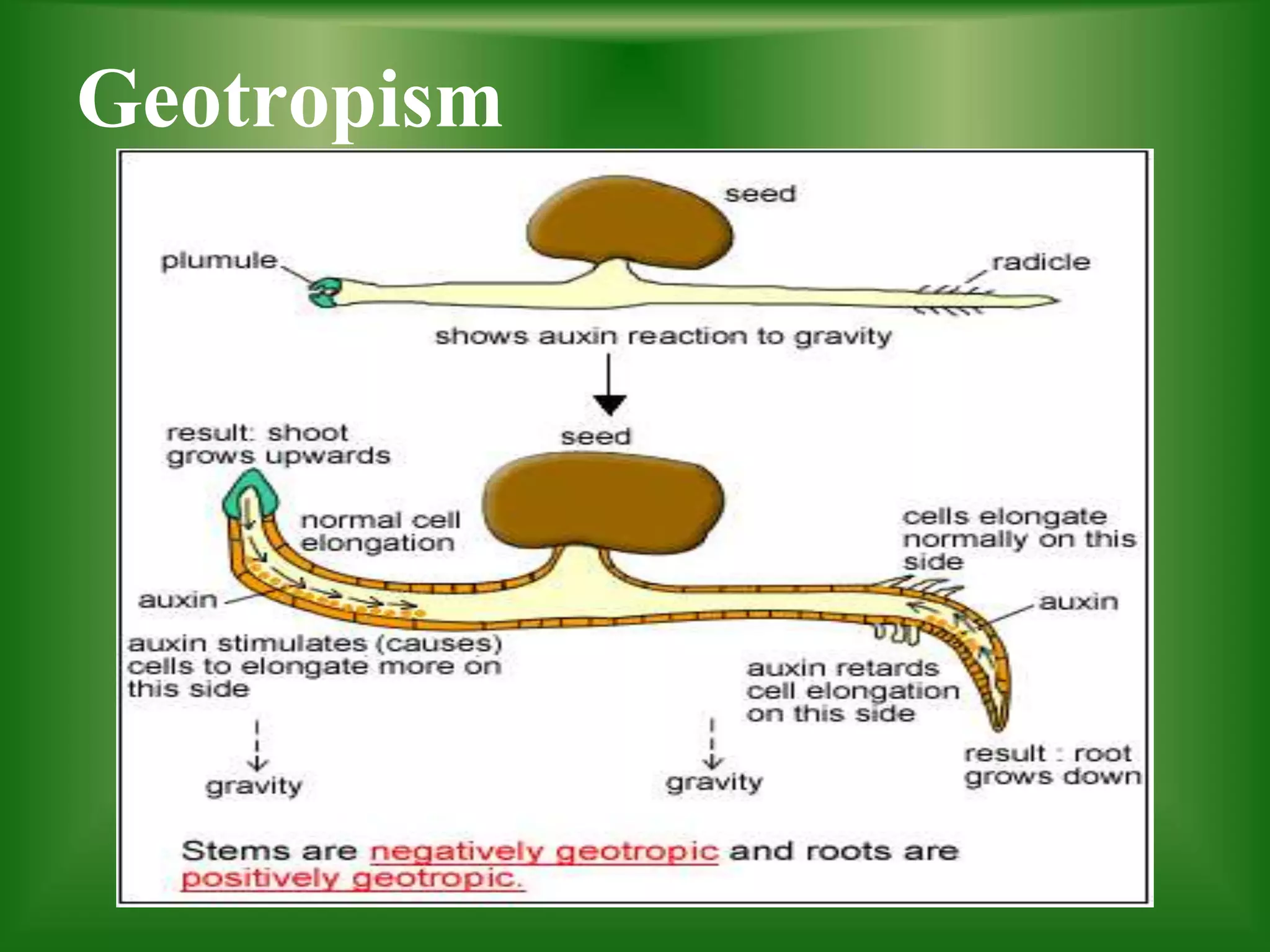
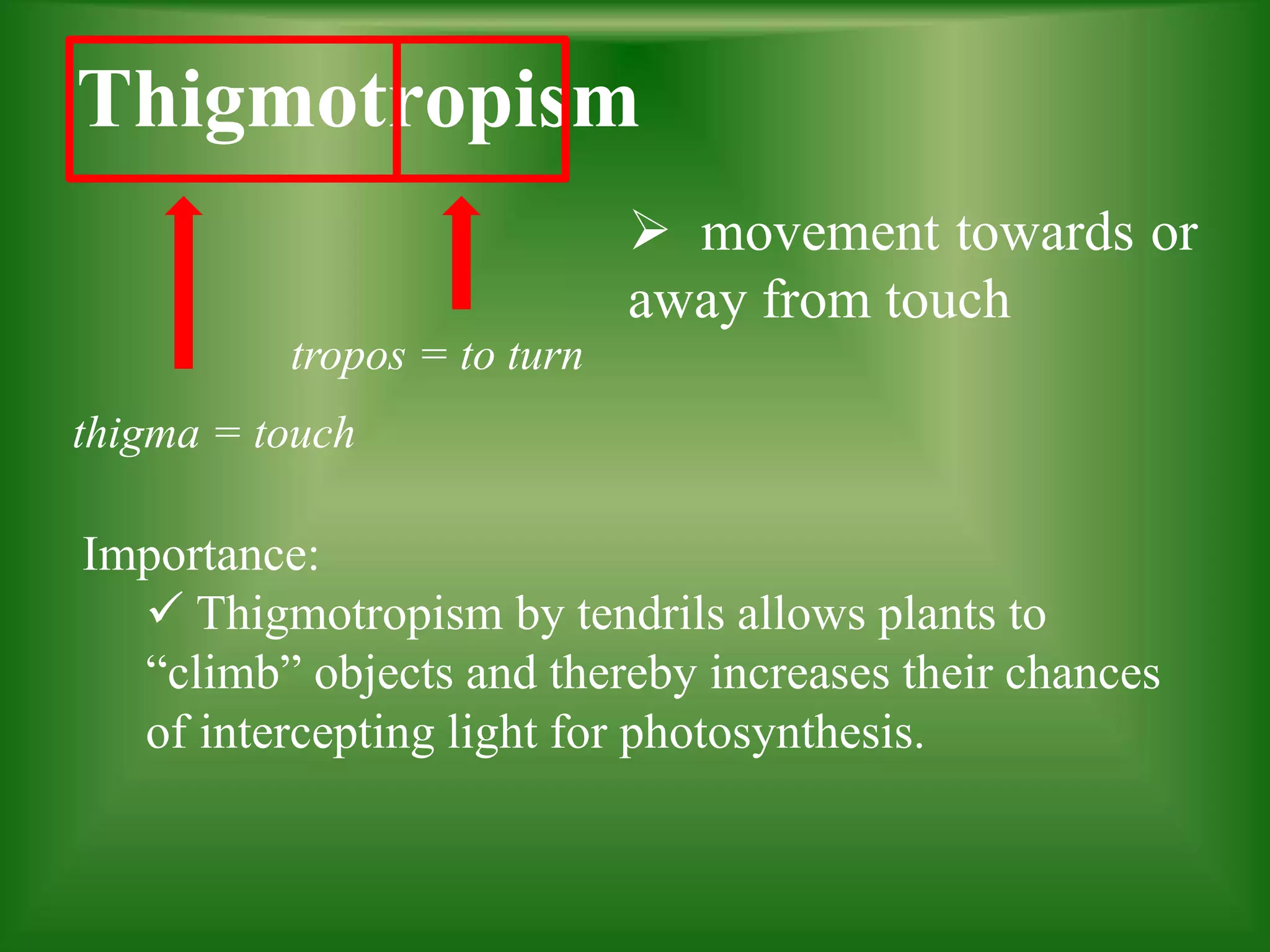



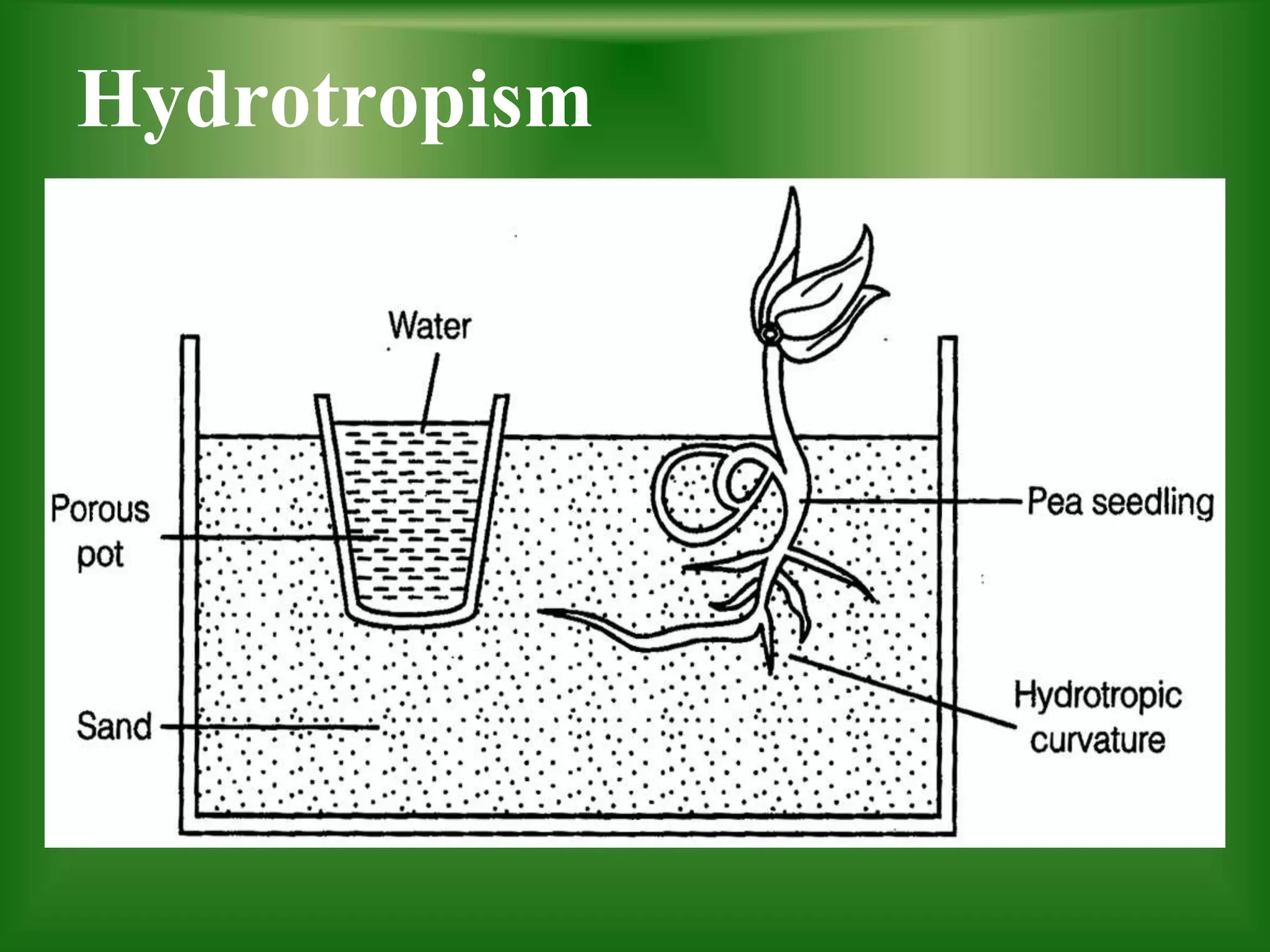


Tropism refers to the growth response of plants towards or away from an external stimulus and comes from the Greek word meaning "to turn". There are several types of tropism defined in the document, including phototropism (movement towards/away from light), geotropism (movement towards/away from gravity), thigmotropism (movement towards/away from touch), and hydrotropism (movement towards/away from water). Each of these tropic responses are important for plants to obtain resources like light, water, and minerals needed for photosynthesis, growth, and survival.












